Derivative Of Exponential Function Fully Explained
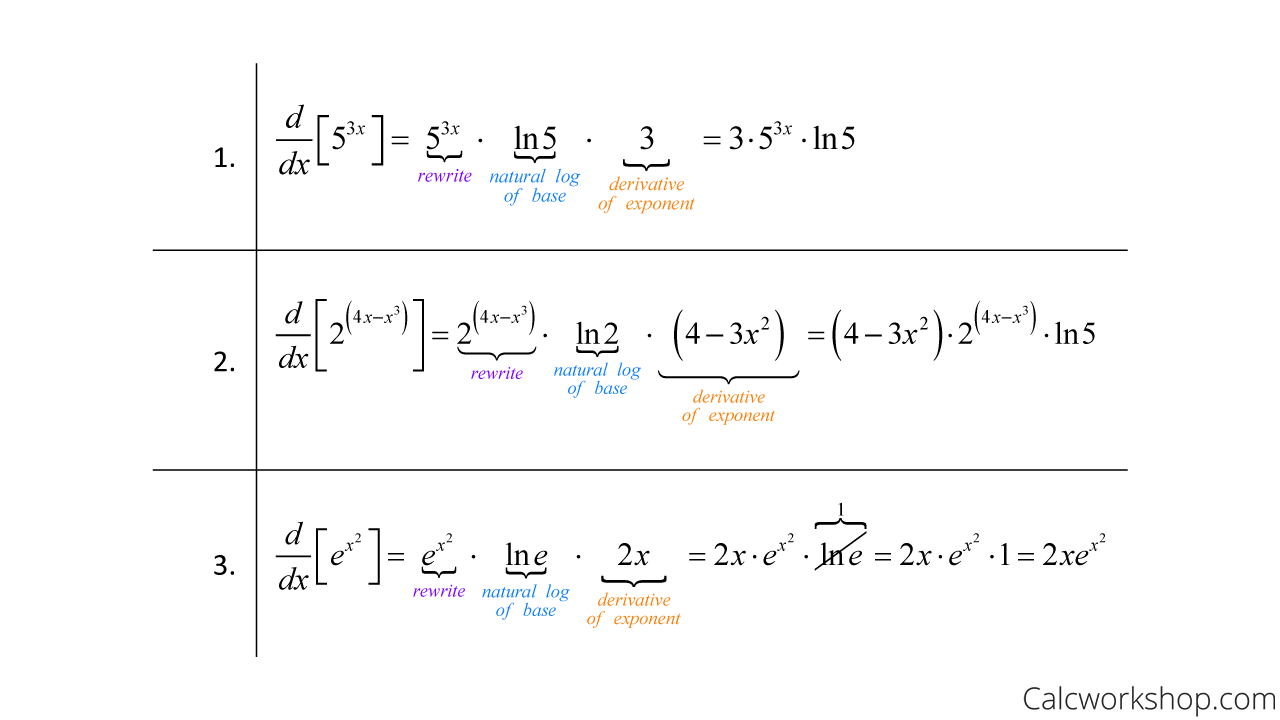
Derivative Of Exponential Function Fully Explained Taking the derivative of an exponential function. see, differentiating exponential functions is a snap — it’s as easy as 1 2 3! is derived from a. this video lesson will look at exponential properties and how to take a derivative of an exponential function, all while walking through several examples in detail. let’s jump right in. Derivatives of exponential functions. in order to differentiate the exponential function. f (x) = a^x, f (x) = ax, we cannot use power rule as we require the exponent to be a fixed number and the base to be a variable. instead, we're going to have to start with the definition of the derivative: \begin {aligned} f' (x) &= \lim {h \rightarrow 0.
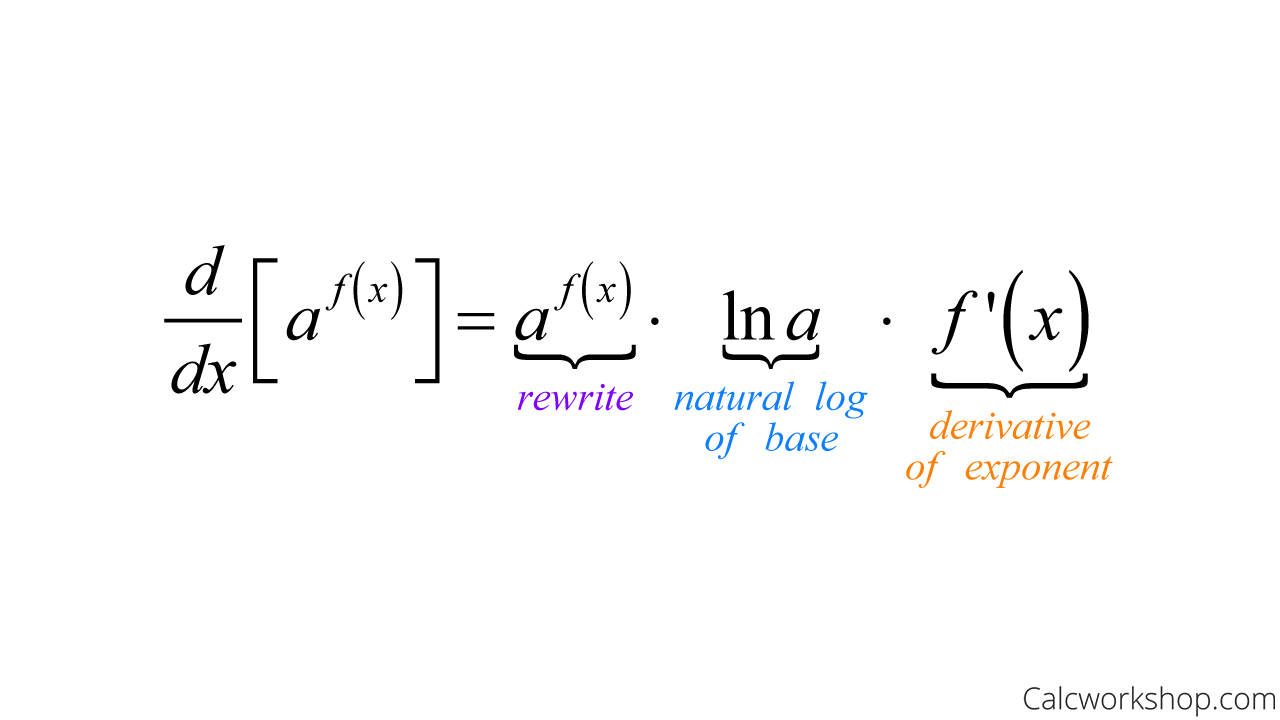
Derivative Of Exponential Function Fully Explained Example 1: find the derivative of exponential function f (x) = 3 x 3x 2. solution: using the formula for derivative of exponential function and other differentiation formulas, the derivative of f (x) = 3 x 3x 2 is given by, f' (x) = 3 x ln 3 6x. answer: the derivative of 3 x 3x 2 is 3 x ln 3 6x. example 2: differentiate the function f. There is still one more “rule” that we need to complete our toolbox and that is the chain rule. however before we get there, we will add a few functions to our list of things we can differentiate 2. the first of these is the exponential function. let \(a \gt 0\) and set \(f(x) = a^x\) — this is what is known as an exponential function. D dx(eg(x)) =eg(x)g(x) d d x ( e g ( x)) = e g ( x) g ′ ( x) if it helps, think of the formula as the chain rule being applied to natural exponential functions. the derivative of e e raised to the power of a function will simply be e e raised to the power of the function multiplied by the derivative of that function. The derivative of the function \(e^{x}\) is \(e^{x}\). the value of base \(e\) is obtained from the limit in equation (10.2.1). this can be written in either of two equivalent forms. the base of the natural exponential function is the real number defined as follows:.

Comments are closed.