Complete Analysis Of The Penney Game For 2 And Loaded Coins

Complete Analysis Of The Penney Game For 2 And Loaded Coins The analysis is quite simple for = 2 and fair coins, see figure 2. the weighted adjacency matrix (forbidding to bet on the sequence chosen by the first player) is the first player chooses a column. Complete analysis of the penney game for = 2 and loaded coins. … victory graph for the penney game with = 2 and loaded coins (p = 0.51).

Complete Analysis Of The Penney Game For 2 And Loaded Coins 10 11 00 01 figure 3. victory graph for the penney game with ℓ = 2 and loaded coins (p = 0.51). a similar analysis is reported in figure 1 for the fair penney game with ℓ = 3. the corresponding victory graph (which sequence is most advantageous given a chosen one) is also represented in figure 1. this graph shows a central loop, signalling. Keywords: transitivity; random walk; penney game; network theory 1. introduction games are an integral part of all cultures and are one of the oldest forms of social interaction. many games use stochastic elements (dice, coins, wheels) and most of them are based on betting for. Penney's game. penney's game, named after its inventor walter penney, is a binary (head tail) sequence generating game between two players. player a selects a sequence of heads and tails (of length 3 or larger), and shows this sequence to player b. player b then selects another sequence of heads and tails of the same length. The penney ante game can be viewed as a special case of this problem corresponding to sequences over the two letter alphabet {h,t} that end in a specified string a and do not contain another specified string b of the same length as a. optimal strategy for player ii. perhaps the most natural question in the penney ante game is the following:.

Victory Graph For The Penney Game With 2 And Loaded Coins P 0 51 Penney's game. penney's game, named after its inventor walter penney, is a binary (head tail) sequence generating game between two players. player a selects a sequence of heads and tails (of length 3 or larger), and shows this sequence to player b. player b then selects another sequence of heads and tails of the same length. The penney ante game can be viewed as a special case of this problem corresponding to sequences over the two letter alphabet {h,t} that end in a specified string a and do not contain another specified string b of the same length as a. optimal strategy for player ii. perhaps the most natural question in the penney ante game is the following:. See [2],[6],[7],[8]. for 2 players penney ante game, a remarkable result says that a player could always win the game at about 2 3 if the other player’s pattern is known, see [7] and [5]. (both should pick up string with the length len ≥ 3) then it is definitely a non transitive game, see [6]. also, there are lots of other statistic. Analysis of the penney game with ℓ = 3, fair coins and fully absorbing traps. (a) transition graph, where every node is a possibly winning sequence, the links go from one sequence to the sequences which can be obtained with a coin toss. each link weights 1 2.
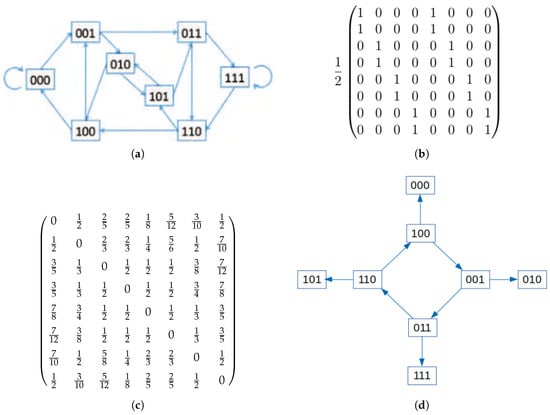
Future Internet Free Full Text Intransitiveness From Games To See [2],[6],[7],[8]. for 2 players penney ante game, a remarkable result says that a player could always win the game at about 2 3 if the other player’s pattern is known, see [7] and [5]. (both should pick up string with the length len ≥ 3) then it is definitely a non transitive game, see [6]. also, there are lots of other statistic. Analysis of the penney game with ℓ = 3, fair coins and fully absorbing traps. (a) transition graph, where every node is a possibly winning sequence, the links go from one sequence to the sequences which can be obtained with a coin toss. each link weights 1 2.

Comments are closed.