Diabetes And The Brain

Pin On Dr Berg Diabetes can damage blood vessels in the brain and cause a stroke or memory loss. this can lead to problems with memory and learning, mood shifts, weight gain, and hormonal changes. over time, it can also lead to other serious problems like alzheimer's disease. both high and low blood sugar levels can cause these harms. Diabetes mellitus is associated with decrements in cognitive function and changes in brain structure. people with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes have been shown to have mild to moderate reductions in cognitive function as measured by neuropsychological testing compared to non diabetic controls. type 2 diabetes (t2dm) has also been associated.
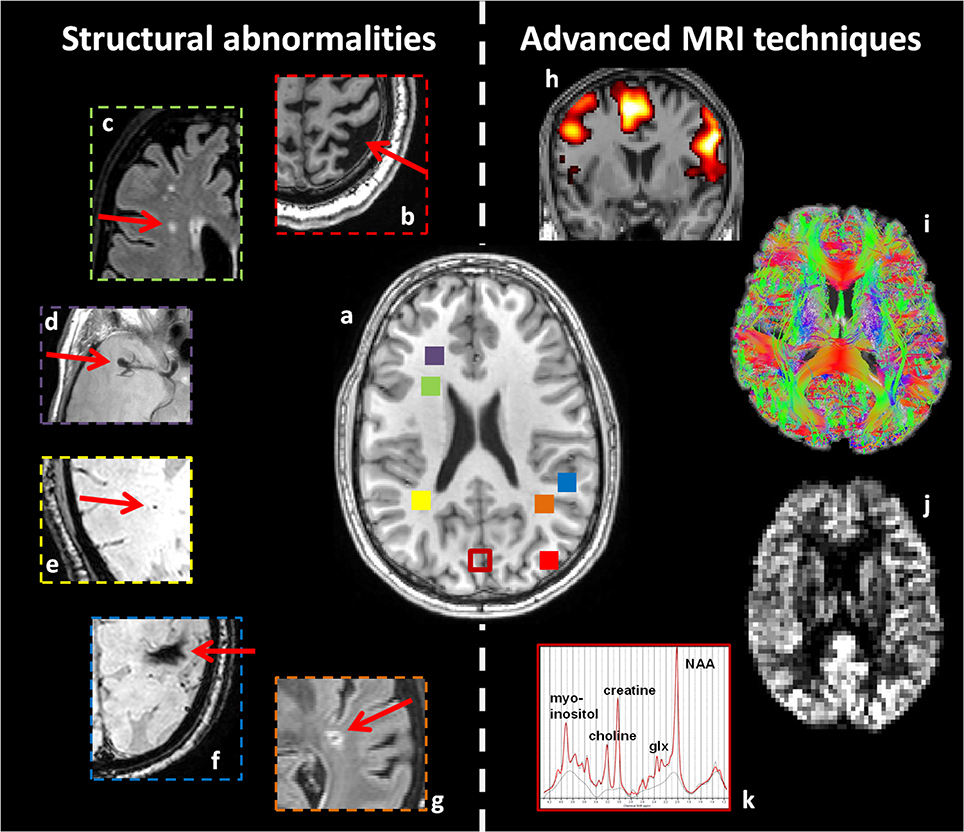
Frontiers Cerebral Pathology And Cognition In Diabetes The Merits Of Several epidemiological studies have clearly identified diabetes mellitus (dm) as a major risk factor for cognitive dysfunction, and it is going to be a major public health issue in the coming years because of the alarming rise in diabetes prevalence across the world. brain and neural tissues predominantly depend on glucose as energy substrate. Learn how type 2 diabetes can slow down mental functioning and increase the risk of alzheimer’s disease. find out the possible factors and ways to prevent or limit the brain damage caused by diabetes. Long term diabetes—either type 1 or type 2—has many consequences for the brain and for neurons in the brain, says novak. high blood glucose levels can affect the brain’s functional connectivity, which links brain regions that share functional properties, and brain matter. it can cause the brain to atrophy or shrink. A: yes. studies have demonstrated that people who have diabetes, compared with people without diabetes, are more likely to develop cognitive problems. older adults with diabetes have higher incidences of dementia, alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia than those with normal glucose tolerance.
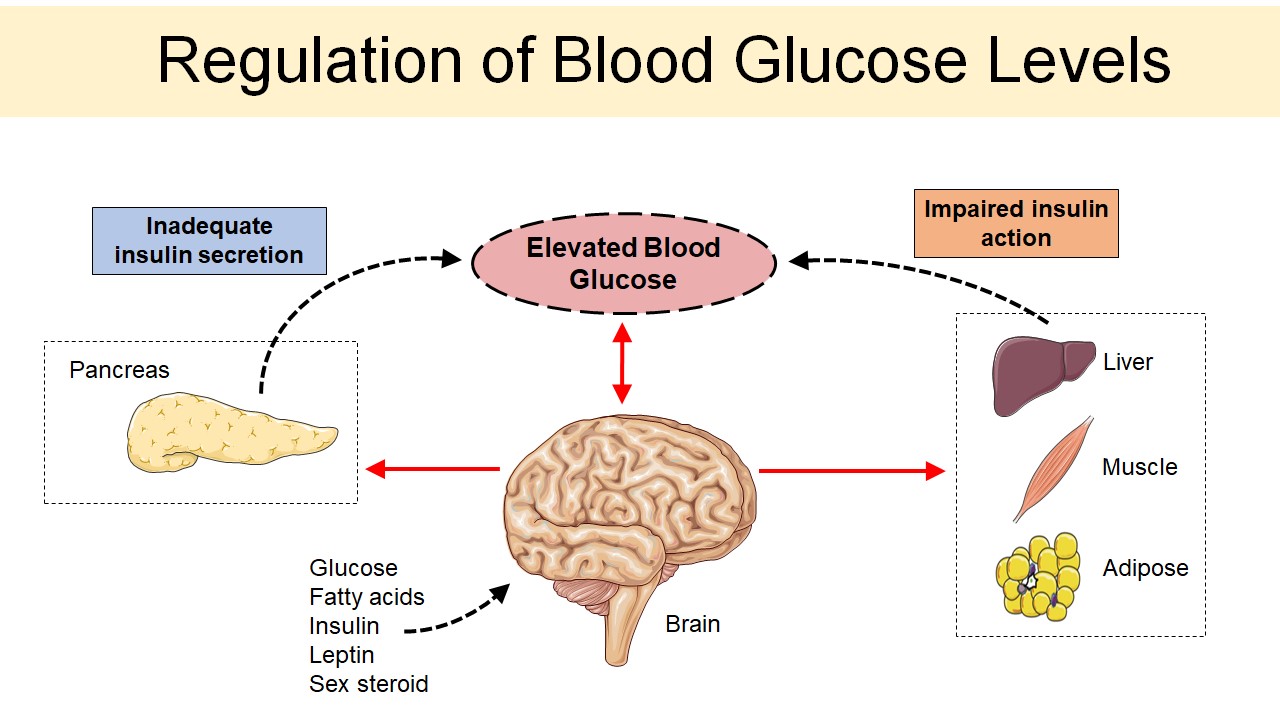
Diabetes And Metabolism Uw Diabetes Institute Long term diabetes—either type 1 or type 2—has many consequences for the brain and for neurons in the brain, says novak. high blood glucose levels can affect the brain’s functional connectivity, which links brain regions that share functional properties, and brain matter. it can cause the brain to atrophy or shrink. A: yes. studies have demonstrated that people who have diabetes, compared with people without diabetes, are more likely to develop cognitive problems. older adults with diabetes have higher incidences of dementia, alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia than those with normal glucose tolerance. Patients with diabetes have been found to have several changes in brain structure that appear to develop over time ( top) and often experience conditions that present risk for subsequent cognitive dysfunction ( bottom ). future study is necessary to define the natural history, structural basis, and risk factors for cognitive dysfunction in. Insulin signalling is essential for brain health, and people with diabetes are at increased risk of cognitive impairment and dementia. the prevention and treatment of diabetes could therefore reduce the incidence of cognitive impairment. a joint series between the lancet neurology and the lancet diabetes & endocrinology covers current advances.

Diabetes Side Effect Brain Degeneration Time Patients with diabetes have been found to have several changes in brain structure that appear to develop over time ( top) and often experience conditions that present risk for subsequent cognitive dysfunction ( bottom ). future study is necessary to define the natural history, structural basis, and risk factors for cognitive dysfunction in. Insulin signalling is essential for brain health, and people with diabetes are at increased risk of cognitive impairment and dementia. the prevention and treatment of diabetes could therefore reduce the incidence of cognitive impairment. a joint series between the lancet neurology and the lancet diabetes & endocrinology covers current advances.

Comments are closed.