Cosine And Sine Rule Mathematics Studying Math Math Methods G

Cazoom Maths Worksheets Maths Worksheets Math Methods Studying The cosine rule. this also works in any triangle: c² = a² b² 2abcosc. which can also be written as: a² = b² c² 2bccosa. this video show you how to use the cosine rule. the area of a triangle. the area of any triangle is ½ absinc (using the above notation). this formula is useful if you don't know the height of a triangle (since. To calculate the height of a church tower, a surveyor measures the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from two points 50 metres apart. the angles are shown in the diagram. 9. the angles of elevation of a hot air balloon from two points, a and b, on level ground, are 24 .2 ° and 46 .8 °, respectively.
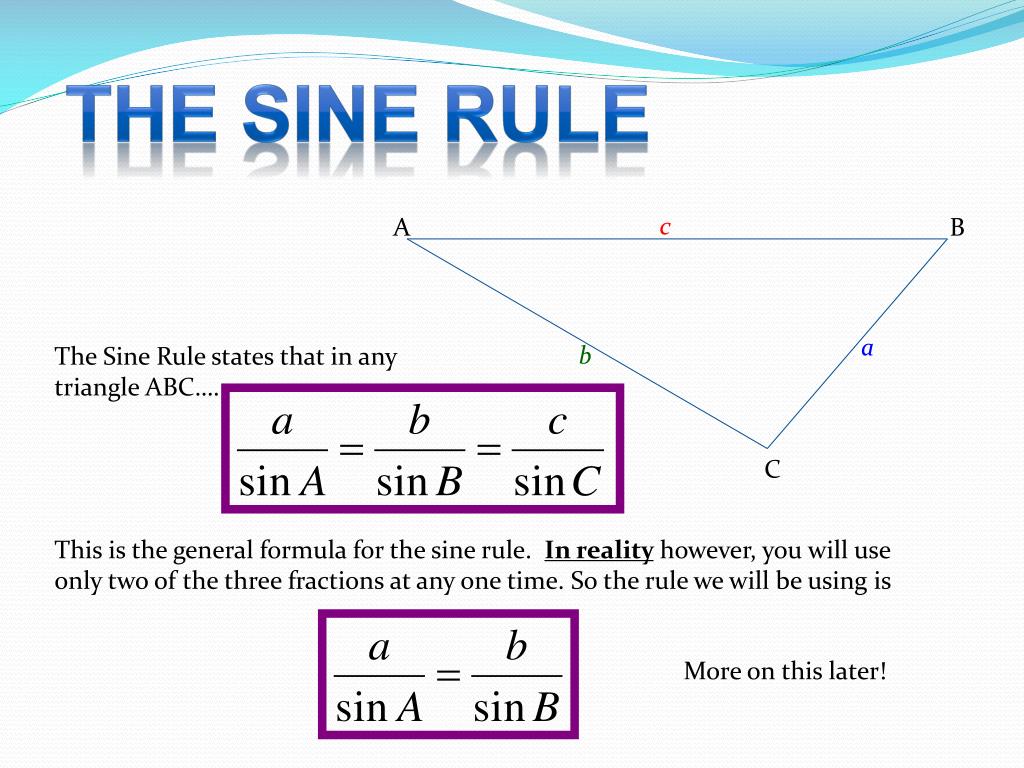
Sin Cos Equation Cosine rule (the law of cosine) the cosine rule is used in the following cases: 1. given two sides and an included angle (sas) 2. given three sides (sss) the cosine rule states that the square of the length of any side of a triangle equals the sum of the squares of the length of the other sides minus twice their product multiplied by the cosine. Devise a strategy using the sine rule and the cosine rule to calculate ∠ b dc and ∠acd exactly. it is worth reflecting on what the cosine rule really tells us: (i) if in a triangle, we know any two sides (a and b) and the included angle (c), then we can calculate the third side (c); and. (ii) if we know all three sides (a, b, c), then we. Law of cosines a b examples: — 2bc(cosa) — 2ac(cosb) — 2ab(cosc) 1) given the following triangle, find the length of d. 2) given the following triangle, find the measure of angle x. note the pattem of the formulas: 2bc(cosa) cosine angle side squared other sides squared minus 2 thnes other sides since we know 2 sides and the included angle,. So far, all you’ve learned about trigonometry only works in right angled triangles. but most triangles are not right angled, and there are two important results that work for all triangles. sine rule. in a triangle with sides a, b and c, and angles a, b and c, sin a a = sin b b = sin c c. cosine rule. in a triangle with sides a, b and c, and.

The Sine And Cosine Rules Animated Powerpoint Gcse Teaching Law of cosines a b examples: — 2bc(cosa) — 2ac(cosb) — 2ab(cosc) 1) given the following triangle, find the length of d. 2) given the following triangle, find the measure of angle x. note the pattem of the formulas: 2bc(cosa) cosine angle side squared other sides squared minus 2 thnes other sides since we know 2 sides and the included angle,. So far, all you’ve learned about trigonometry only works in right angled triangles. but most triangles are not right angled, and there are two important results that work for all triangles. sine rule. in a triangle with sides a, b and c, and angles a, b and c, sin a a = sin b b = sin c c. cosine rule. in a triangle with sides a, b and c, and. Sine rule. sin 90° = 1 so if one of the angles is 90°, this becomes ‘soh’ from sohcahtoa. the sine rule can also be 'flipped over'. this is more useful when we are using the rule to find angles. cosine rule. cos 90° = 0 so if a = 90°, this becomes pythagoras’ theorem. the cosine rule is 'cyclic' so there are two other versions of it. Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is. to calculate them: divide the length of one side by another side.

Sine And Cosine Rule 1 Gcse Higher Maths Tutorial 17 Youtube Sine rule. sin 90° = 1 so if one of the angles is 90°, this becomes ‘soh’ from sohcahtoa. the sine rule can also be 'flipped over'. this is more useful when we are using the rule to find angles. cosine rule. cos 90° = 0 so if a = 90°, this becomes pythagoras’ theorem. the cosine rule is 'cyclic' so there are two other versions of it. Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is. to calculate them: divide the length of one side by another side.

Comments are closed.