Deep Neck Space Infections Teachmesurgery
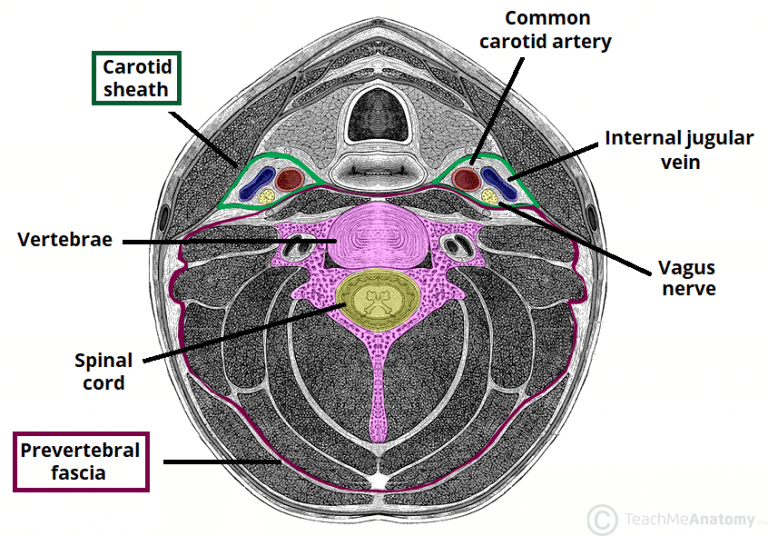
Deep Neck Space Infections Teachmesurgery Deep neck space infections (dnsis) are serious ent presentations, with the potential for the patient to rapidly deteriorate with airway compromise. mortality rate is between 1% to 2%. the infection will typically spread from the oropharyngeal region and into the fascial planes (see below). the main types of dnsi are: submandibular space abscess. Neck. the neck is the area between the skull base and the clavicles, and despite being a relatively small region, it contains a range of important anatomical features, including the oesophagus, blood vessels, nerves, and spinal cord. as such, the differentials for a neck lump are large, as in theory any part of the make up of the neck can give.
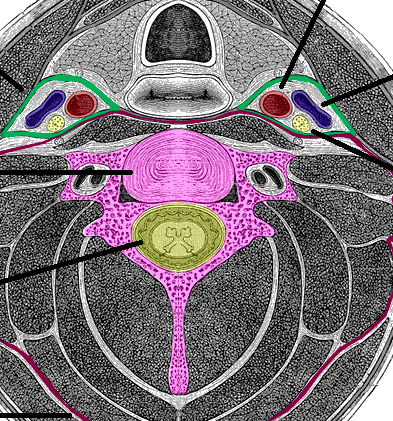
Deep Neck Space Infections Teachmesurgery Introduction. deep neck space infections most commonly arise from a septic focus of the mandibular teeth, tonsils, parotid gland, deep cervical lymph nodes, middle ear, or sinuses. these deep cervical space infections have become relatively uncommon in the post antibiotic era. consequently, many clinicians are unfamiliar with these conditions. Deep neck infections are serious but treatable infections that affect the deep cervical spaces. these infections can rapidly progress and lead to life threatening complications, making them a significant health concern with notable morbidity and potential mortality. deep neck infections commonly arise from local extensions of infections in the tonsils, parotid glands, cervical lymph nodes, and. Deep neck space infections refer to infection or abscess formation in the deep tissues, fascial planes and potential spaces in the neck. 1. the deep cervical fascia of the neck creates potential spaces where infection can spread and develop. the classic deep space neck infections occur in the peri tonsillar, parapharyngeal or retropharyngeal. The report, using the korean national health insurance service national sample cohort (2002 2019), compared 46,293 patients with deep neck space infections to 185,172 controls and found the adjusted odds ratio for deep neck space infections in individuals with a prior history of chronic periodontitis to be 1.55.
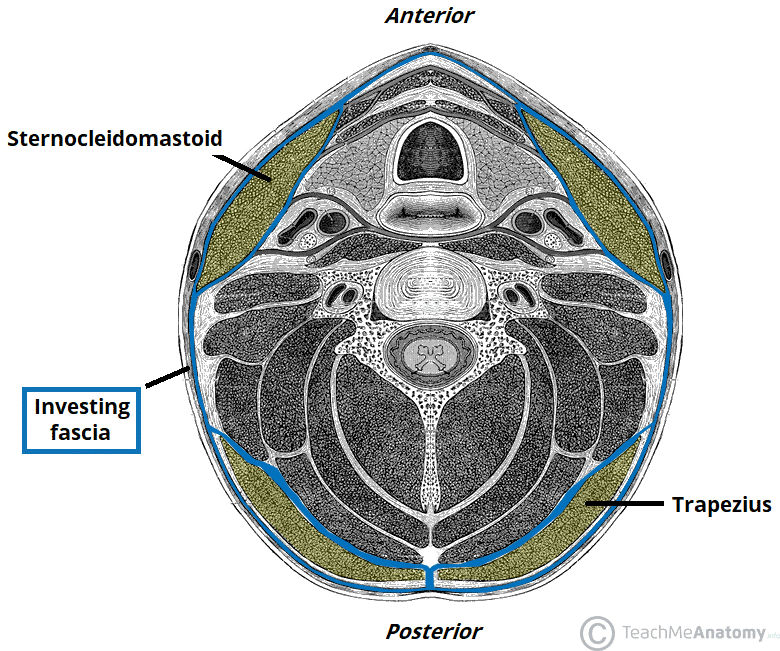
Deep Neck Space Infections Teachmesurgery Deep neck space infections refer to infection or abscess formation in the deep tissues, fascial planes and potential spaces in the neck. 1. the deep cervical fascia of the neck creates potential spaces where infection can spread and develop. the classic deep space neck infections occur in the peri tonsillar, parapharyngeal or retropharyngeal. The report, using the korean national health insurance service national sample cohort (2002 2019), compared 46,293 patients with deep neck space infections to 185,172 controls and found the adjusted odds ratio for deep neck space infections in individuals with a prior history of chronic periodontitis to be 1.55. 1.2 clinical relevance and rationale. deep neck space infections (dnsis) have considerable morbidity and mortality. the most serious complications include airway obstruction, descending mediastinitis, great vessel thrombosis, necrotising fasciitis and sepsis. 6 10 rates of tracheostomy in dnsis have been reported up to 30% 8 with mortality around 5%. 6. The anterior visceral or pretracheal space located below the hyoid. 2. a deep neck space infection (dni) is defined as an infection in the potential spaces and actual fascial planes of the neck. 3. once the natural resistance of fascial planes is overcome, spread of infection occurs along communicating fascial boundries. 2.
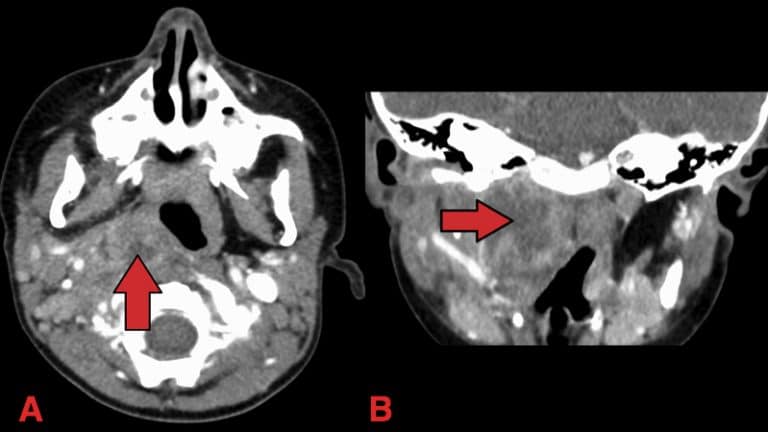
Deep Neck Space Infections Teachmesurgery 1.2 clinical relevance and rationale. deep neck space infections (dnsis) have considerable morbidity and mortality. the most serious complications include airway obstruction, descending mediastinitis, great vessel thrombosis, necrotising fasciitis and sepsis. 6 10 rates of tracheostomy in dnsis have been reported up to 30% 8 with mortality around 5%. 6. The anterior visceral or pretracheal space located below the hyoid. 2. a deep neck space infection (dni) is defined as an infection in the potential spaces and actual fascial planes of the neck. 3. once the natural resistance of fascial planes is overcome, spread of infection occurs along communicating fascial boundries. 2.

Deep Neck Space Infections Youtube

Comments are closed.