Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infections Lesson 1

Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infections Lesson 1 An overview of a practical classification scheme for pathological fungi, as well as a summary of their microscopic structure. differences between yeast and. Kingdom fungi structure, characteristics & classification.
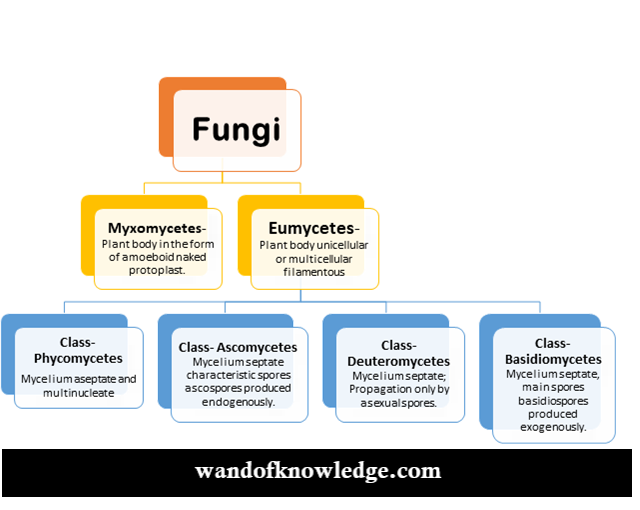
Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infectio Vrogue Co Fungal infection (mycosis): types, causes & treatments. Fungal classification, or taxonomy, is a way of organizing the vast diversity within the fungal kingdom. historically, fungi were classified based on their morphology, reproduction, and growth patterns. with advances in molecular biology, though, the focus has shifted to dna sequencing, offering more accurate insights into evolutionary. What are fungal infections? pmc. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that exist as yeast, molds, or both forms. yeasts consist of solitary cells that reproduce by budding. molds occur in filaments, also known as hyphae, which extend by apical elongation. dimorphic fungi grow as mold in the environment and as yeast cells or spherules (sac like cells that are the reproductive form of.
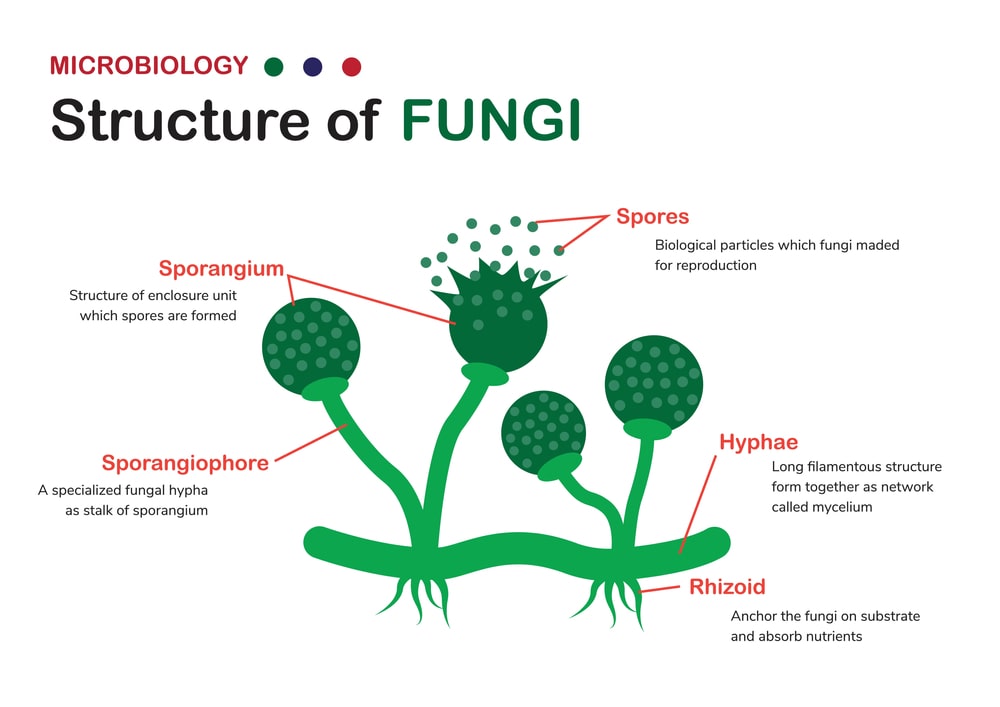
Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infectio Vrogue Co What are fungal infections? pmc. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that exist as yeast, molds, or both forms. yeasts consist of solitary cells that reproduce by budding. molds occur in filaments, also known as hyphae, which extend by apical elongation. dimorphic fungi grow as mold in the environment and as yeast cells or spherules (sac like cells that are the reproductive form of. Fungal infection. Based on the gross morphological characteristics, pathogenic fungi infecting humans are conveniently separated into two basic groups, yeasts and molds. the simplest morphological form of a fungus is the unicellular budding yeast cell. a number of pathogenic fungi alternate between a yeast phase (at 37 °c or in tissues) and a hyphal phase (at.

Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infectio Vrogue Co Fungal infection. Based on the gross morphological characteristics, pathogenic fungi infecting humans are conveniently separated into two basic groups, yeasts and molds. the simplest morphological form of a fungus is the unicellular budding yeast cell. a number of pathogenic fungi alternate between a yeast phase (at 37 °c or in tissues) and a hyphal phase (at.
Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infectio Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.