Clinical Guidelines Nursing Neurovascular Observations Hand

Clinical Guidelines Nursing Neurovascular Observations Hand Nursing guidelines : neurovascular observations. Neurovascular assessment is an essential element of clinical practice. nurses have a unique opportunity for assessment with every patient interaction. judicious observations, timely identification and reporting, and appropriate intervention in the event of compromise can reduce complications and prevent poor patient outcomes (turney et al., 2013).
Nursing Assessment Form Templates Orthopedics 22. clinical observations for alcs (pain on passive extension and out of proportion to the injury, poor or no response to analgesia) for at risk patients should be: a. carried out at least hourly for the first 24 hours, reducing to four hourly observations for a further 24 hours if pain is stable minimal (consensus). Neurovascular assessment: what is it, why it's performed,. Guideline: neurovascular assessment. Neurovascular assessment | nursing pocket card.

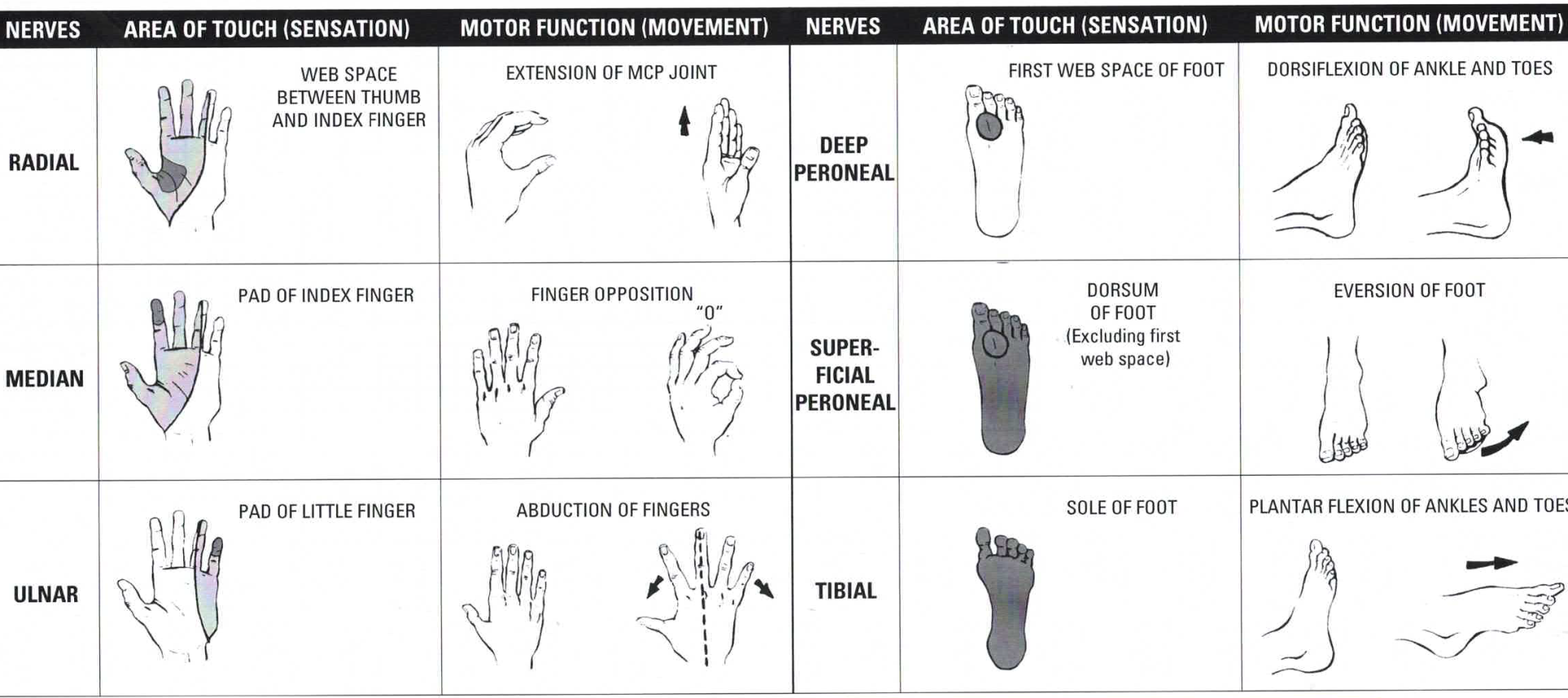
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Neurovascular Observations Guideline: neurovascular assessment. Neurovascular assessment | nursing pocket card. Peripheral neurovascular observations for acute limb. Assessment for the signs and symptoms of neurovascular deficit should take into consideration the classic 'five ps'; pain, paralysis, paraesthesia, pulses and pallor (dykes 1993, brinker and miller 1999, crowther 1999, judge 2005, solomon et al 2005). in addition, assessment should take into account the warmth of the limb and evidence of swelling.
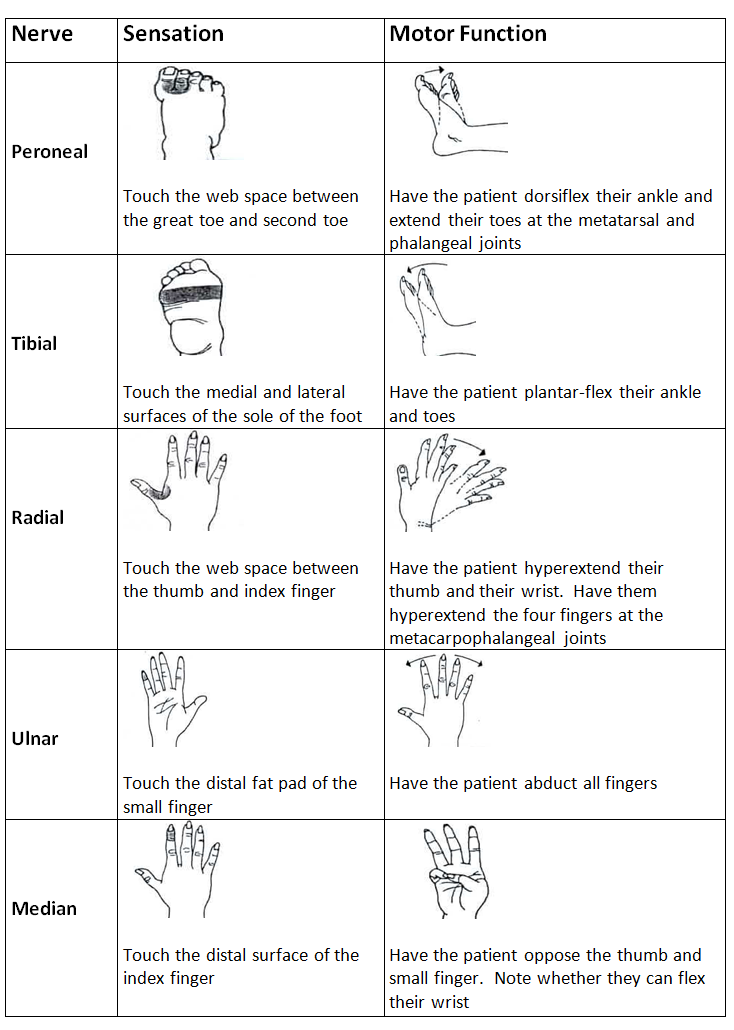
Neurovascular Points Chart Peripheral neurovascular observations for acute limb. Assessment for the signs and symptoms of neurovascular deficit should take into consideration the classic 'five ps'; pain, paralysis, paraesthesia, pulses and pallor (dykes 1993, brinker and miller 1999, crowther 1999, judge 2005, solomon et al 2005). in addition, assessment should take into account the warmth of the limb and evidence of swelling.

Comments are closed.