Copper Cu Diagram Of The Nuclear Composition And Electron
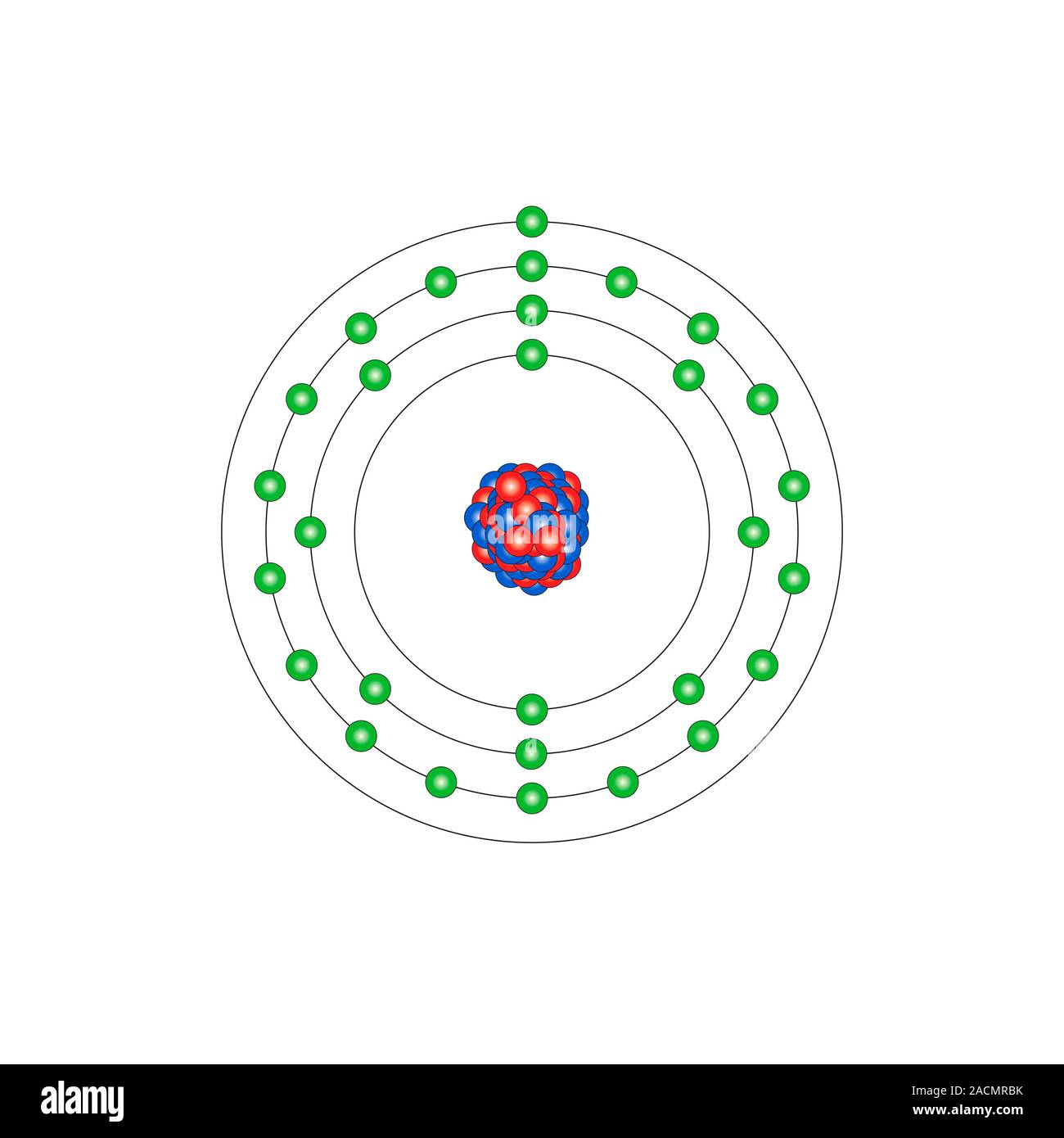
Copper Cu Diagram Of The Nuclear Composition And Electron Copper (cu). diagram of the nuclear composition and electron configuration of an atom of copper 63 (atomic number: 29), the most common isotope of this element. the nucleus consists of 29 protons (red) and 34 neutrons (blue). 29 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Video: cu, cu , and cu2 electron configuration notation. in writing the electron configuration for copper the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for copper go in the 2s orbital. the next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. the p orbital can hold up to six electrons.

Copper Cu Diagram Of The Nuclear Composition And Electron Caption. copper (cu). diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of copper 64 (atomic number: 29), an isotope of this element. the nucleus consists of 29 protons (red) and 35 neutrons (orange). 29 electrons (white) successively occupy available electron shells (rings). Relative atomic mass. the ratio of the average mass per atom of an isotope to 1 12 the mass of a carbon 12 atom. relative atomic mass is also known as atomic weight (symbol: a r). notes (cu) m: standard atomic weight. cu: 63.546 (3) isotopic composition 63 69.15% 63 69.15% 65 30.85% 65 30.85%. Copper. face centered cubic (fcc) (cf4) copper is a chemical element; it has symbol cu (from latin cuprum) and atomic number 29. it is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. a freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish orange color. copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity. Copper (cu). diagram of the nuclear composition and electron configuration of an atom of copper 64 (atomic number: 29), an isotope of this element. the nucleus consists of 29 protons (red) and 35 neutrons (yellow). 29 electrons (white) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).
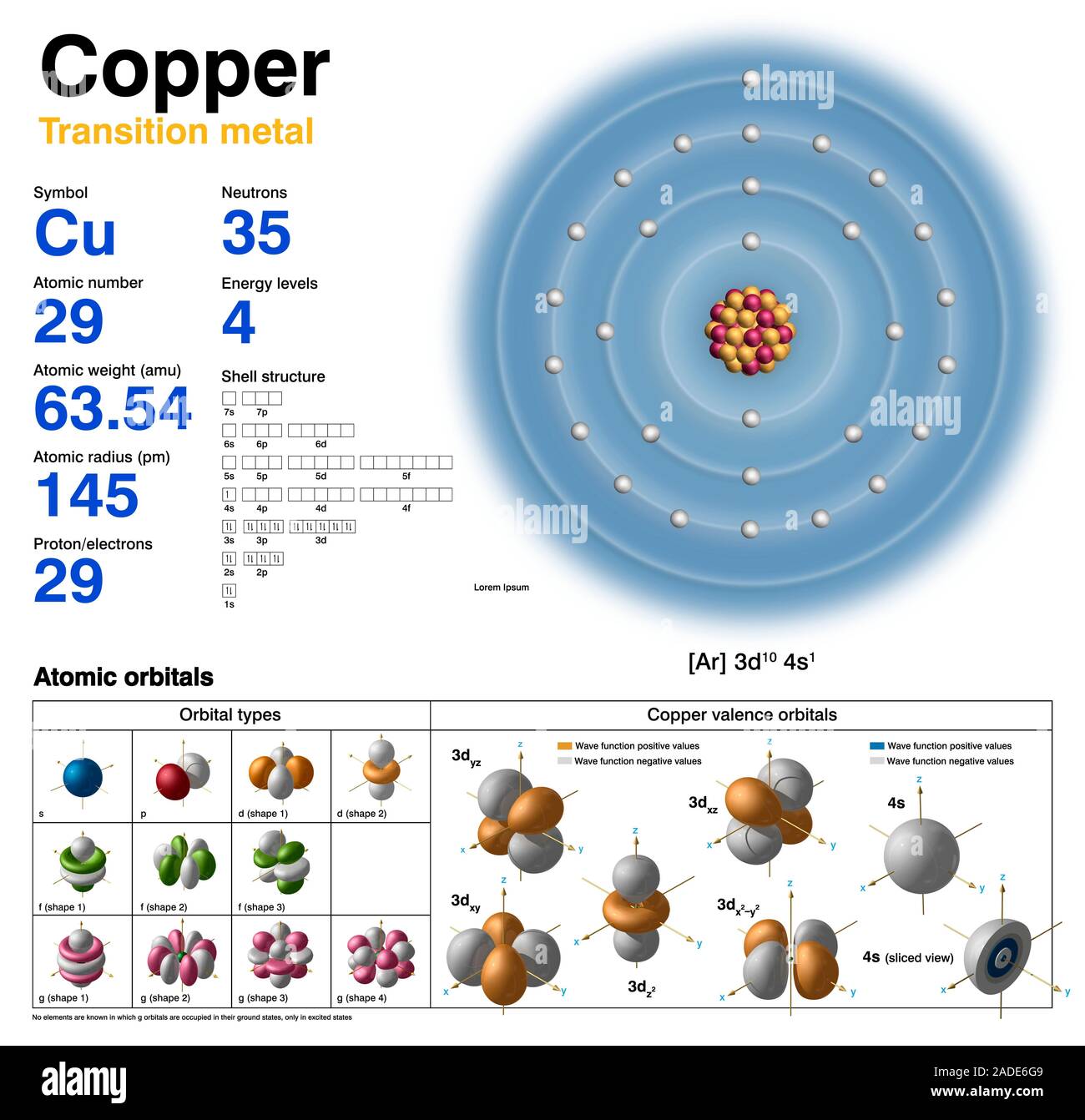
Copper Cu Diagram Of The Nuclear Composition Electron Configurat Copper. face centered cubic (fcc) (cf4) copper is a chemical element; it has symbol cu (from latin cuprum) and atomic number 29. it is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. a freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish orange color. copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity. Copper (cu). diagram of the nuclear composition and electron configuration of an atom of copper 64 (atomic number: 29), an isotope of this element. the nucleus consists of 29 protons (red) and 35 neutrons (yellow). 29 electrons (white) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Copper is the 29th element in the periodic table and has a symbol of cu and atomic number of 29. it has an atomic weight of 63.546 and a mass number of 63. copper has twenty nine protons and thirty four neutrons in its nucleus, and twenty nine electrons in four shells. it is located in group eleven, period four and block d of the periodic table. For example, a carbon atom weighs less than 2 × × 10 −23 g, and an electron has a charge of less than 2 × × 10 −19 c (coulomb). when describing the properties of tiny objects such as atoms, we use appropriately small units of measure, such as the unified atomic mass unit (u) and the fundamental unit of charge (e) .

Comments are closed.