Computational Thinking Overview Materials Resources

Computational Thinking Overview Materials Resources Computational thinking represents solutions as computational steps or algorithms to be performed by a computer, regardless of the subject area. other countries have implemented computational thinking the royal society published a wake up call to governments to fix their computing education curriculum and implementation, including teacher. This guide explores eleven terms and definitions for computational thinking (ct) concepts, enabling you to incorporate them into existing lesson plans, projects, and demonstrations. teaching tips are included for each concept. this guide contains codes for seven differentiation strategies and their meanings.
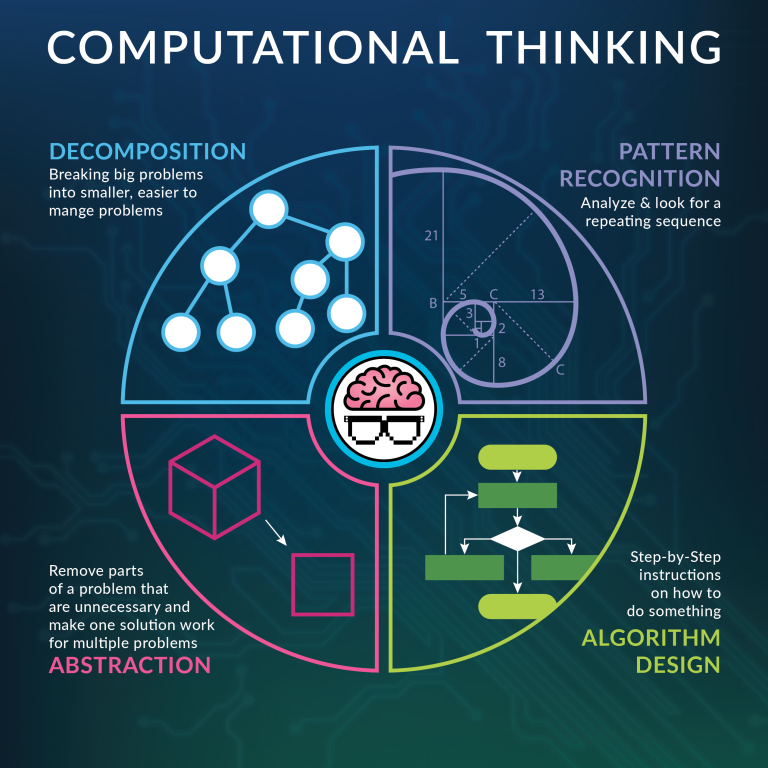
Computational Thinking The Way We Think In Libraries Global 1.a apply existing knowledge to generate new ideas, products, or processes. 1.c use models and simulation to explore complex systems and issues. 2.d contribute to project teams to solve problems. 4.b plan and manage activities to develop a solution or complete a project. The computational thinking (ct) teacher resources relect our commitment to the universal idea that ct can work across all disciplines and with all school age children. csta and iste intend for the ct teacher resources to be a package of introductory materials that makes sense to and inspires teachers who don’t teach computer science. in. This lesson gives students the opportunity to practice the four arts of computational thinking (decomposition, pattern matching, abstraction, and algorithms) in one cohesive activity. teaching summary getting started 15 minutes 1) vocabulary 2) figuring it out activity: computational thinking 25 minutes 3) computational thinking. Computational thinking (ct) — an essential literacy for all students combines four pillars — problem decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction and algorithms. it involves expressing solutions as a series of steps to automate a process. although ct is the foundation for fields such as programming, data science and machine learning.

Comments are closed.