Chest Muscles Anatomy Muscles Of Anterolateral Chest Vrogue Co
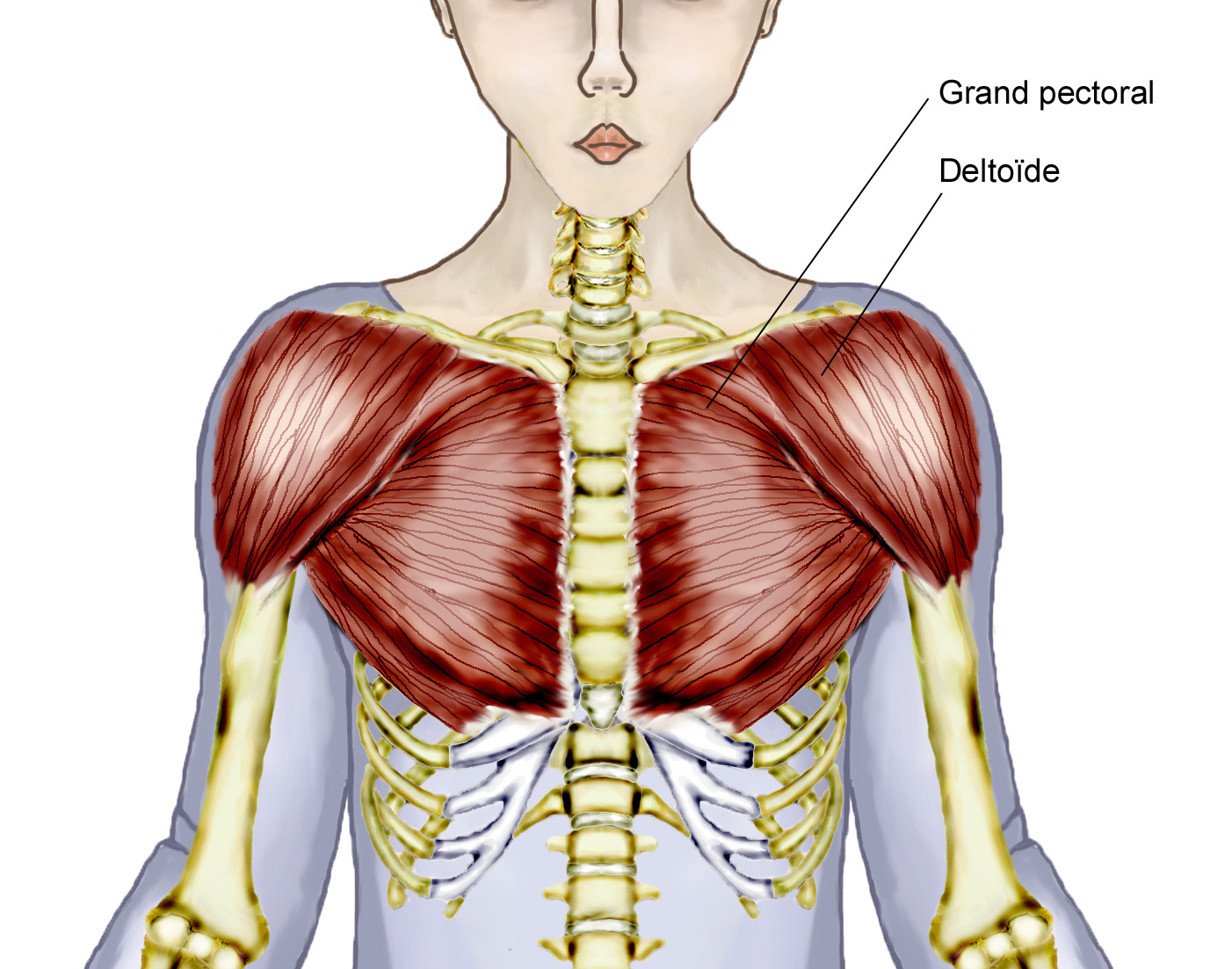
Chest Muscles Anatomy Muscles Of Anterolateral Chest Vrogue Co Teres major: this muscle helps rotate the upper arm. serratus anterior: located in the rib cage, this muscle keeps the shoulder blade against the chest wall and helps rotate the shoulder blade. Muscles of the anterior chest wall. major muscles of the anterior and anterolateral chest wall include the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior, rectus abdominal, and external oblique (fig. 1‑19, fig. 1‑20). the sternalis muscle is an uncommon accessory muscle (please see fig. 1‑71, fig. 1‑72 at the end of the chapter).

Figure 6 From Introduction To Chest Wall Reconstructi Vrogue Co The pectoral region is located on the anterior chest wall. it contains four muscles that exert a force on the upper limb: the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior and subclavius. in this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the muscles of the pectoral region – their attachments, actions and innervation. Unlock your elbows and lower the bar down slowly until it touches your torso between your nipple line and your sternum. once you make contact (or descend as low as you’re comfortably able. Pectoralis major. the biggest chest muscle, extending from the shoulder region across the front of the chest, covering the ribs. origin: in two heads, from the clavicle and the costal cartilages of the 1st 6th ribs. insertion: bicipital groove and greater tubercle of the humerus. The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature – all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage. the thorax has two major openings: the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracic aperture located inferiorly.

Chest Muscles Anatomy Muscles Of Anterolateral Chest Vrogue Co Pectoralis major. the biggest chest muscle, extending from the shoulder region across the front of the chest, covering the ribs. origin: in two heads, from the clavicle and the costal cartilages of the 1st 6th ribs. insertion: bicipital groove and greater tubercle of the humerus. The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature – all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage. the thorax has two major openings: the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracic aperture located inferiorly. There are 11 pairs of external intercostal muscles. they run inferoanteriorly from the rib above to the rib below, and are continuous with the external oblique of the abdomen. attachments: originate at the lower border of the rib, inserting into the superior border of the rib below. actions: elevates the ribs, increasing the thoracic volume. The thoracic wall is made up of five muscles: the external intercostal muscles, internal intercostal muscles, innermost intercostal muscles, subcostalis, and transversus thoracis. these muscles are primarily responsible for changing the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration. other muscles that do not make up the thoracic wall, but attach to it include the pectoralis major and minor.

Chest Muscles Anatomy Muscles Of Anterolateral Chest Vrogue Co There are 11 pairs of external intercostal muscles. they run inferoanteriorly from the rib above to the rib below, and are continuous with the external oblique of the abdomen. attachments: originate at the lower border of the rib, inserting into the superior border of the rib below. actions: elevates the ribs, increasing the thoracic volume. The thoracic wall is made up of five muscles: the external intercostal muscles, internal intercostal muscles, innermost intercostal muscles, subcostalis, and transversus thoracis. these muscles are primarily responsible for changing the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration. other muscles that do not make up the thoracic wall, but attach to it include the pectoralis major and minor.
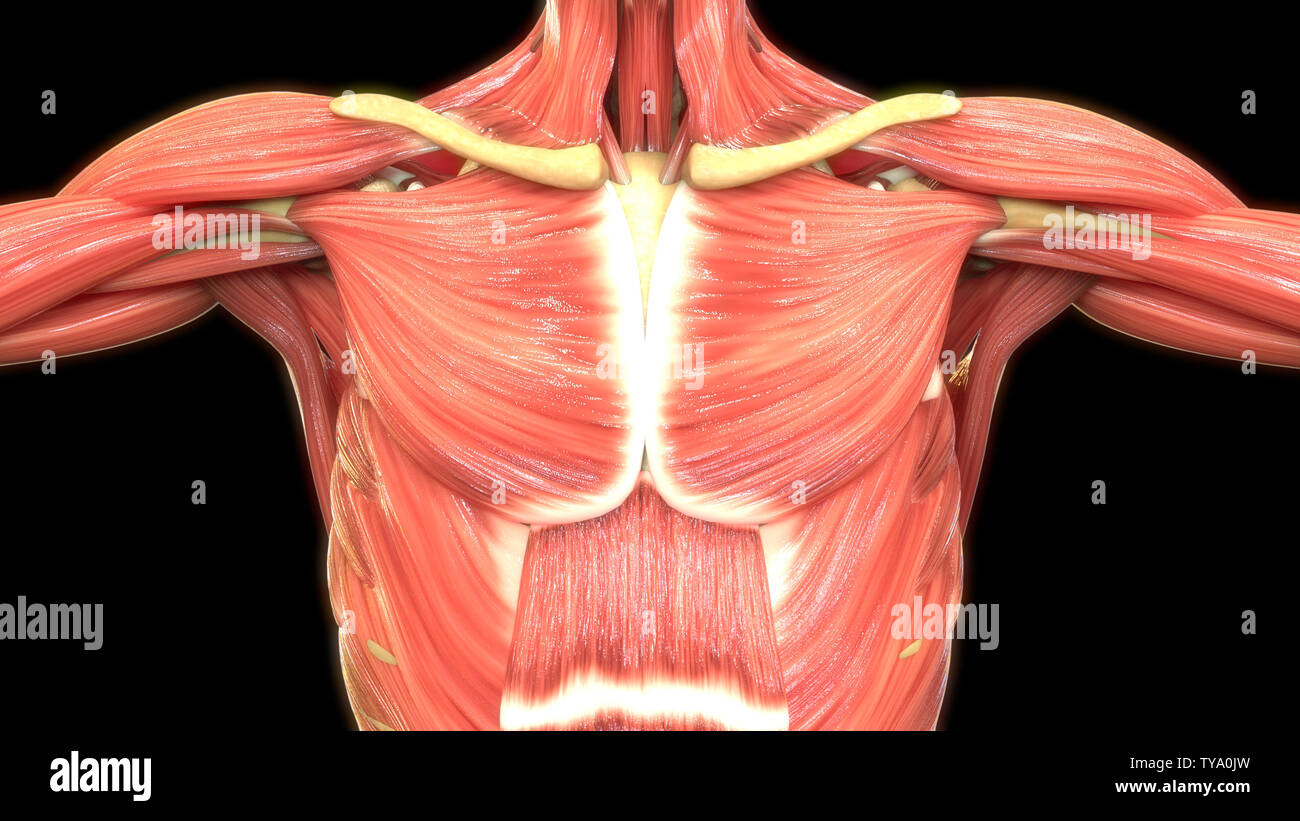
Chest Muscles Anatomy Muscles Of Anterolateral Chest Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.