Development Of Chronic Kidney Disease And Chronic Inflammation A

Development Of Chronic Kidney Disease And Chronic Inflammation A Resident kidney cells in chronic inflammation . ckd progression occurs mainly by kidney fibrosis, a process in which activated myofibroblasts are the main collagen producing cells.36, 37, 38 collagen, predominantly fibrillar collagens i and iii, is a major contributor to fibrosis induced cellular loss in ckd. 39 among a number of approaches that reduce experimental fibrosis, such as targeting. Indeed, chronic inflammatory diseases have been recognized as the most significant cause of death in the world today, with more than 50% of all deaths being attributable to inflammation related.
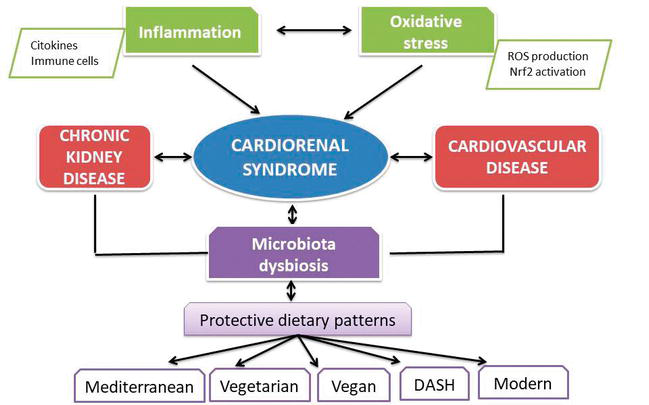
Inflammation And Chronic Kidney Disease Current Approaches And Recent Chronic kidney disease as a systemic inflammatory syndrome. we describe the principal pathologic conditions connected to ckd and the related inflammatory mechanisms. a1 ag alpha1 acid glycoprotein; adc: central adiposity; aki: acute kidney injury; aki a p rec aki apparent partial recovery; ckd mbd: chronic kidney disease mineral bone disorder; crp: c reactive protein; cyt: cytokines; damps. Indeed, chronic inflammatory diseases have been recognized as the most significant cause of death in the world today, with more than 50% of all deaths being attributable to inflammation related diseases such as ischemic heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, non alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) and. Key messages: chronic inflammation should be regarded as a common comorbid condition in ckd and especially in dialysis patients. a number of interventions have been proven to be safe and effective in well designed clinical studies. this includes such inexpensive approaches as modification of physical activity and dietary supplementation. Despite recent advances in the management of chronic kidney disease (ckd), morbidity and mortality rates in these patients remain high. although pressure mediated injury is a well recognized mechanism of disease progression in ckd, emerging data indicate that an intermediate phenotype involving chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, hypoxia, senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction plays a.
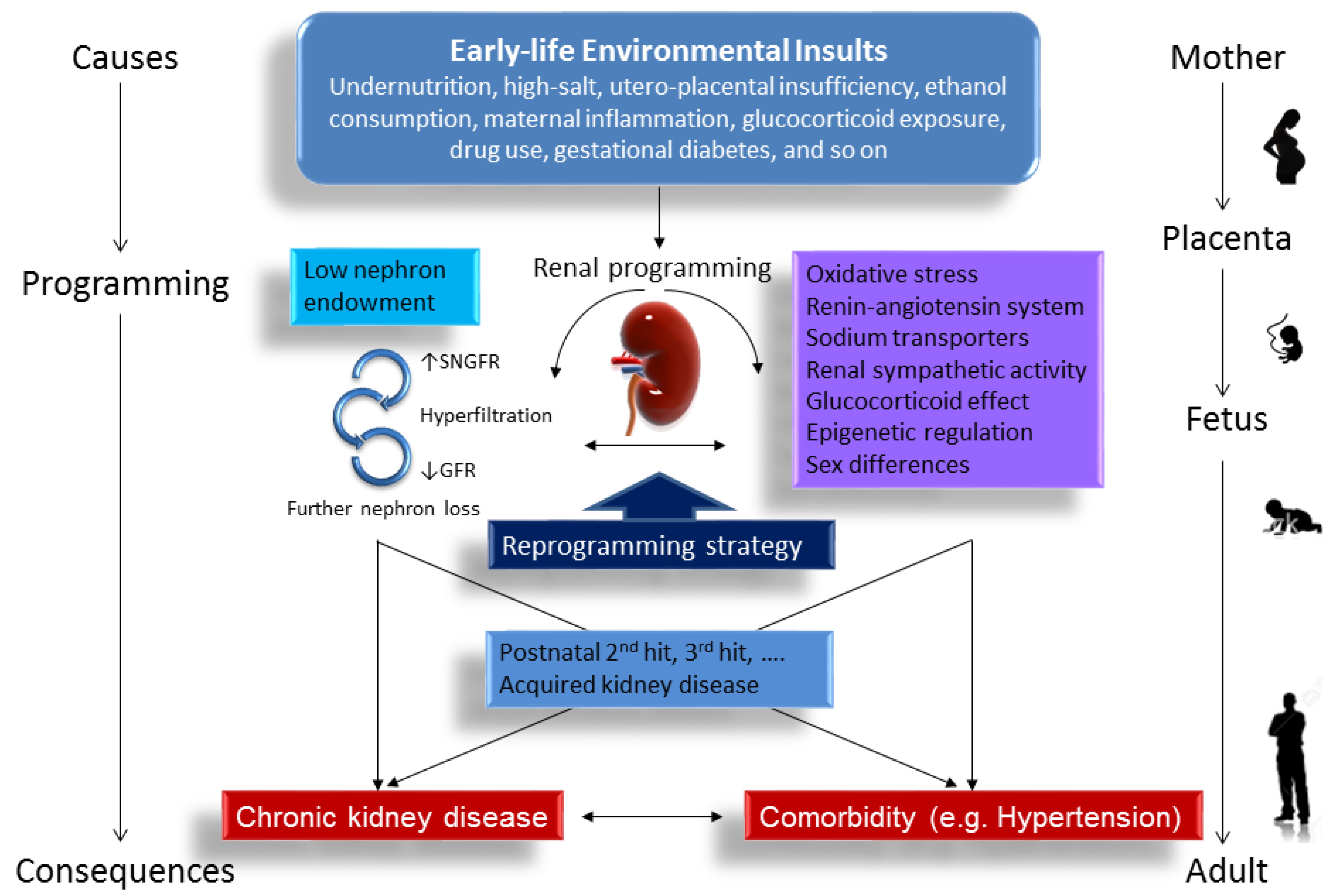
Ijms Free Full Text Developmental Origins Of Chronic Kidney Disease Key messages: chronic inflammation should be regarded as a common comorbid condition in ckd and especially in dialysis patients. a number of interventions have been proven to be safe and effective in well designed clinical studies. this includes such inexpensive approaches as modification of physical activity and dietary supplementation. Despite recent advances in the management of chronic kidney disease (ckd), morbidity and mortality rates in these patients remain high. although pressure mediated injury is a well recognized mechanism of disease progression in ckd, emerging data indicate that an intermediate phenotype involving chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, hypoxia, senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction plays a. Regulation of proinflammatory and anti inflammatory factors through nf κb and nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like 2 (nrf2) mediated gene transcription, respectively, plays a critical role in the glomerular and tubular cell response to kidney injury. chronic inflammation contributes to the decline in glomerular filtration rate (gfr) in ckd. Abstract. chronic kidney disease (ckd) is a devastating condition that is reaching epidemic levels owing to the increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus, hypertension and obesity, as well as.

Comments are closed.