Developmental Dysplasia Hip

Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip The Bmj Developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh) is a disorder of abnormal development resulting in dysplasia, subluxation, and possible dislocation of the hip secondary to capsular laxity and mechanical factors. treatment varies from pavlik bracing to surgical reduction and osteotomies depending on the age of the patient and degree of dysplasia. The hip is a ball and socket joint. in a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the thighbone (femur) fits firmly into the socket, which is part of the large pelvis bone. in babies and children with developmental dysplasia (dislocation) of the hip (ddh), the hip joint has not formed normally. the ball is loose in the socket and may be easy to.
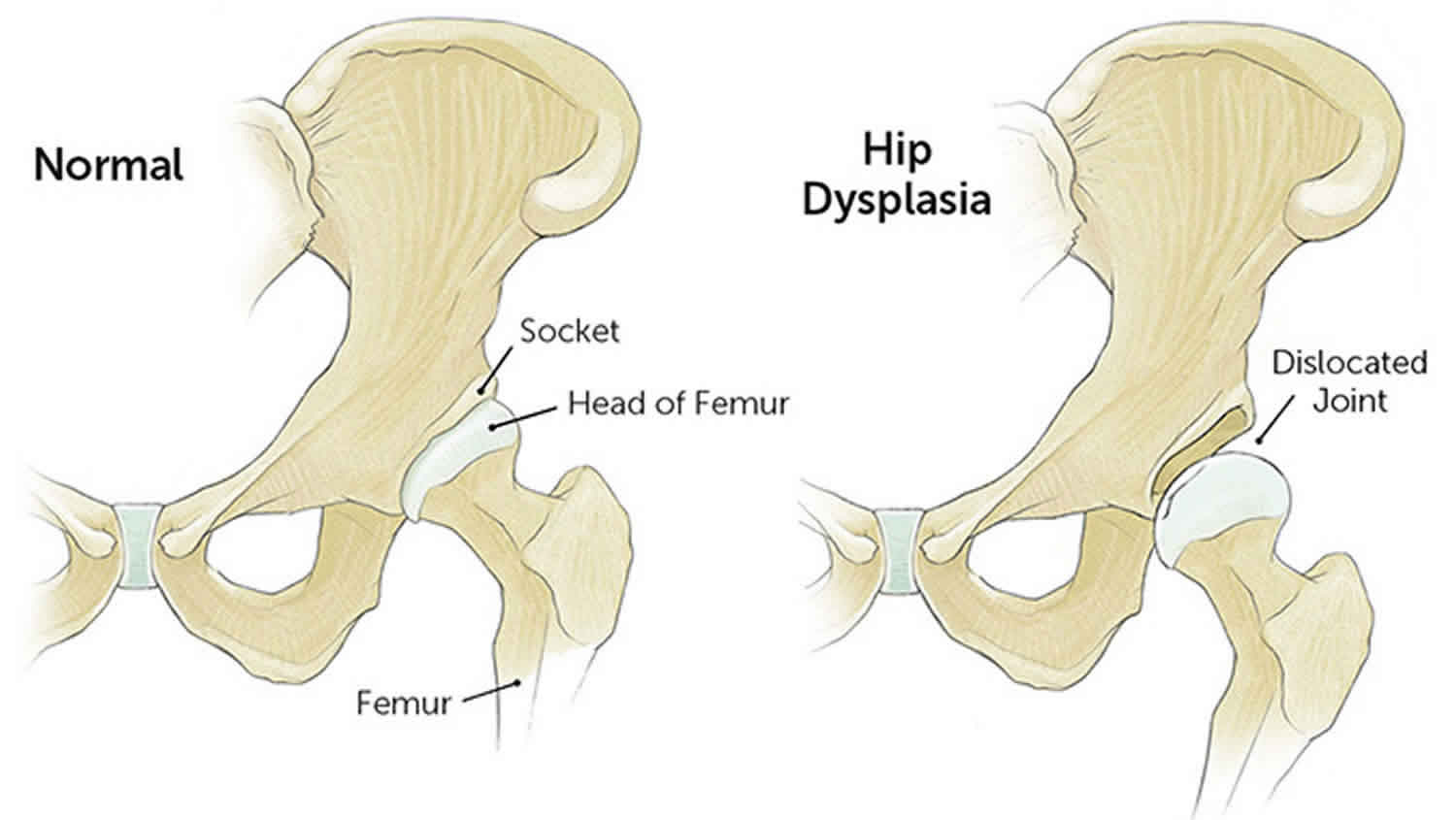
Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Request an appointment. 410 955 5000 maryland. 855 695 4872 outside of maryland. 1 410 502 7683 international. developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh) is a condition in which an infant’s hip joint is not forming properly. the “ball” part of the hip joint is not securely fitting into the “socket.”. Developmental dysplasia of the hip occurs due to an abnormal hip development, presenting in infancy or early childhood with a spectrum ranging from dysplasia to dislocation of the hip joint. developmental dysplasia of the hip encompasses several hip abnormalities, including instability, acetabular dysplasia, subluxation, and dislocation. these issues often occur in children with no other. Developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh or hip dysplasia) is a relatively common condition in the developing hip joint. it occurs once in every 1,000 live births. the hip joint is made up of a ball (femur) and socket (acetabulum) joint. in ddh, this joint may be unstable with the ball slipping in and out of the socket. Unlike congenital dislocation of the hip, developmental dysplasia of the hip is not confined to congenital malformations and includes perturbations in development 12. there is a clear female predominance, and it usually occurs from ligamentous laxity and abnormal position in utero. therefore, it is more common with oligohydramniotic pregnancies.

Comments are closed.