Conditional Probability And Bayes Theorem Intro To Statistics

Conditional Probability And Bayes Theorem Intro To Statistics Youtube In this video, we'll learn about conditional probability, which arises when dealing with related events. we'll cover bayes' theorem and work through a few ex. Definition 2.2.1. for events a and b, with p(b) > 0, the conditional probability of a given b, denoted p(a | b), is given by. p(a | b) = p(a ∩ b) p(b). in computing a conditional probability we assume that we know the outcome of the experiment is in event b and then, given that additional information, we calculate the probability that the.

юааbayesюабтащ Rule With A Simple And Practical Example By Tirthajyoti Sarkar Bayes' theorem is a formula that describes how to update the probabilities of hypotheses when given evidence. it follows simply from the axioms of conditional probability, but can be used to powerfully reason about a wide range of problems involving belief updates. given a hypothesis \ (h\) and evidence \ (e\), bayes' theorem states that the. In the rest of this article, i’ll cover conditional probability in detail. specifically, i’ll cover the following: the definition of conditional probability. how to calculate conditional probabilities in a real life setting. how to visualize conditional probability. an introduction to bayes’ theorem and how conditional probability fits. Bayes' theorem (alternatively bayes' law or bayes' rule, after thomas bayes) gives a mathematical rule for inverting conditional probabilities, allowing us to find the probability of a cause given its effect. [1] for example, if the risk of developing health problems is known to increase with age, bayes' theorem allows the risk to an individual. Bayes' theorem is an extremely important formula, which underpins a powerful concept. it involves conditional probability. this video introduces bayes' theor.

Lesson Video Conditional Probability Nagwa Bayes' theorem (alternatively bayes' law or bayes' rule, after thomas bayes) gives a mathematical rule for inverting conditional probabilities, allowing us to find the probability of a cause given its effect. [1] for example, if the risk of developing health problems is known to increase with age, bayes' theorem allows the risk to an individual. Bayes' theorem is an extremely important formula, which underpins a powerful concept. it involves conditional probability. this video introduces bayes' theor. Disease –. a test is 98% effective at detecting zika (“true positive”). however, the test has a “false positive” rate of 1%. 0.5% of the us population has zika. let: = you test positive , disease = you actually have the disease , test true positive let: = you test negative | for zika with this test. Bayes’ theorem is a formulaic approach to complex conditional probability problems like the last example. however, using the formula is itself complicated, so we will focus on a more intuitive approach. example 7. suppose a certain disease has an incidence rate of 0.1% (that is, it afflicts 0.1% of the population).

Beginnerтащs Guide To юааbayesюабтащ юааtheoremюаб юааand Bayesianюаб юааstatisticsюаб Disease –. a test is 98% effective at detecting zika (“true positive”). however, the test has a “false positive” rate of 1%. 0.5% of the us population has zika. let: = you test positive , disease = you actually have the disease , test true positive let: = you test negative | for zika with this test. Bayes’ theorem is a formulaic approach to complex conditional probability problems like the last example. however, using the formula is itself complicated, so we will focus on a more intuitive approach. example 7. suppose a certain disease has an incidence rate of 0.1% (that is, it afflicts 0.1% of the population).
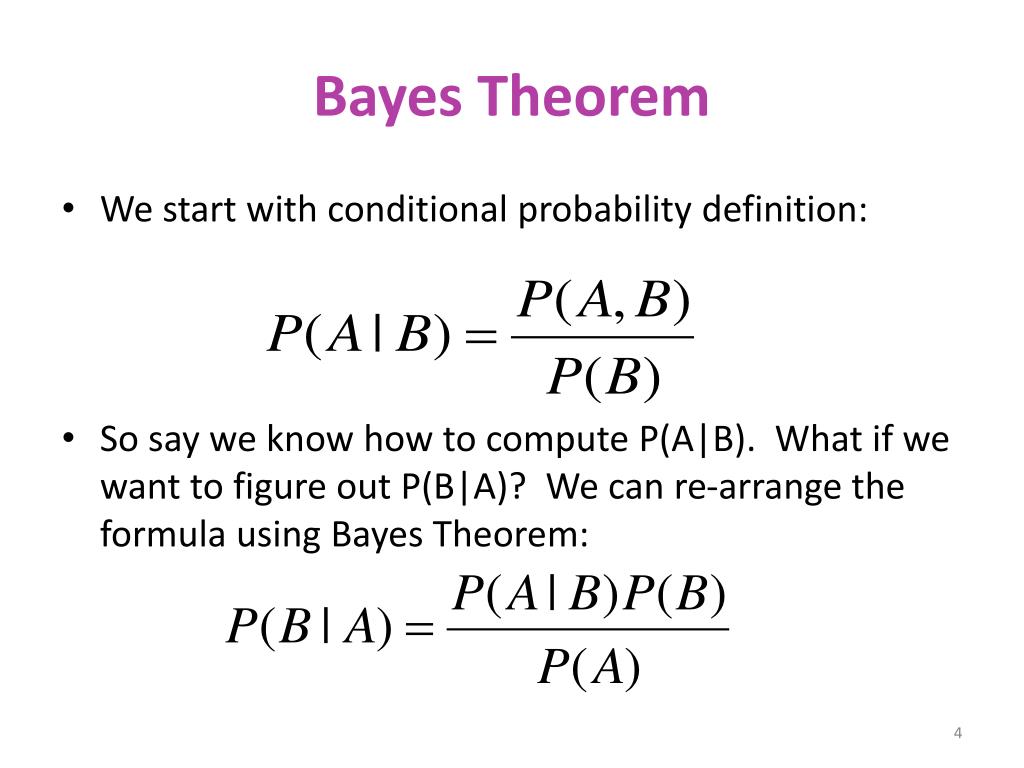
Ppt юааprobabilityюаб юааbayesюабтащ юааtheoremюаб Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.