Cystic Fibrosis Pneumonia Tuberculosis Ventilation Asthma Copd Tb
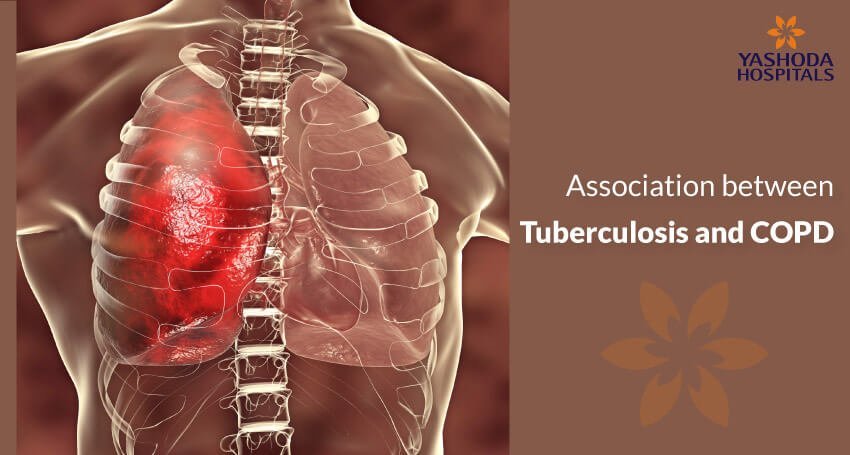
Does Tuberculosis Cause Copd Pulmonary Fibrosis Or Restrictive Lung Over 3 million canadians cope with one of five serious respiratory diseases – asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd), lung cancer, tuberculosis (tb), and cystic fibrosis. these and other respiratory diseases such as influenza, pneumonia, bronchiolitis, respiratory distress syndrome and sleep apnea affect individuals of all ages. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (mtb) infection is rarely seen in cystic fibrosis (cf) patients. we report a 24 year old cf patient with fever, cough, hemoptysis, and weight loss of 1week duration prior to admission. past sputum cultures grew methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus and pseudomonas aeruginosa. the patient was treated with broad.
Does Tuberculosis Cause Copd Pulmonary Fibrosis Or Restrictive Lung Tuberculosis and lung damage: from epidemiology to. Pneumonia due to s. pneumoniae continues to be the most common single agent and is continually evolving resistance to a wider array of antibiotics. viral and atypical agents are the most rapidly growing causes. pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and tuberculosis (tb) are significant pathogens, particularly in the developing world. the severe acute. Patients with cystic fibrosis (cf) have no substantial shunt when managed according to modern treatment regimens. interstitial lung diseases demonstrate impaired oxygen diffusion across the alveolar capillary barrier, particularly during exercise, although a inequality still accounts for most of the gas exchange abnormality. hypoxemia may. The causative agent of tb is mycobacterium tuberculosis. acute tuberculous pneumonia (tp) is an acute form of pulmonary tb. however, acute tp and non tuberculous community acquired pneumonia can be easily confused, resulting in deterioration of tp due to delayed treatment. therefore, rapid and accurate diagnosis of acute tp is crucial in order.
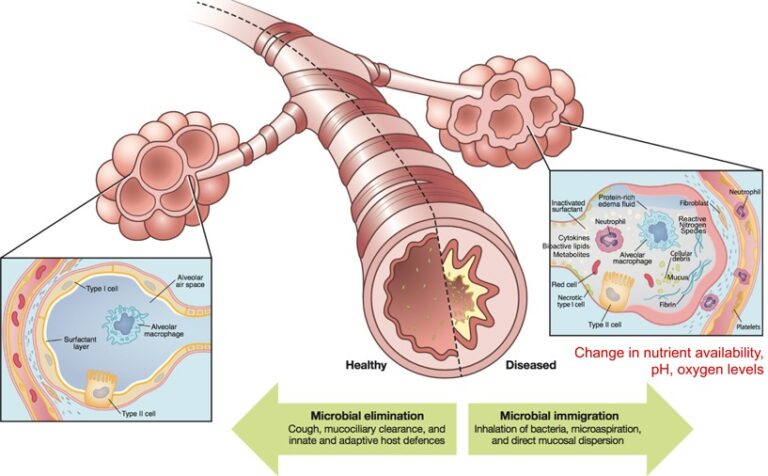
The Changing Microbiome In Cystic Fibrosis A Key To Diagnosis And Patients with cystic fibrosis (cf) have no substantial shunt when managed according to modern treatment regimens. interstitial lung diseases demonstrate impaired oxygen diffusion across the alveolar capillary barrier, particularly during exercise, although a inequality still accounts for most of the gas exchange abnormality. hypoxemia may. The causative agent of tb is mycobacterium tuberculosis. acute tuberculous pneumonia (tp) is an acute form of pulmonary tb. however, acute tp and non tuberculous community acquired pneumonia can be easily confused, resulting in deterioration of tp due to delayed treatment. therefore, rapid and accurate diagnosis of acute tp is crucial in order. Treatment of pulmonary exacerbations in cf is multifaceted, involving antibiotics, chest physiotherapy, inhaled medications to promote secretion clearance, and, sometimes, antiinflammatory agents. an overview of these interventions will be reviewed here. selection of antibiotics for pulmonary exacerbations is discussed in a separate topic review. Purpose of review cystic fibrosis (cf) is a multisystem, autosomal recessive disease that leads to progressive loss of lung function. respiratory symptoms for both cf and asthma include cough, wheezing, and dyspnea. there is debate within the cf community on how to best define and distinguish cf asthma overlap syndrome (cfaos) from asthma like features, though cfaos is well recognized. we aim.
/Illo_CysticFibrosis-56f5b0b45f9b582986653714.png)
Cystic Fibrosis Symptoms And Diagnosis Treatment of pulmonary exacerbations in cf is multifaceted, involving antibiotics, chest physiotherapy, inhaled medications to promote secretion clearance, and, sometimes, antiinflammatory agents. an overview of these interventions will be reviewed here. selection of antibiotics for pulmonary exacerbations is discussed in a separate topic review. Purpose of review cystic fibrosis (cf) is a multisystem, autosomal recessive disease that leads to progressive loss of lung function. respiratory symptoms for both cf and asthma include cough, wheezing, and dyspnea. there is debate within the cf community on how to best define and distinguish cf asthma overlap syndrome (cfaos) from asthma like features, though cfaos is well recognized. we aim.

Comments are closed.