Describe The General Metabolic Pathways Of Carbohydrate Metabolism
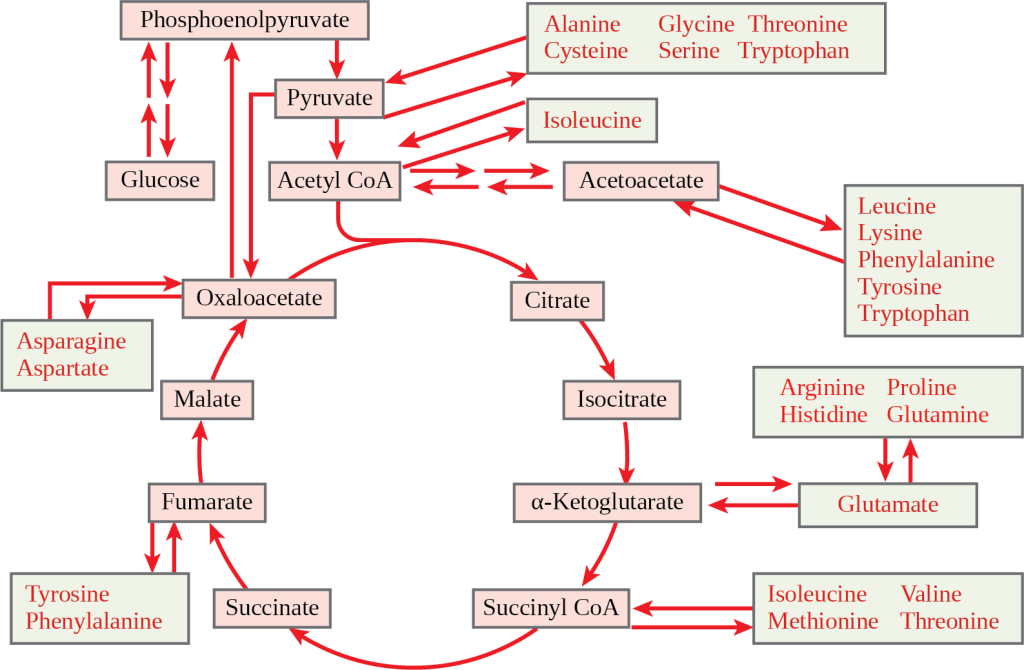
Connections Of Carbohydrate Protein And Lipid Metabolic Pathways Figure 24.2.6 – carbohydrate metabolism: carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. this process takes place primarily in the liver during. Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic formation, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms . carbohydrates are central to many essential metabolic pathways. [ 1] plants synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis, allowing them.

File 2509 Carbohydrate Metabolism Jpg Wikimedia Commons Aging and the body’s metabolic rate. the human body’s metabolic rate decreases nearly 2 percent per decade after age 30. changes in body composition, including reduced lean muscle mass, are mostly responsible for this decrease. the most dramatic loss of muscle mass, and consequential decline in metabolic rate, occurs between 50 and 70 years. When these molecules are broken down during metabolism, the energy in the chemical bonds is released and can be harnessed for cellular processes. figure 6.4.1 6.4. 1: all living things use carbohydrates as a form of energy.: plants, like this oak tree and acorn, use energy from sunlight to make sugar and other organic molecules. Carbohydrate metabolism. carbohydrates are the most abundant macromolecules on our planet, in part because of the plant carbohydrates cellulose and starch, both composed of multiple conjugated glucose molecules. cellulose is an important structural element of plant cell walls. animals lack enzymes that can break down the cellulose into smaller. Carbohydrates are important cellular energy sources. they provide energy quickly through glycolysis and passing of intermediates to pathways, such as the citric acid cycle, amino acid metabolism (indirectly), and the pentose phosphate pathway. it is important, therefore, to understand how these important molecules are made.
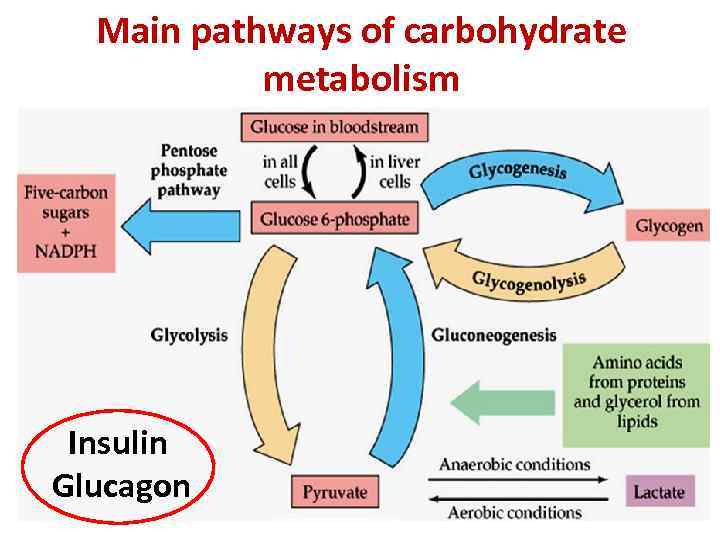
Carbohydrate Metabolism Main Pathways Of Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism. carbohydrates are the most abundant macromolecules on our planet, in part because of the plant carbohydrates cellulose and starch, both composed of multiple conjugated glucose molecules. cellulose is an important structural element of plant cell walls. animals lack enzymes that can break down the cellulose into smaller. Carbohydrates are important cellular energy sources. they provide energy quickly through glycolysis and passing of intermediates to pathways, such as the citric acid cycle, amino acid metabolism (indirectly), and the pentose phosphate pathway. it is important, therefore, to understand how these important molecules are made. Glucose from the diet can be metabolized via glycolysis or glycogenesis. resulting metabolic products can return to glucose via gluconeogenesis or glycogenolysis, respectively, or proceed further along carbohydrate metabolism to the citric acid cycle. alternatively, glucose products can be shunted off to fat or amino acid metabolism as indicated. Glycogen metabolism. glycolysis. this osmosis high yield note provides an overview of carbohydrate metabolism essentials. all osmosis notes are clearly laid out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. find more information about carbohydrate metabolism: company.
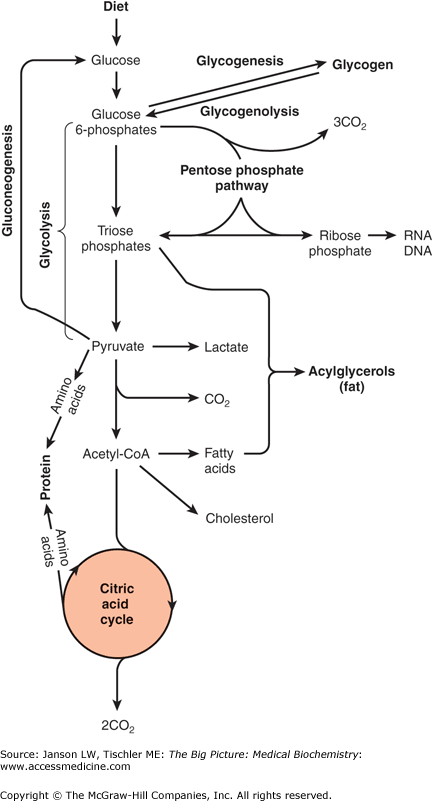
Chapter 6 Carbohydrate Metabolism Basicmedical Key Glucose from the diet can be metabolized via glycolysis or glycogenesis. resulting metabolic products can return to glucose via gluconeogenesis or glycogenolysis, respectively, or proceed further along carbohydrate metabolism to the citric acid cycle. alternatively, glucose products can be shunted off to fat or amino acid metabolism as indicated. Glycogen metabolism. glycolysis. this osmosis high yield note provides an overview of carbohydrate metabolism essentials. all osmosis notes are clearly laid out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. find more information about carbohydrate metabolism: company.
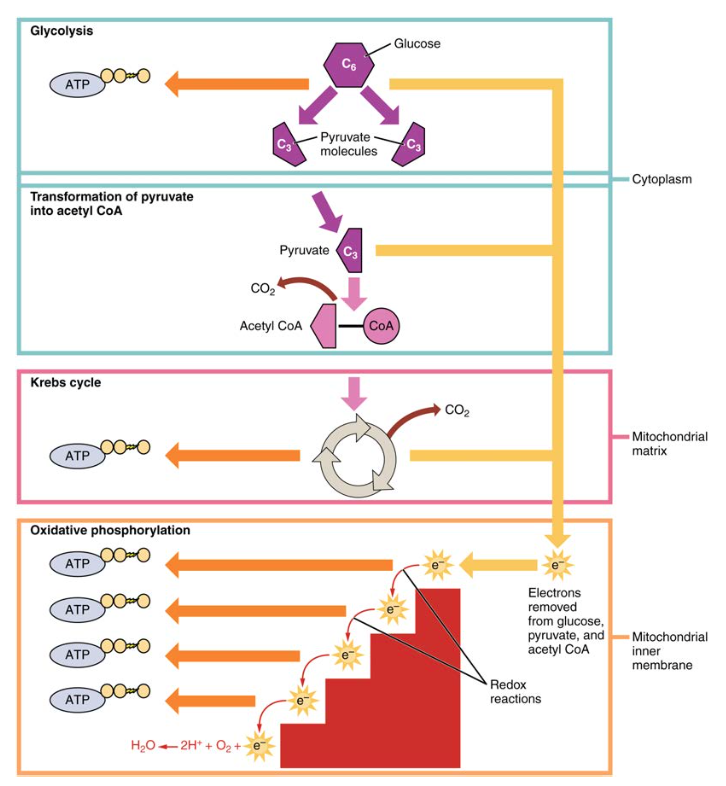
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Comments are closed.