Counting Cells Using A Hemocytometer And Trypan Blue Medicine Notes

Counting Cells Using A Hemocytometer And Trypan Blue Medicine Notes Steps. 1. using a pipette, take 100 µl of trypan blue treated cell suspension and apply to the hemocytometer. if using a glass hemocytometer, very gently fill both chambers underneath the coverslip, allowing the cell suspension to be drawn out by capillary action. if using a disposable hemocytometer, pipette the cell suspension into the well. A 1:1 ratio of trypan blue to cell suspension (equals 2 fold dilution)1. vortex briefly (touch spin if using 1.5 ml microfuge tubes to bring contents down from lid). pipette 10 μl of trypan blue cell suspension into hemocytometer chamber, between chamber notch and glass coverslip (figure 1a, black arrow). count cells in boxes 1 4 (figure 1b.

Haemocytometer Cell Counting Cell Counting Calculation Cell An blue (fi. ration 0.32%). mix gently.countingusing a pipette, take 100 μl of trypan blue treated cell suspe. sion and apply to the hemocytometer. if using a glass hemocytometer, very gently fill both chambers underneath the coverslip, allowing the cell suspension. to be drawn out by capillary action. if using a disposable hemocytometer. Position the coverslip over the chambers. resuspend the cell mixture and place 10 μl of stained cells into the hemocytometer chamber using a 20 µl pipettor. note: be careful not to move the coverslip. allow capillary action to draw the sample in. place the hemocytometer on the stage of a binocular light microscope. Move the hemocytometer to the next set of 16 corner squares and continue to count until all 4 sets of 16 squares are counted. take the picture below as an example, the cell numbers of 4 sets of 16 squares are 3, 5, 6, 4, respectively. therefore, the average cell number of this counting is (3 5 6 4) 4 = 4.5. Part 3: counting cells. gently clean microscope lens with a kimwipe and 70% etoh. this only needs to be done once per day of use. place hemocytometer onto microscope stage. adjust microscope objective to 10x and adjust focus so that the cells are clearly visible.
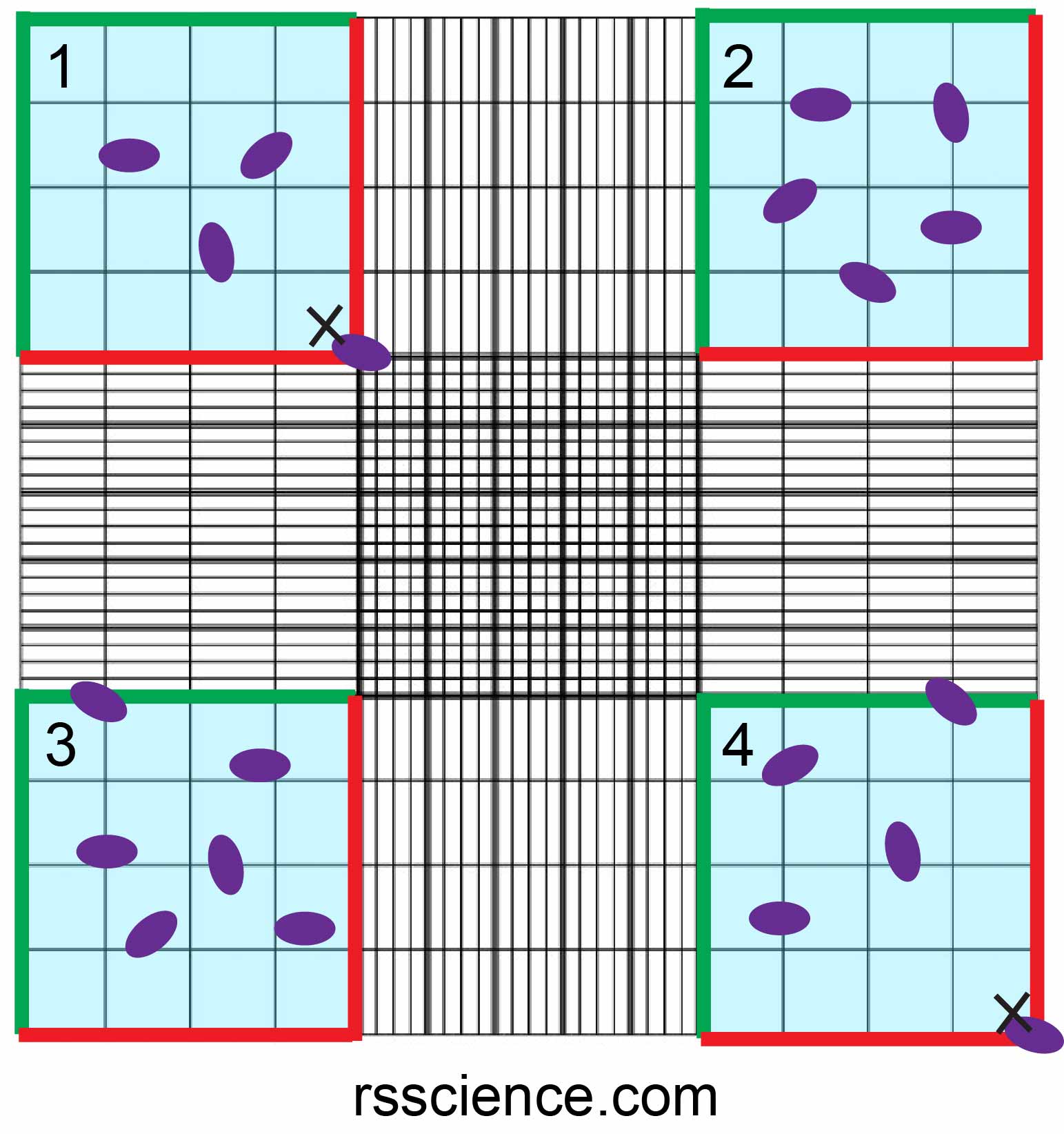
How To Use A Hemocytometer To Count Cells Rs Science Move the hemocytometer to the next set of 16 corner squares and continue to count until all 4 sets of 16 squares are counted. take the picture below as an example, the cell numbers of 4 sets of 16 squares are 3, 5, 6, 4, respectively. therefore, the average cell number of this counting is (3 5 6 4) 4 = 4.5. Part 3: counting cells. gently clean microscope lens with a kimwipe and 70% etoh. this only needs to be done once per day of use. place hemocytometer onto microscope stage. adjust microscope objective to 10x and adjust focus so that the cells are clearly visible. Count the number of dead and alive cells in 5 of the large squares of the hemocytometer grid, using phase contrast microscope under ~10x power. for standardization, count those in the 4 corner squares and center square. for cells touching an edge, count the ones touching the top and left edges and exclude those touching bottom and right edges. Figure 2.counting cells using a hemocytometer and trypan blue. viable cells contain intact cell membranes and do not uptake trypan blue, appearing bright clear in the hemocytometer. dead cells have damaged cell membranes and uptake trypan blue, appearing blue in the hemocytometer. cell viability can be estimated by taking the ratio of live dead.

Mammalian Cell Culture Cell Counting 02 Introduction Hemocytometer Count the number of dead and alive cells in 5 of the large squares of the hemocytometer grid, using phase contrast microscope under ~10x power. for standardization, count those in the 4 corner squares and center square. for cells touching an edge, count the ones touching the top and left edges and exclude those touching bottom and right edges. Figure 2.counting cells using a hemocytometer and trypan blue. viable cells contain intact cell membranes and do not uptake trypan blue, appearing bright clear in the hemocytometer. dead cells have damaged cell membranes and uptake trypan blue, appearing blue in the hemocytometer. cell viability can be estimated by taking the ratio of live dead.

Comments are closed.