Complex Ions Ligands Coordination Compounds Basic Introduction Chemistry
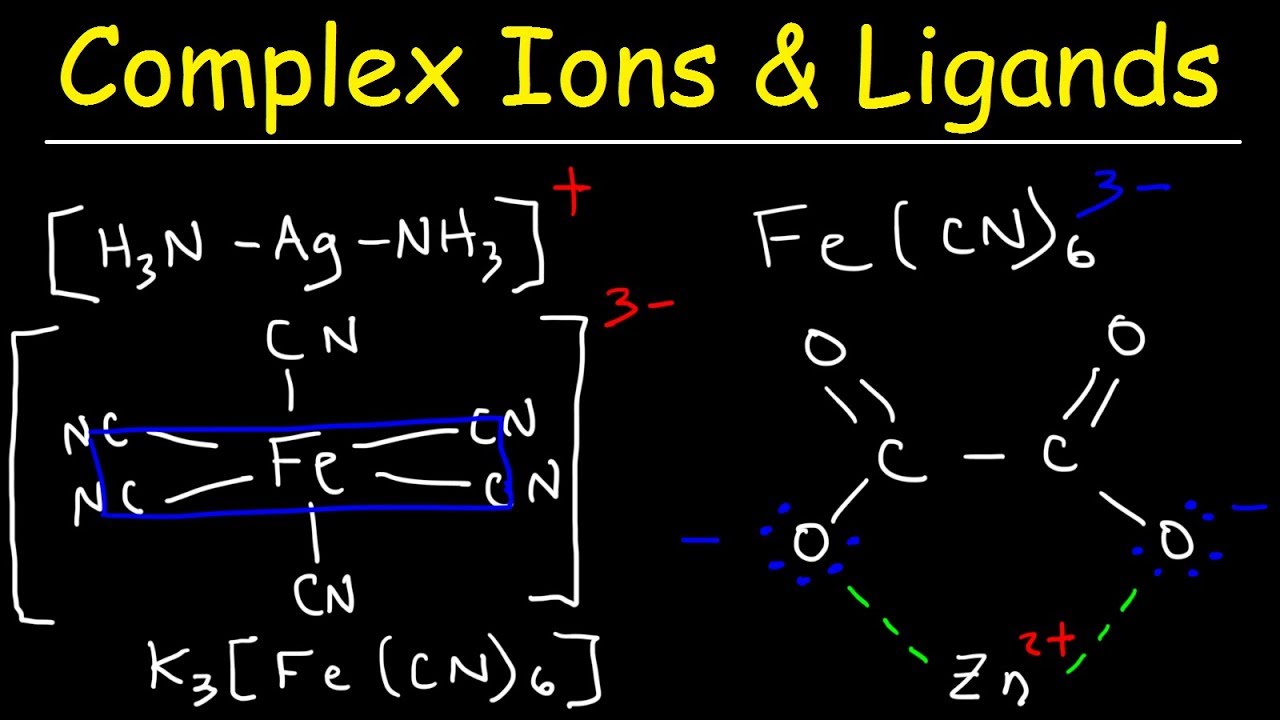
Complex Ions Ligands Coordination Compounds Basic Introductio This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into complex ions, ligands, and coordination compounds. a complex ion typically consist of a tra. 24.1: werner’s theory of coordination compounds. a metal complex consists of a central metal atom or ion that is bonded to one or more ligands, which are ions or molecules that contain one or more pairs of electrons that can be shared with the metal. metal complexes can be neutral, positively charged, or negatively charged.

Complex Ions A Level Chemistrystudent Introduction to coordination chemistry. complexes or coordination compounds are molecules that posess a metal center that is bound to ligands (atoms, ions, or molecules that donate electrons to the metal). these complexes can be neutral or charged. when the complex is charged, it is stabilized by neighboring counter ions. In chemistry, a ligand is a molecule or ion that binds to a central atom or ion to form a coordination complex. ligands are often used in coordination chemistry to form coordination compounds, which are molecules or ions that consist of a central atom or ion bonded to one or more ligands. ligands are sometimes classified based on at how many. The number of ligands bound to the transition metal ion is called the coordination number. although coordination complexes are particularly important in the chemistry of the transition metals, some main group elements also form complexes. aluminum, tin, and lead, for example, form complexes such as the alf 63 , sncl 42 and pbi 42 ions. Coordination chemistry is the study of the compounds that form between metals and ligands, where a ligand is any molecule or ion that binds to the metal. a metal complex is the unit containing the metal bound to its ligands. for example, [ptcl 2 (nh 3) 2] is the neutral metal complex where the pt (ii) metal is bound to two cl ligands and two nh.
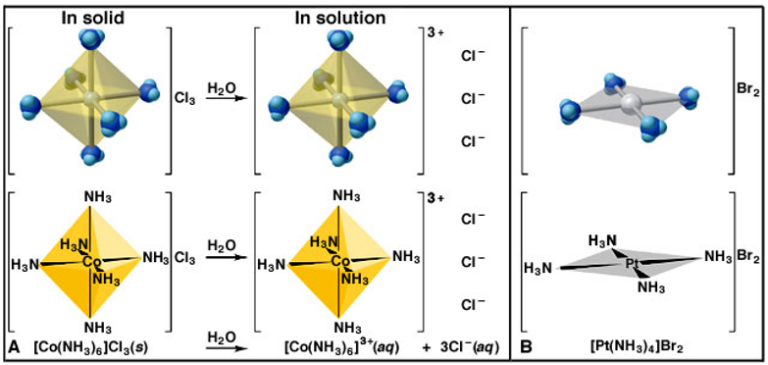
Introduction Of Coordination Compounds W3schools The number of ligands bound to the transition metal ion is called the coordination number. although coordination complexes are particularly important in the chemistry of the transition metals, some main group elements also form complexes. aluminum, tin, and lead, for example, form complexes such as the alf 63 , sncl 42 and pbi 42 ions. Coordination chemistry is the study of the compounds that form between metals and ligands, where a ligand is any molecule or ion that binds to the metal. a metal complex is the unit containing the metal bound to its ligands. for example, [ptcl 2 (nh 3) 2] is the neutral metal complex where the pt (ii) metal is bound to two cl ligands and two nh. Exam 4, mo theory and coordination compounds chapter 9, end and chapter 24. mo theory: rules: 1. the number of mo’s equals the # of atomic orbitals. 2. the overlap of two atomic orbitals gives two molecular orbitals, bonding, one antibonding. 3. atomic orbitals combine with other atomic orbitals of similar energy. The molecules or ions surrounding the central metal ion are called ligands. the nature of ligands. simple ligands include water, ammonia and chloride ions. what all these have got in common is active lone pairs of electrons in the outer energy level. these are used to form co ordinate bonds with the metal ion.
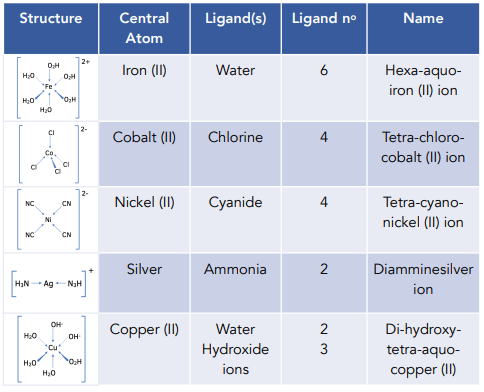
Transition Metals Introduction To Complex Ions A Level Chemistry Exam 4, mo theory and coordination compounds chapter 9, end and chapter 24. mo theory: rules: 1. the number of mo’s equals the # of atomic orbitals. 2. the overlap of two atomic orbitals gives two molecular orbitals, bonding, one antibonding. 3. atomic orbitals combine with other atomic orbitals of similar energy. The molecules or ions surrounding the central metal ion are called ligands. the nature of ligands. simple ligands include water, ammonia and chloride ions. what all these have got in common is active lone pairs of electrons in the outer energy level. these are used to form co ordinate bonds with the metal ion.

Comments are closed.