Curve Sketching Graphing Functions Using Derivatives Calculus

Discover More Than 57 Curve Sketching Derivatives Best Seven Edu Vn This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into curve sketching. it explains how to graph polynomial functions using the signs of the first. Using the checklist above, we can sketch a curve while identifying the critical characteristics and components along the way. step by step example. for example, suppose we are asked to analyze and sketch the graph of the function. \begin{equation} f(x)= \frac{1}{3} x^{3} x \frac{2}{3} \end{equation} function analysis.

Curve Design Edit Pencil Sketch Stroke Drawing Icon D Vrogue Co Example 3.5.3: curve sketching. sketch f(x) = 5 ( x − 2) ( x 1) x2 2x 4. solution. we again follow key idea 4. we assume that the domain of f is all real numbers and consider restrictions. the only restrictions come when the denominator is 0, but this never occurs. therefore the domain of f is all real numbers, r. This calculus video tutorial provides a summary of the techniques of curve sketching. it shows you how to graph polynomials, rational functions with horizon. You just take the derivative of that function and plug the x coordinate of the given point into the derivative. so say we have f (x) = x^2 and we want to evaluate the derivative at point (2, 4). we take the derivative of f (x) to obtain f' (x) = 2x. afterwards, we just plug the x coordinate of (2,4) into f' (x). Now we can sketch the derivative. we know a few values for the derivative function, and on each interval we know the shape we need. we can use this to create a rough idea of what the graph should look like. figure 4.24. smoothing this out gives us a good estimate for the graph of the derivative. figure 4.25.
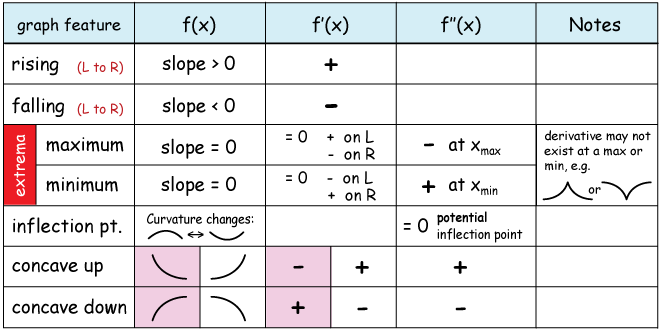
Details More Than 53 Curve Sketching Using Derivatives Super Hot You just take the derivative of that function and plug the x coordinate of the given point into the derivative. so say we have f (x) = x^2 and we want to evaluate the derivative at point (2, 4). we take the derivative of f (x) to obtain f' (x) = 2x. afterwards, we just plug the x coordinate of (2,4) into f' (x). Now we can sketch the derivative. we know a few values for the derivative function, and on each interval we know the shape we need. we can use this to create a rough idea of what the graph should look like. figure 4.24. smoothing this out gives us a good estimate for the graph of the derivative. figure 4.25. Step 6: the second derivative of is. the second derivative is zero at therefore, to determine the concavity of , divide the interval into the smaller intervals and , and choose test points and to determine the concavity of on each of these smaller intervals as shown in the following table. interval. test point. Goal: use rst and second derivatives to make a rough sketch of the graph of a function f(x). recall: critical points: points c in the domain of f(x) where f0(c) does not existor f0(c) = 0.
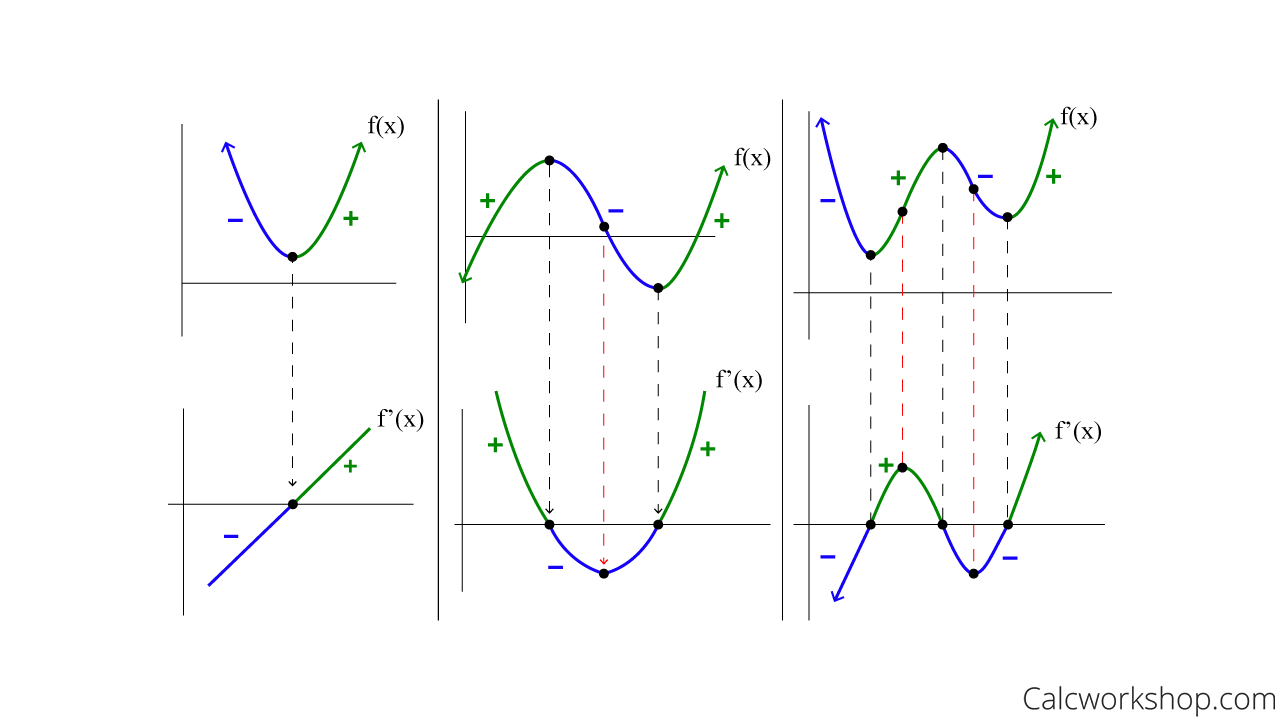
Top 15 Favorites First Derivative Graph Step 6: the second derivative of is. the second derivative is zero at therefore, to determine the concavity of , divide the interval into the smaller intervals and , and choose test points and to determine the concavity of on each of these smaller intervals as shown in the following table. interval. test point. Goal: use rst and second derivatives to make a rough sketch of the graph of a function f(x). recall: critical points: points c in the domain of f(x) where f0(c) does not existor f0(c) = 0.

Comments are closed.