Club Mosses Labeled
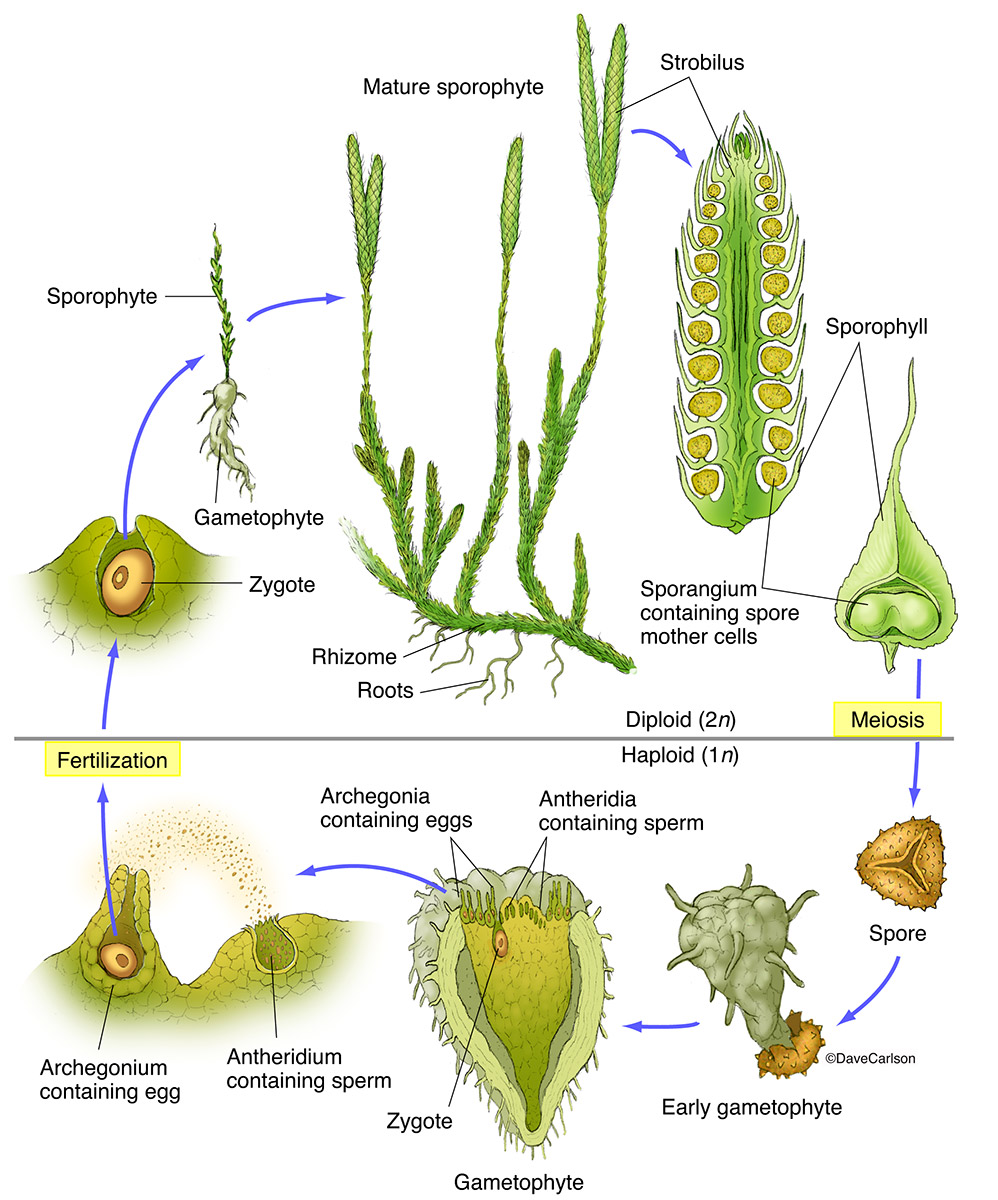
Club Mosses Labeled Lycopodium (from greek lykos, wolf and podion, diminutive of pous, foot) [ 2] is a genus of clubmosses, also known as ground pines or creeping cedars, [ 3] in the family lycopodiaceae. two very different circumscriptions of the genus are in use. in the pteridophyte phylogeny group classification of 2016 (ppg i), lycopodium is one of nine genera. Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants also known as lycopods or lycophytes.members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts.they have dichotomously branching stems bearing simple leaves called microphylls and reproduce by means of spores borne in sporangia on the sides of the stems at the bases of the leaves.
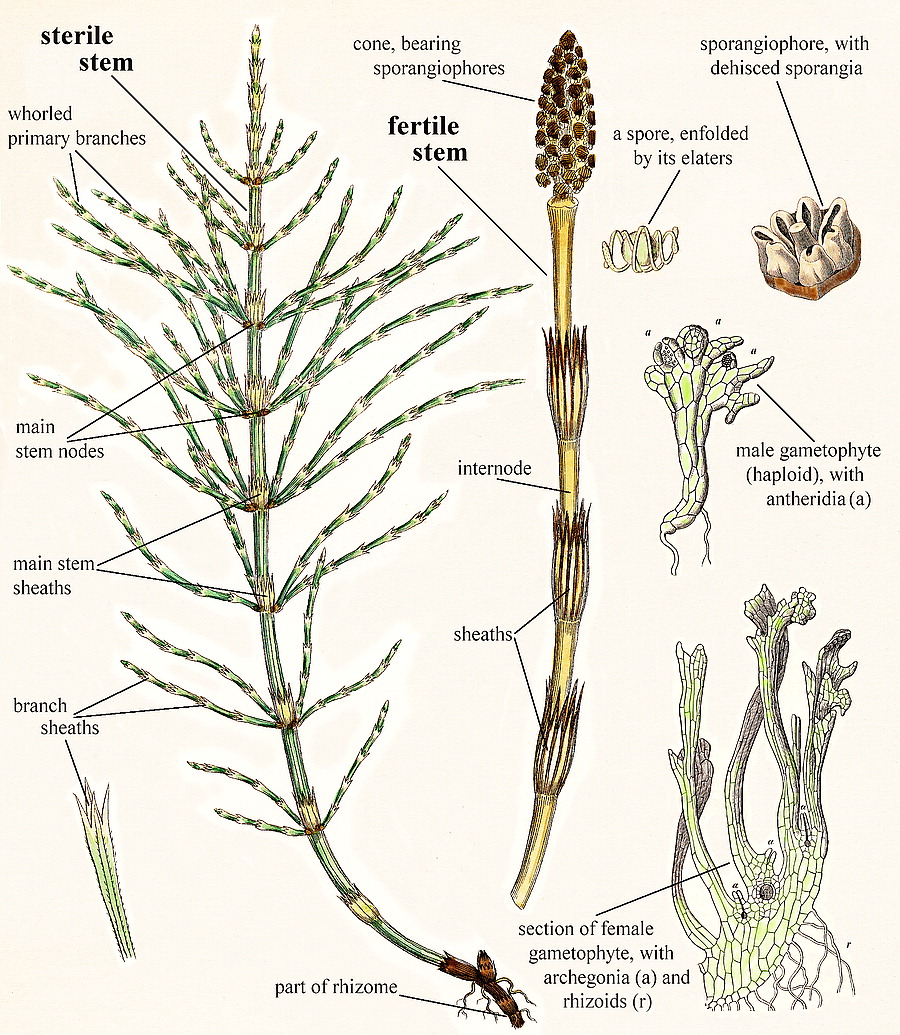
Club Mosses Labeled Club moss, (family lycopodiaceae), any of some 400 species of seedless vascular plants constituting the only family of the lycophyte order lycopodiales. the taxonomy of the family has been contentious, and the number of genera vary depending on the source. the plants are native mainly to tropical mountains but are also common in northern. The club mosses form a distinct group that is generally recognized at the phylum level (lycopodiophyta). they are one the groups of 'fern allies' , groups unified by having vascular tissue but lacking seeds. the other groups are the ferns, horse tails and wisk ferns (some people lump these three groups together into one phylum). Homosporous or heterosporous. haploid spores grow into bisexual gametophytes in lycopodium. in selaginella, microspores develop into microgametophytes that produce sperm and megaspores develop into megagametophytes that produce eggs. figure 2.5.3.1.1 2.5.3.1. 1: a club moss, genus lycopodium. the upright, yellowish structures are developing. Lycophyte, class of spore bearing vascular plants, comprising more than 1,200 extant species. the class comprises three orders: the club mosses (lycopodiales), the quillworts (isoetales), and the spike mosses (selaginellales). learn about the taxonomy, life cycle, and physical characteristics of lycophytes.

Parts Plant Structure Clubmoss Lycopodium Running Clubmoss Lycopodium Homosporous or heterosporous. haploid spores grow into bisexual gametophytes in lycopodium. in selaginella, microspores develop into microgametophytes that produce sperm and megaspores develop into megagametophytes that produce eggs. figure 2.5.3.1.1 2.5.3.1. 1: a club moss, genus lycopodium. the upright, yellowish structures are developing. Lycophyte, class of spore bearing vascular plants, comprising more than 1,200 extant species. the class comprises three orders: the club mosses (lycopodiales), the quillworts (isoetales), and the spike mosses (selaginellales). learn about the taxonomy, life cycle, and physical characteristics of lycophytes. Lycopodium clavatum is a spore bearing vascular plant, growing mainly prostrate along the ground with stems up to 1 m (39 in) long; the stems are much branched, and densely clothed with small, spirally arranged microphyll leaves. the leaves are 3–5 mm long and 0.7–1 mm broad, tapered to a fine hair like white point. The lycophytes are a small and inconspicuous group of plants today, but in the carboniferous some lycophytes were forest forming trees more than 35 meters tall. lycophytes are the oldest extant group of vascular plants, and dominated major habitats for 40 million years. the club mosses (lycopodiales) are usually evergreen, and have been used as.
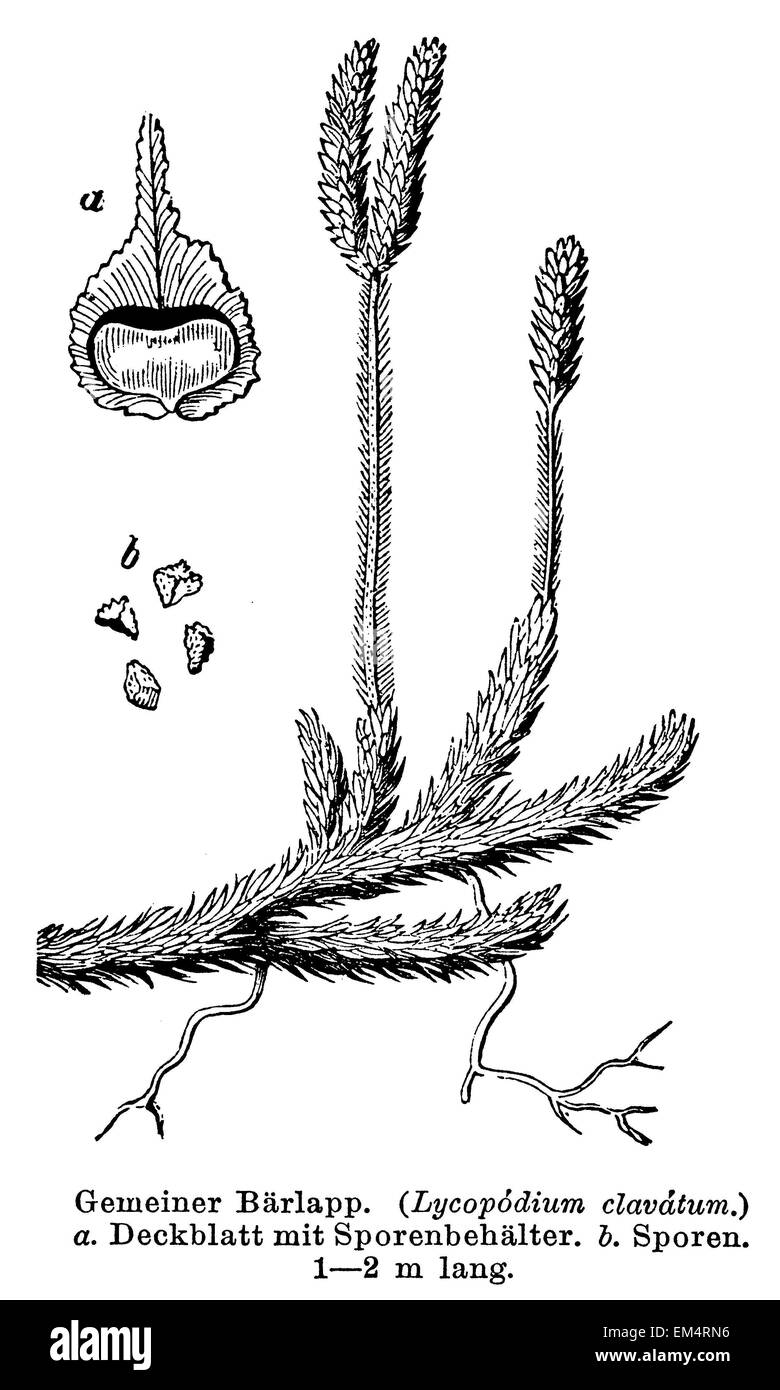
Club Mosses Labeled Lycopodium clavatum is a spore bearing vascular plant, growing mainly prostrate along the ground with stems up to 1 m (39 in) long; the stems are much branched, and densely clothed with small, spirally arranged microphyll leaves. the leaves are 3–5 mm long and 0.7–1 mm broad, tapered to a fine hair like white point. The lycophytes are a small and inconspicuous group of plants today, but in the carboniferous some lycophytes were forest forming trees more than 35 meters tall. lycophytes are the oldest extant group of vascular plants, and dominated major habitats for 40 million years. the club mosses (lycopodiales) are usually evergreen, and have been used as.
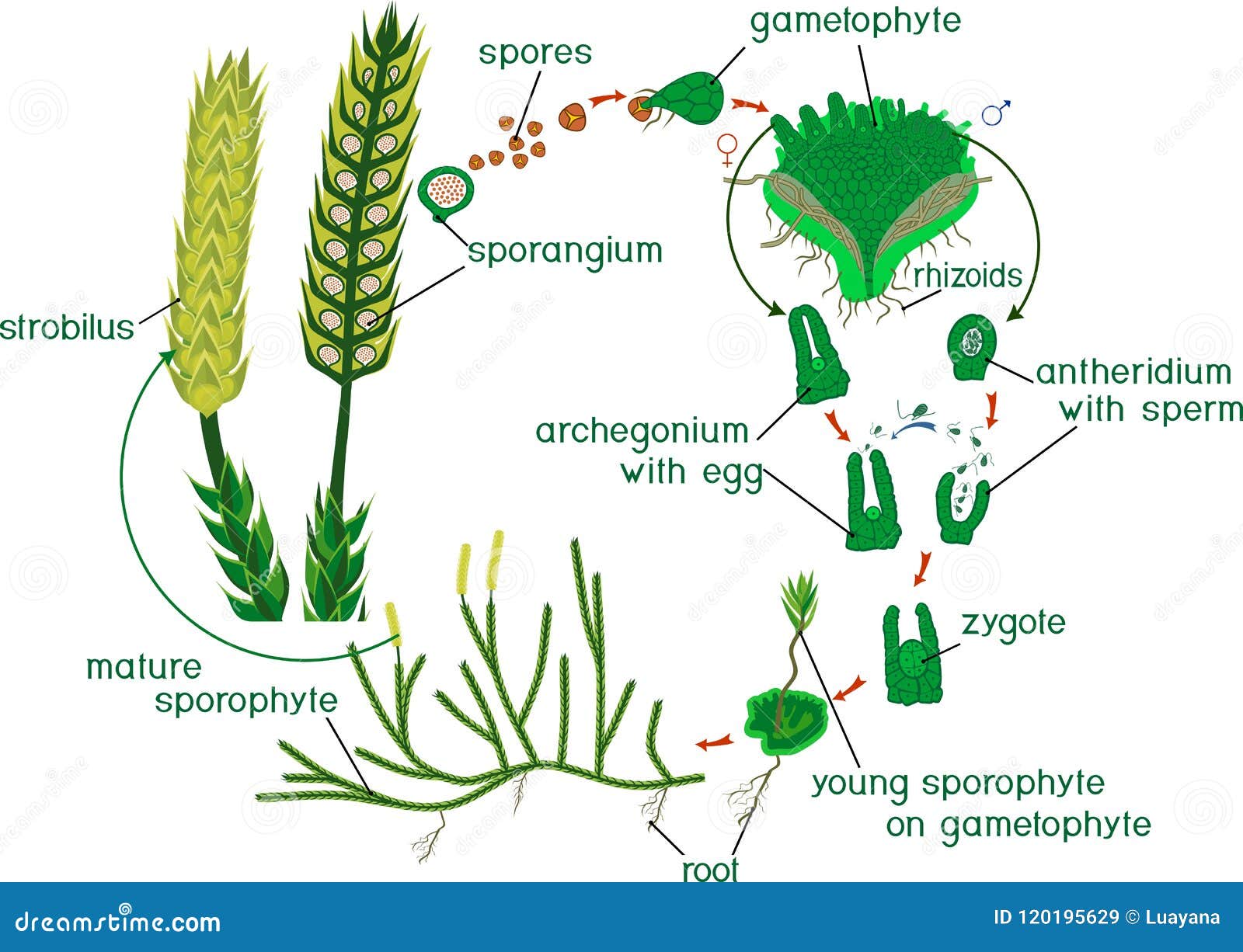
Club Mosses Labeled

Comments are closed.