Data Suggest Universe Is Expanding Faster Than Expected But How Fast
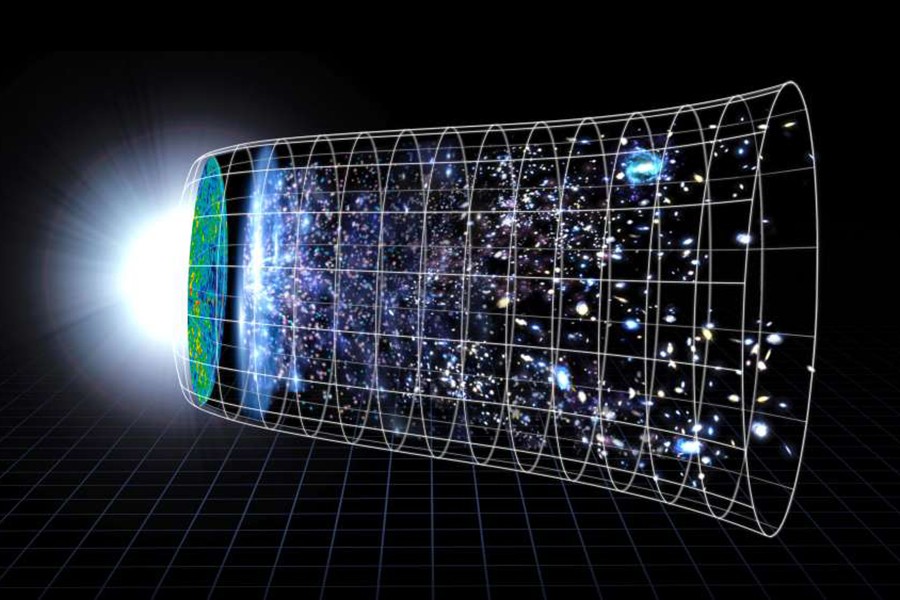
Data Suggest Universe Is Expanding Faster Than Expected But How Fast But how fast is the universe expanding? as hubble and other telescopes seek to answer this question, they have run into an intriguing difference between what scientists predict and what they observe. hubble measurements suggest a faster expansion rate in the modern universe than expected, based on how the universe appeared more than 13 billion. September 20, 2023. • 5 min read. new data from nasa's james webb space telescope have deepened a mystery about how fast the universe is expanding. the discovery hints that unknown physics may.

New Data Suggests The Universe Expanding More Rapidly Than Believed R This method predicts that the universe should be expanding at a rate of about 67.36 kilometers per second per megaparsec (a megaparsec equals 3.26 million light years). by contrast, other teams. The puzzle, called the "hubble tension," is that the current rate of the expansion of the universe is faster than what astronomers expect it to be, based on the universe's initial conditions and our present understanding of the universe’s evolution. scientists using nasa's hubble space telescope and many other telescopes consistently find a. Astronomers using nasa’s hubble space telescope have discovered that the universe is expanding 5 percent to 9 percent faster than expected. this hubble space telescope image shows one of the galaxies in the survey to refine the measurement for how fast the universe expands with time, called the hubble constant. nasa, esa and a. riess (stsci jhu). Depending on the values deduced for the expansion rate, the universe could be anywhere between 10 and 20 billion years old. over the past 34 years hubble has shrunk this measurement to an accuracy of less than one percent, splitting the difference with an age value of 13.8 billion years. this has been accomplished by refining the so called.

Comments are closed.