Conservation Agriculture And Soil Organic Carbon Principles Processes
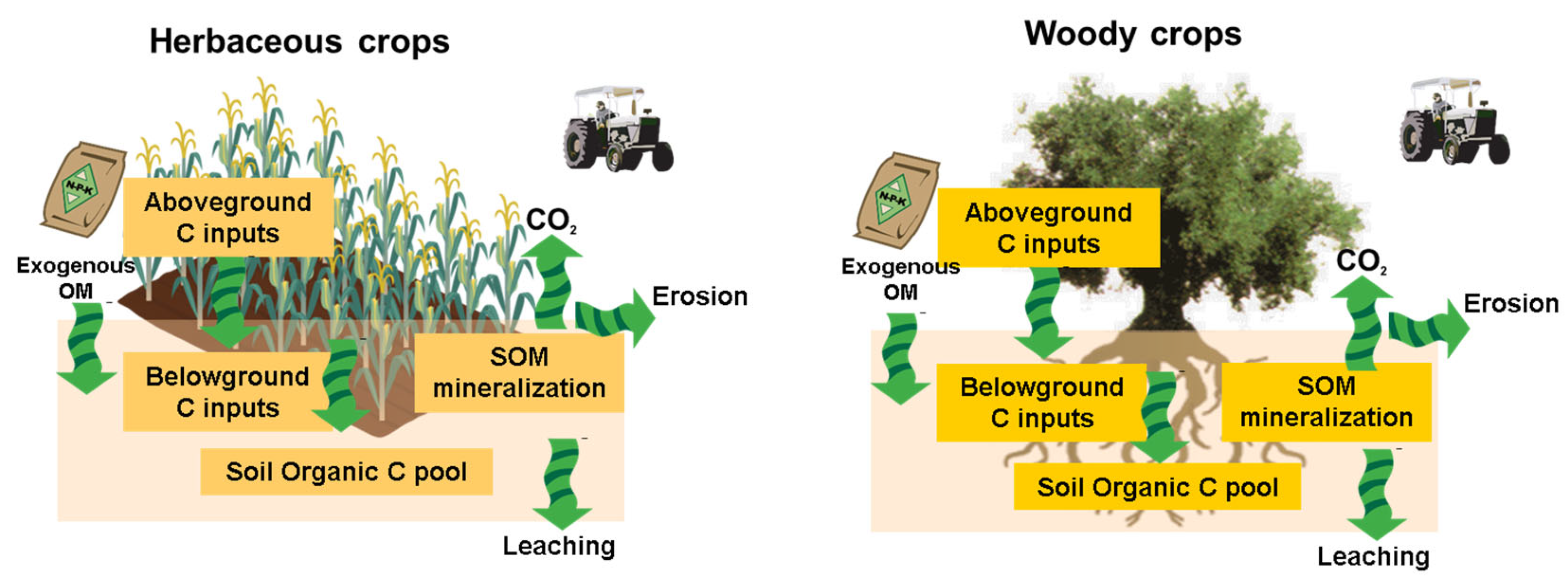
Soil Systems Free Full Text Conservation Agriculture And Soil Intensive agriculture causes land degradation and other environmental problems, such as pollution, soil erosion, fertility loss, biodiversity decline, and greenhouse gas (ghg) emissions, which exacerbate climate change. sustainable agricultural practices, such as reduced tillage, growing cover crops, and implementing crop residue retention measures, have been proposed as cost effective. The soil carbon balance in herbaceous (left) and woody (right) cropping systems depends on the difference between carbon inputs and outputs throughout the agroecosystem, as explained in the text.
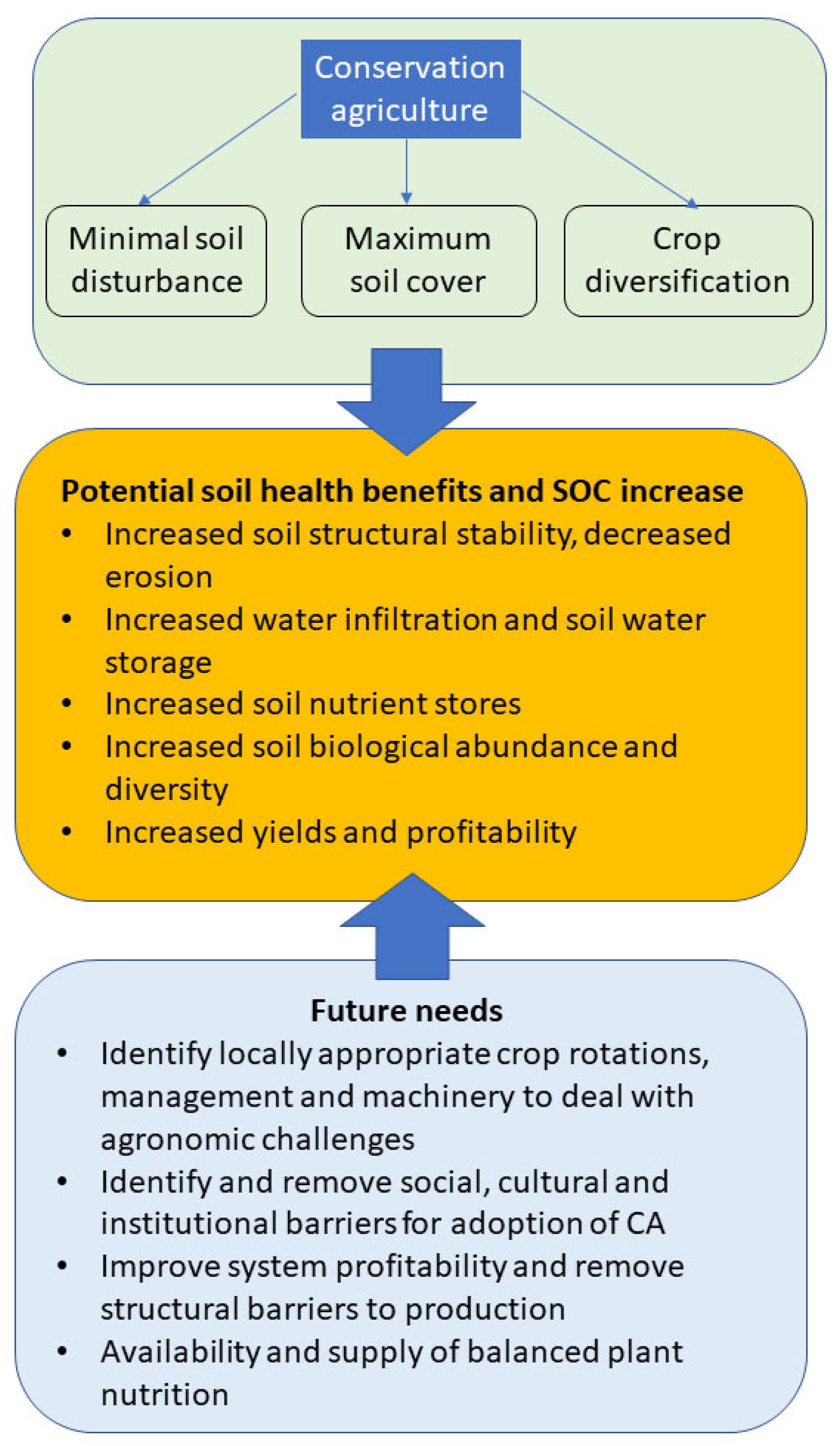
Soil Systems Free Full Text Conservation Agriculture And Soil The results indicated that total soil c (tc) increased by 3.6% on average with the addition of one or more crops in the rotation compared to a monoculture. tc increased by 1.9% with two crops in. Manuscript soilsystems 2181992 “conservation agriculture and soil organic carbon: principles, processes, practices and policy options” authors discussed conservation agriculture and soil organic carbon management as adoption strategies for sustainable agriculture. Sustainable agricultural practices, such as reduced tillage, growing cover crops, and implementing crop residue retention measures, have been proposed as cost effective solutions that can address land degradation, food security, and climate change mitigation and adaptation by enhancing soil organic carbon (soc) sequestration in soils and its. Among the numerous benefits of conservation agricultural practices such as minimized soil disturbance, cover cropping, and crop diversification, 16 has suggested that improved soil organic carbon.

Pdf Conservation Agriculture And Soil Organic Carbon Principles Sustainable agricultural practices, such as reduced tillage, growing cover crops, and implementing crop residue retention measures, have been proposed as cost effective solutions that can address land degradation, food security, and climate change mitigation and adaptation by enhancing soil organic carbon (soc) sequestration in soils and its. Among the numerous benefits of conservation agricultural practices such as minimized soil disturbance, cover cropping, and crop diversification, 16 has suggested that improved soil organic carbon. 1 introduction. soil organic carbon (soc), the major component of soil organic matter, has a great impact in all soil processes. soc dynamics are regulated by climatic variables, geographical characteristics, soil physico chemical properties, quantity and quality of c inputs into the soil and management practices, as well their interactions (haddaway et al., 2017; lal, 2004; lorenz & lal, 2018. Keywords: conservation agriculture, no till, soil organic carbon, yield, soil physical, chemical and biological properties. citation: page kl, dang yp and dalal rc (2020) the ability of conservation agriculture to conserve soil organic carbon and the subsequent impact on soil physical, chemical, and biological properties and yield. front. sustain.

Comments are closed.