Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Explained 2019
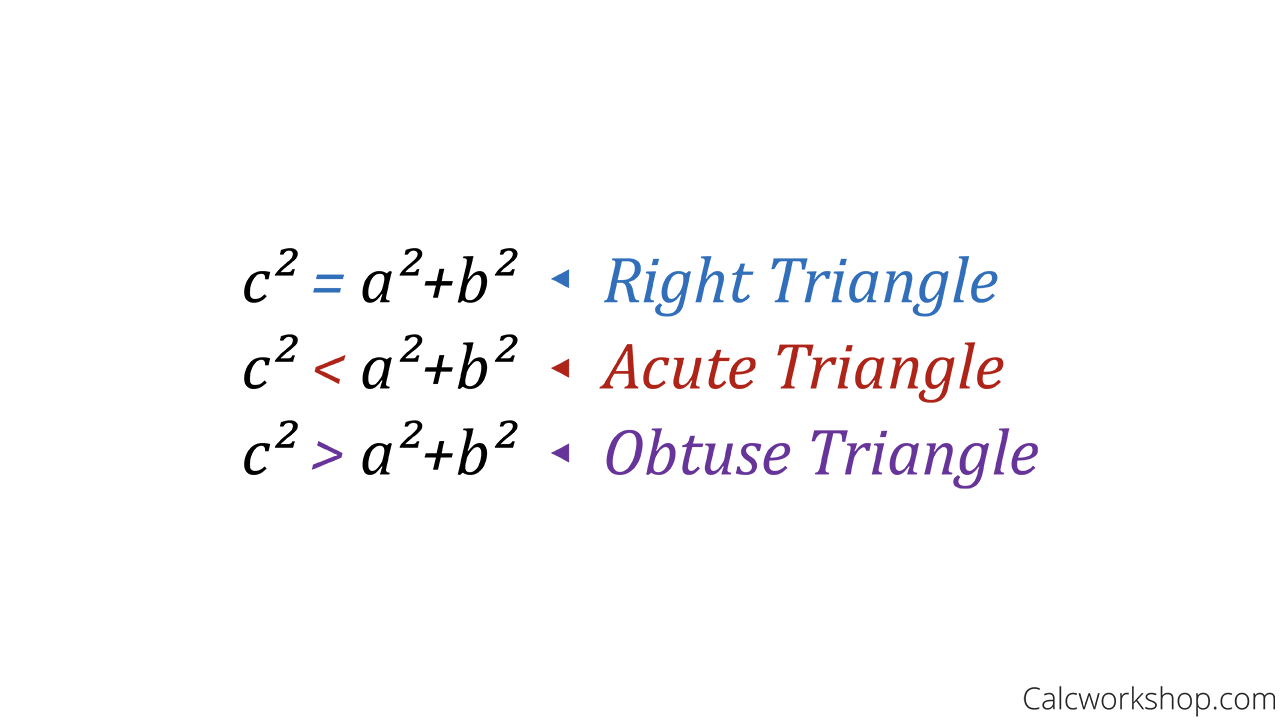
Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Explained 2019 The theorem states that if the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. and the corollary states, if a triangle with side lengths a, b, and c where c is the length of the longest side, we can determine if the triangle is acute or obtuse. Using the converse of pythagoras theorem, we get, (10) 2 = (8) 2 (6) 2. 100 = 64 36. 100 = 100. since both sides are equal, the triangle is a right triangle. example 2: check if the triangle is acute, right, or an obtuse triangle with side lengths as 6, 8, and 11 units. solution: according to the length, we know that 11 units are the.
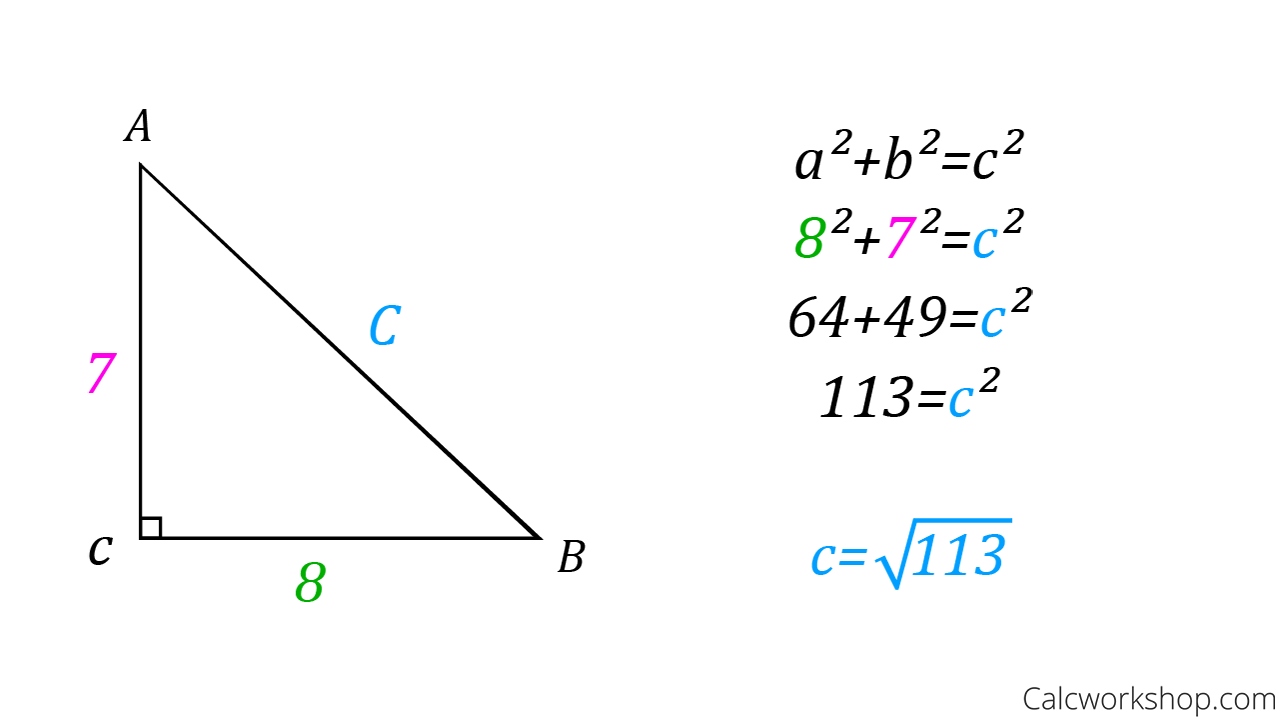
Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Explained 2019 In any right triangle, the sum of the squared lengths of the two legs is equal to the squared length of the hypotenuse. the converse of the pythagorean theorem states that. for any triangle with sides a, b, c, if a2 b2 = c2, then the angle between a and b measures 90° and the triangle is a right triangle. The converse of the pythagorean theorem tells us that if 𝑎 𝑏 = 𝑐 , then the triangle has a right angle. a corollary of this result is that if 𝑎 𝑏 ≠ 𝑐 , the triangle does not have a right angle. from the diagram, the given triangle has side lengths of 13 cm, 12 cm, and 5 cm, so the longest side has length 𝑐 = 1 3 c m. If we come to know that the given sides belong to a right angled triangle, it helps in the construction of such a triangle. using the concept of the converse of pythagoras theorem, one can determine if the given three sides form a pythagorean triplet. converse of pythagoras theorem examples. question 1: the sides of a triangle are 5, 12 and 13. The converse of the pythagorean theorem. the pythagorean theorem states that for a right triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. this theorem can be modeled by the equation \(c^2=a^2 b^2\) where ‘\(c\)’ represents the length of the hypotenuse, ‘a.
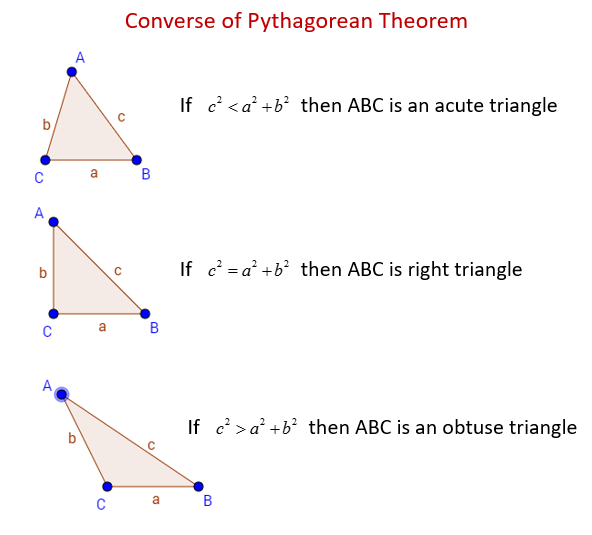
The Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Examples Solutions Videos If we come to know that the given sides belong to a right angled triangle, it helps in the construction of such a triangle. using the concept of the converse of pythagoras theorem, one can determine if the given three sides form a pythagorean triplet. converse of pythagoras theorem examples. question 1: the sides of a triangle are 5, 12 and 13. The converse of the pythagorean theorem. the pythagorean theorem states that for a right triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. this theorem can be modeled by the equation \(c^2=a^2 b^2\) where ‘\(c\)’ represents the length of the hypotenuse, ‘a. Definition: the reverse of the pythagorean theorem states that we may determine whether a triangle is right angled by comparing the sum of the squares of its two sides to the square of its third longer side. to recap, the pythagorean theorem is a well known theorem that lets us determine the length of the sides of a right triangle. The converse of the pythagorean theorem is: if the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. that is, in Δ a b c , if c 2 = a 2 b 2 then ∠ c is a right triangle, Δ p q r being the right angle. we can prove this by contradiction.
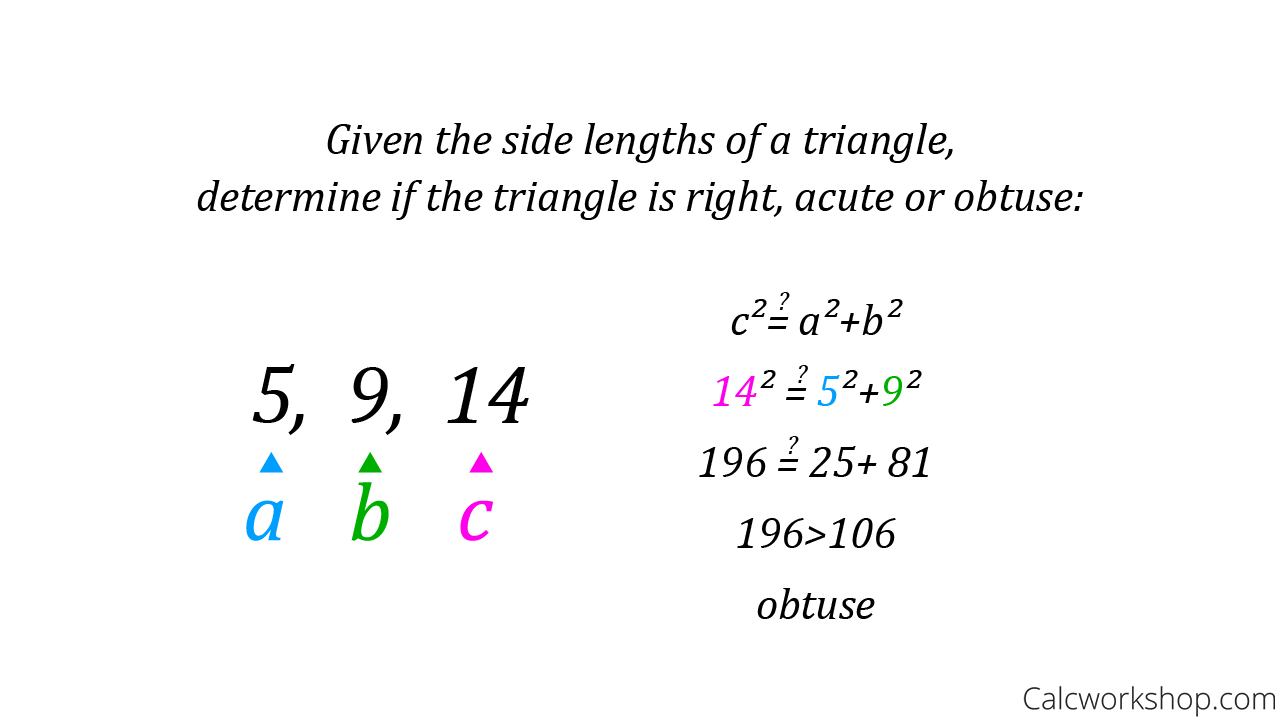
Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Explained 2019 Definition: the reverse of the pythagorean theorem states that we may determine whether a triangle is right angled by comparing the sum of the squares of its two sides to the square of its third longer side. to recap, the pythagorean theorem is a well known theorem that lets us determine the length of the sides of a right triangle. The converse of the pythagorean theorem is: if the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. that is, in Δ a b c , if c 2 = a 2 b 2 then ∠ c is a right triangle, Δ p q r being the right angle. we can prove this by contradiction.

Comments are closed.