Dairy And Cardiovascular Disease
Foods Free Full Text Dairy Fats And Cardiovascular Disease Do We Milk and other dairy foods provide protein, calcium, potassium, phosphorus, vitamins a, d, and b12 and other nutrients that are vital to your body and how it functions. on the flip side, however, some dairy foods also contain saturated fat — a fat that can raise low density lipoprotein (ldl) cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart disease. People with heart disease should aim for about half that limit, or about 9 to 10 grams per day. because one serving of full fat dairy has about 5 grams of saturated fat, most people could certainly consider using whole milk or 2% milk on their morning cereal, if they choose, or snacking on full fat yogurt — if the rest of their diet has.

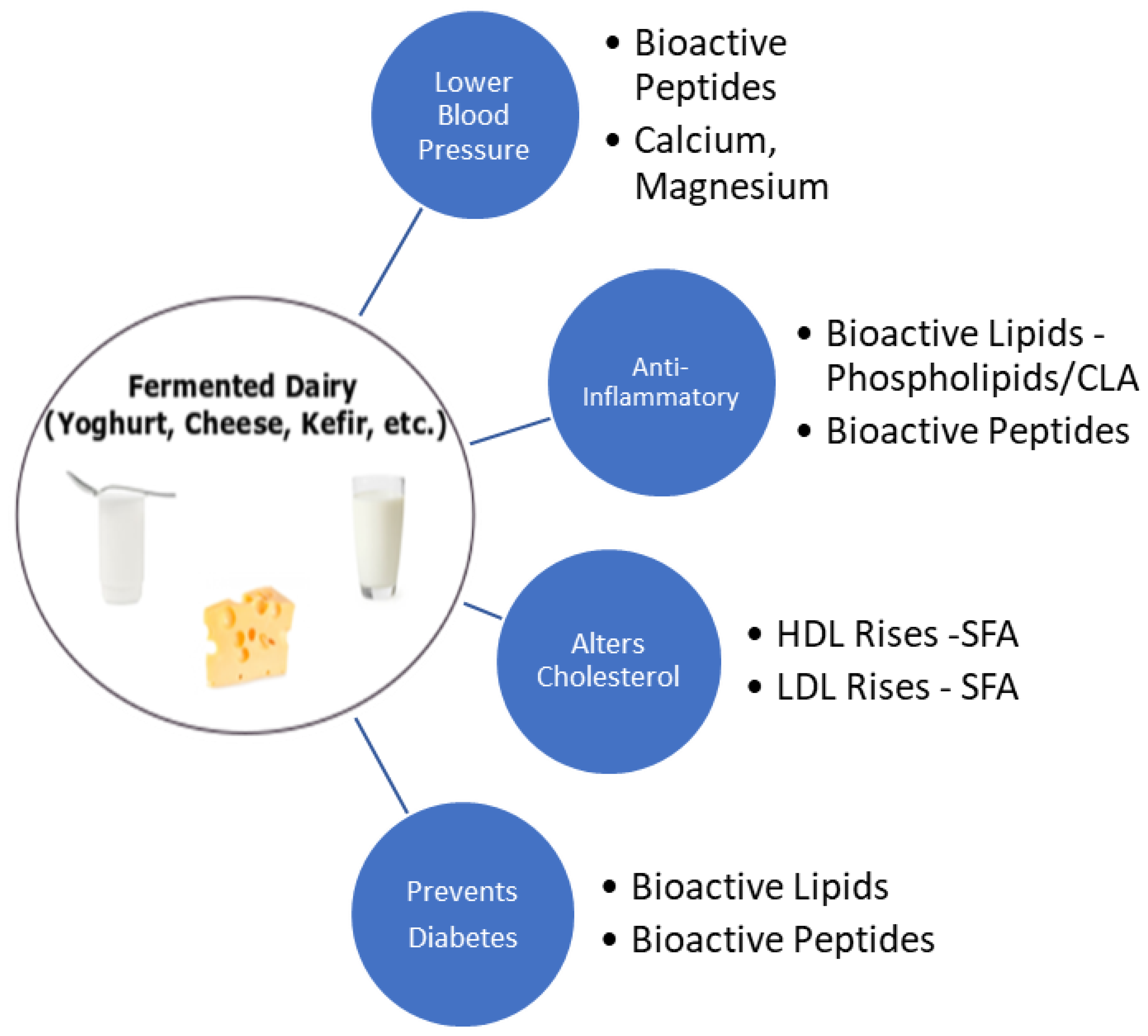
Dairy And Cardiovascular Disease Rediscover Dairy Limited consumption of dairy foods and use of low fat products is recommended for cardiovascular (cv) prevention; however, other features besides fat content modulate their metabolic effects. we analyze updated evidence on the relationship of different dairy products (low full fat dairy, milk, cheese, yogurt) with cvd by reviewing meta analyses. Abstract. the consumption of dairy, including milk, cheese and yogurt, has been associated with better quality of diet and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death globally. the purpose of this review is to examine recent literature on the relationship between dairy consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease. Using this framework, dietary guidelines recommend minimising consumption of whole fat dairy products for cardiovascular disease prevention in populations. 2 however, dairy products and dairy fat also contain potentially beneficial compounds—including specific aminoacids, medium chain and odd chain saturated fats, milk fat globule. Milk and dairy products containing milk fat are major food sources of saturated fatty acids, which have been linked to increased risk of cardiovascular related clinical outcomes such as cardiovascular disease (cvd), coronary heart disease (chd), and stroke.

Science Summary Dairy And Cardiovascular Disease Dairy Discovery Zone Using this framework, dietary guidelines recommend minimising consumption of whole fat dairy products for cardiovascular disease prevention in populations. 2 however, dairy products and dairy fat also contain potentially beneficial compounds—including specific aminoacids, medium chain and odd chain saturated fats, milk fat globule. Milk and dairy products containing milk fat are major food sources of saturated fatty acids, which have been linked to increased risk of cardiovascular related clinical outcomes such as cardiovascular disease (cvd), coronary heart disease (chd), and stroke. The association between dairy product consumption and cardiovascular health remains highly debated. we quantitatively synthesized prospective cohort evidence on the associations between dairy consumption and risk of hypertension (htn), coronary heart disease (chd), and stroke. we systematically sear …. With a growing number of prospective cohort studies, an updated dose–response meta analysis of milk and dairy products with all cause mortality, coronary heart disease (chd) or cardiovascular disease (cvd) have been conducted. pubmed, embase and scopus were searched for articles published up to september 2016.

Comments are closed.