Day 1 Climate Smart Agriculture Basics
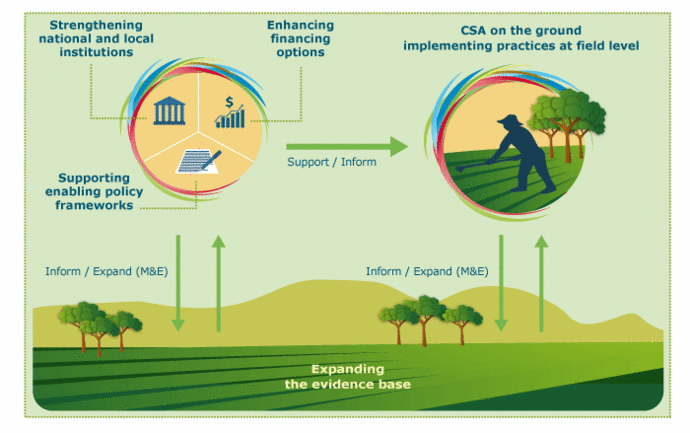
A1 2 Climate Smart Agriculture Climate Smart Agriculture Sourceb Introduction. climate smart agriculture (csa) may be defined as an approach for transforming and reorienting agricultural development under the new realities of climate change (lipper et al. 2014). 1 the most commonly used definition is provided by the food and agricultural organisation of the united nations ( fao ), which defines csa as. The global technical mitigation potential from agriculture (excluding fossil fuel offsets from biomass) by 2030, considering all gases, is estimated to be approximately 5500–6000 mt co2 eq. yr−1, with economic potentials of approximately 1500–1600, 2500–2700 and 4000–4300 mt co2 eq. yr−1 at carbon prices of up to 20, up to 50 and up to 100 us$ t co2 eq.−1, respectively.
The Carbon Cycle And Climate Smart Agriculture Climate smart agriculture (csa) helps address a number of important challenges:. 1. csa addresses food security, misdistribution and malnutrition. despite the attention paid to agricultural development and food security over the past decades, there are still about 800 million undernourished and 1 billion malnourished people in the world. This course analyses climate change impacts on agriculture, food security and food systems and provides an overview of the main climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies in agriculture. it also introduces the climate smart agriculture (csa)approach and describes the 5 step process to implement it. this course addresses the subject matter from a technical perspective, but is written. Climate smart agriculture. climate smart agriculture (csa) is an approach to help the people who manage agricultural systems respond effectively to climate change. the csa approach pursues the triple objectives of sustainably increasing productivity and incomes, adapting to climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions where possible. Climate smart agriculture. climate smart agriculture (csa) is an approach that helps guide actions to transform agri food systems towards green and climate resilient practices. csa supports reaching internationally agreed goals such as the sdgs and the paris agreement. it aims to tackle three main objectives: sustainably increasing agricultural.

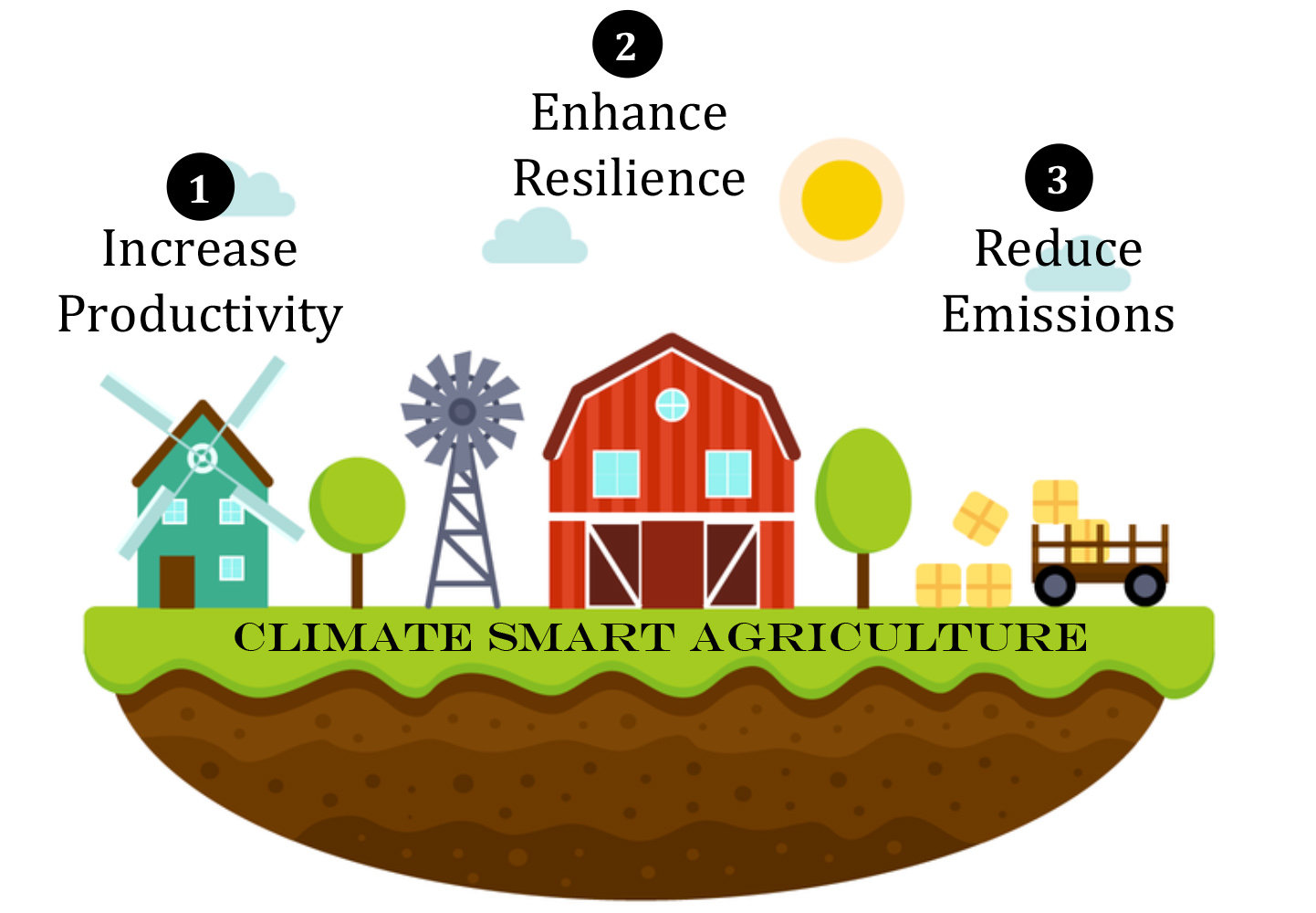
Our Recommendations Arable Climate Change Group A New Blueprint For Climate smart agriculture. climate smart agriculture (csa) is an approach to help the people who manage agricultural systems respond effectively to climate change. the csa approach pursues the triple objectives of sustainably increasing productivity and incomes, adapting to climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions where possible. Climate smart agriculture. climate smart agriculture (csa) is an approach that helps guide actions to transform agri food systems towards green and climate resilient practices. csa supports reaching internationally agreed goals such as the sdgs and the paris agreement. it aims to tackle three main objectives: sustainably increasing agricultural. Reaches 9 billion, while climate change is projected to reduce global average yields. climate change will affect agriculture through higher temperatures, greater crop water demand, more variable rainfall and extreme climate events such as heat waves, floods and droughts. marginal areas, where low yields and poverty go hand in hand, may. The 3 pillars of climate smart agriculture. any climate smart program aims to: improve farmer productivity, and as a result, livelihoods; make farms more resilient to climate impacts they’re facing now, and to those likely to hit in the future; and, where feasible, curb greenhouse gas emissions associated with growing food.
Climate Smart Agriculture Bferst Bferst Reaches 9 billion, while climate change is projected to reduce global average yields. climate change will affect agriculture through higher temperatures, greater crop water demand, more variable rainfall and extreme climate events such as heat waves, floods and droughts. marginal areas, where low yields and poverty go hand in hand, may. The 3 pillars of climate smart agriculture. any climate smart program aims to: improve farmer productivity, and as a result, livelihoods; make farms more resilient to climate impacts they’re facing now, and to those likely to hit in the future; and, where feasible, curb greenhouse gas emissions associated with growing food.

Climate Smart Agriculture For Development

Comments are closed.