Deep Posterior Lower Leg Muscles

Muscles Of The Posterior Leg Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy The posterior muscles are natural antagonists to the anterior muscle group. generally, their main functions are plantarflexion, inversion of the foot, and flexion of the toes. additionally, the natural tension of these muscles, especially the tibialis anterior, supports the medial arch of the foot. namely, the deep flexor muscles of the leg are. The posterior compartment of the leg contains seven muscles and can be subdivided into superficial and deep compartments. the muscles in this compartment act to plantarflex and invert the foot. they are innervated by the tibial nerve (a branch of the sciatic nerve). blood supply chiefly from the posterior tibial artery.
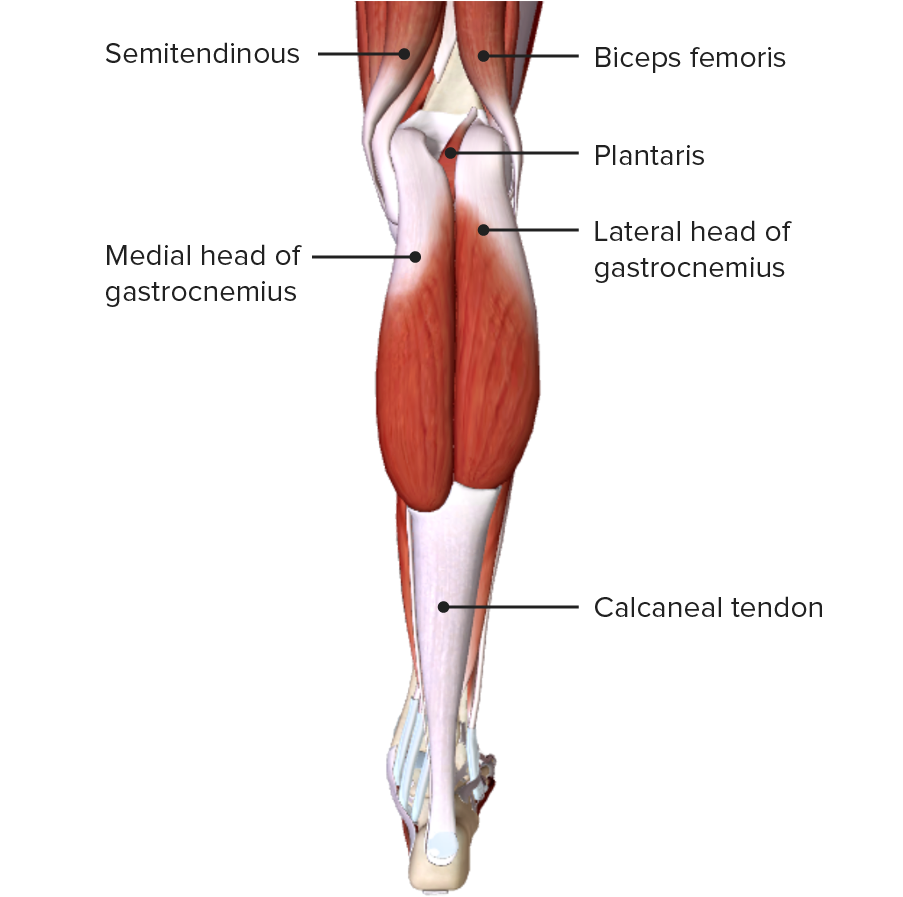
Deep Posterior Lower Leg Muscles Deep posterior muscle. the most superior muscle of the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg is the popliteus muscle. the popliteus has its origin at the lateral condyle of the femur and inserts onto the posterior tibial surface superior to the soleus muscle. the popliteus muscle facilities unlocking of the knee joint via internal rotation. The lower leg is divided into four compartments that contain the various muscles of the lower leg—anterior, lateral, posterior and deep posterior. anterior compartment the anterior compartment, in the front of the shin, holds the tibialis anterior, the extensor digitorum longus, the extensor hallucis longus, and the peroneus tertius muscles. The tibialis posterior muscle (tpm) is the deepest muscle of the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg. its long muscle belly arises from the posterior aspect of the interosseous membrane and superior two thirds of the posterior and medial surface of the fibula, and the superior aspect of the proximal tibia. the tpm tendon inserts distally onto many attachment points on the plantar. Soleus. posterior aspect of head and superior quarter of posterior surface of fibula; soleal line and middle third of medial border of tibia; and tendinous arch extending between the bony attachments. plantarflexes ankle independent of position of knee; steadies leg on foot. [ 1 ].

Comments are closed.