Children S Mental Health During Covid 19 Thewaveclinic

Children S Mental Health During Covid 19 Thewaveclinic Studies examining parent well being during the covid 19 pandemic found that it was directly related to hardships such as decreases in work, incomes and increased caregiving burden. 15 in a us study of 1000 parents, 26.9% reported worsening of their own mental health since onset of the pandemic, especially in mothers, unmarried parents, and. Since the start of the covid 19 pandemic, survey data for children and adolescents reported higher rates of anxiety and depressive symptoms and parental concerns about their children’s mental health. 1,4,5 a 2021 meta analysis 7 found a 2 fold increase in the global prevalence of depression and anxiety for children and adolescents, with.
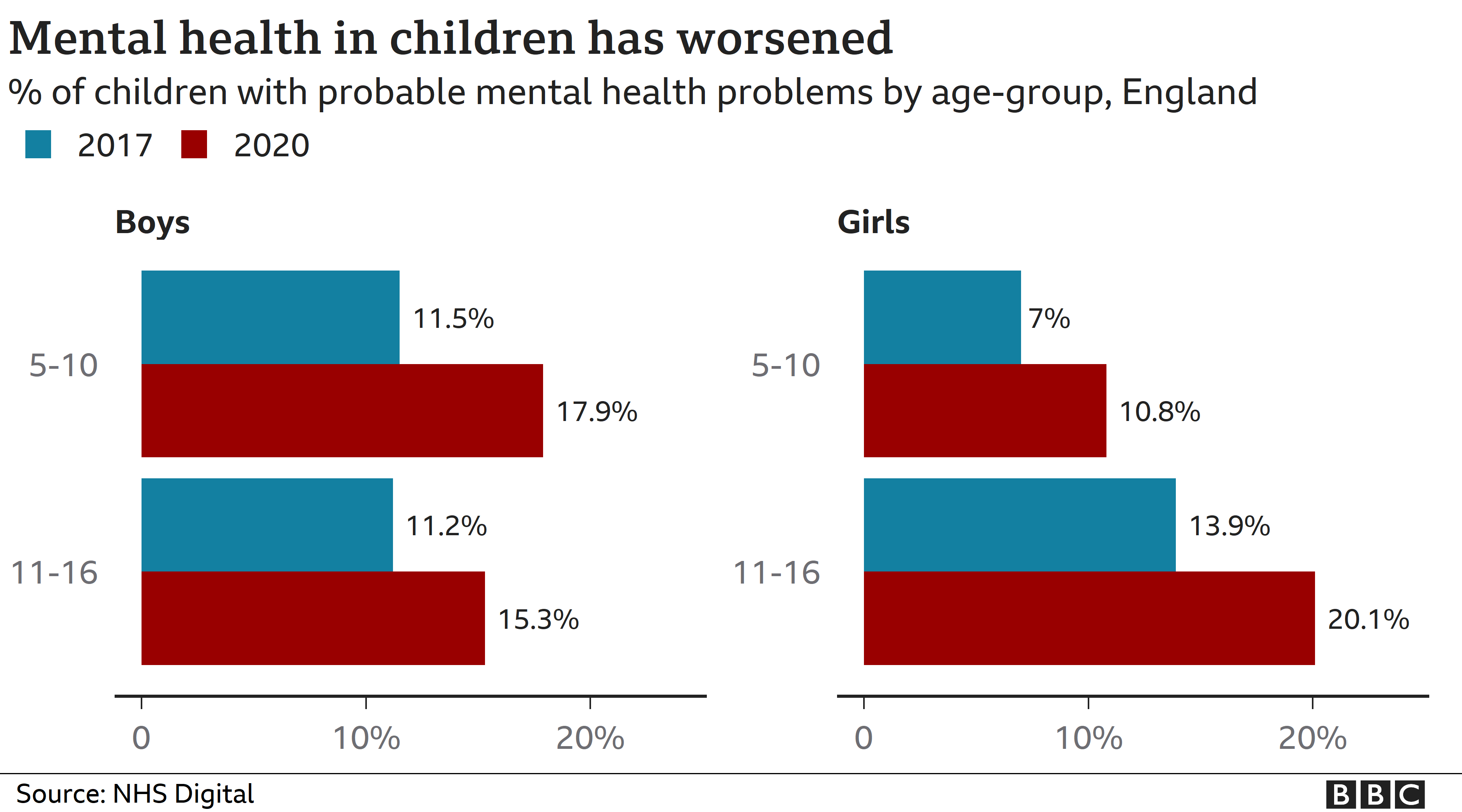
Covid The Devastating Toll Of The Pandemic On Children Bbc News One, focusing on children ages 4 to 10, found that the level of lockdown greatly affected mental health and behavioral issues, with england’s first complete lockdown greatly exacerbating issues from hyperactivity to depression. another study looked at teens, who may have felt particularly isolated during lockdown. Purpose: examine children's mental health symptoms, including changes during the covid 19 pandemic. methods: the covid experiences surveys, designed to be representative of the u.s. household population, were administered online to parents of children aged 5 12 years (wave 1 (w1), october november 2020, n = 1561; wave 2 (w2), march may 2021, n = 1287). 2. what factors have contributed to mental health risk and resilience during covid 19? various factors have contributed to the harmful impact of the pandemic on youth mental health, including individual (e.g., age, gender, disability), familial (e.g., parent child conflict, domestic violence), community (e.g., access to peers and teachers, learning environment), and social (e.g., racism. Respondents were 54 percent female, 46 percent male, and ranged in age from 21 to 64, with an average age of 37. for parents of multiple children, we asked them to answer questions in consideration of the single child whose mental health they are most concerned about. for media inquiries, contact media@digitalthirdcoast .

Covid 19 2. what factors have contributed to mental health risk and resilience during covid 19? various factors have contributed to the harmful impact of the pandemic on youth mental health, including individual (e.g., age, gender, disability), familial (e.g., parent child conflict, domestic violence), community (e.g., access to peers and teachers, learning environment), and social (e.g., racism. Respondents were 54 percent female, 46 percent male, and ranged in age from 21 to 64, with an average age of 37. for parents of multiple children, we asked them to answer questions in consideration of the single child whose mental health they are most concerned about. for media inquiries, contact media@digitalthirdcoast . According to the new data, in 2021, more than a third (37%) of high school students reported they experienced poor mental health during the covid 19 pandemic, and 44% reported they persistently felt sad or hopeless during the past year. The mental health of the uk’s children and young people was deteriorating before the pandemic, while health, educational, and social outcomes for children with mental health conditions are worse than for previous cohorts. 4 5 6 between 2004 and 2017 anxiety, depression, and self harm increased, particularly among teenage girls. 7 self harm is.

Comments are closed.