Diagram Of Wave Erosion

Coastal Erosion Illustration Stock Image C028 1135 Science Photo Wave energy does the work of erosion at the shore. waves approach the shore at some angle so the inshore part of the wave reaches shallow water sooner than the part that is further out. the shallow part of the wave ‘feels’ the bottom first. this slows down the inshore part of the wave and makes the wave “bend.”. this bending is called. Wave energy does the work of erosion at the shore. waves approach the shore at some angle so the inshore part of the wave reaches shallow water sooner than the part that is further out. the shallow part of the wave ‘feels’ the bottom first. this slows down the inshore part of the wave and makes the wave ‘bend.’. this bending is called.
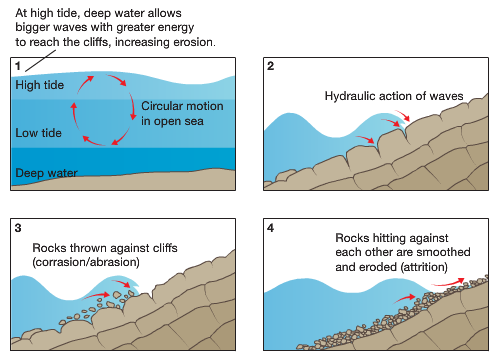
Erosional Landforms Year 8 Geography Wave energy does the work of erosion at the shore. waves approach the shore at some angle so the inshore part of the wave reaches shallow water sooner than the part that is further out. the shallow part of the wave ‘feels’ the bottom first. this slows down the inshore part of the wave and makes the wave “bend.”. this bending is called. Erosion by waves can create unique landforms ( figure below). wave cut cliffs form when waves erode a rocky shoreline. they create a vertical wall of exposed rock layers. wave cut platforms are level areas formed by wave erosion. since these platforms are above sea level, it means that either sea level was higher relative or the rock was lower. Many years of this type of erosion can form a wave cut platform (figure 10.16). figure 10.16 : this large wave cut platform was formed by the cutting action of waves on the cliffs to the left. figure 10.18 : a sea stack forms if the upper layers of rock collapse, leaving an isolated pinnacle. 21.2: coastal landforms and processes. a coast or the coastal zone is a dynamic region where land is sculpted and shaped by wave action and currents. barring the effects of tectonic uplift and sea level change, erosion is the dominate geomorphic process acting on coasts.

Wave Erosion Diagram Images гѓ гѓјгѓѓ Many years of this type of erosion can form a wave cut platform (figure 10.16). figure 10.16 : this large wave cut platform was formed by the cutting action of waves on the cliffs to the left. figure 10.18 : a sea stack forms if the upper layers of rock collapse, leaving an isolated pinnacle. 21.2: coastal landforms and processes. a coast or the coastal zone is a dynamic region where land is sculpted and shaped by wave action and currents. barring the effects of tectonic uplift and sea level change, erosion is the dominate geomorphic process acting on coasts. Wave erosion is greatest in the surf zone, where the wave base is impinging strongly on the sea floor and where the waves are breaking. the result is that the substrate in the surf zone is typically eroded to a flat surface known as a wave cut platform (or wave cut terrace) (figure 17.12). a wave cut platform extends across the intertidal zone. Erosion of beaches by waves occurs on several different spatial and temporal scales. every rise and fall in the tide is accompanied by the migration up or down the beach of a scour zone, ( strahler, 1966 ). this zone, which is found at the tide level, is also the zone where the backwash meets the incoming surge and is an area of turbulence.

The Geophile Pages Wave erosion is greatest in the surf zone, where the wave base is impinging strongly on the sea floor and where the waves are breaking. the result is that the substrate in the surf zone is typically eroded to a flat surface known as a wave cut platform (or wave cut terrace) (figure 17.12). a wave cut platform extends across the intertidal zone. Erosion of beaches by waves occurs on several different spatial and temporal scales. every rise and fall in the tide is accompanied by the migration up or down the beach of a scour zone, ( strahler, 1966 ). this zone, which is found at the tide level, is also the zone where the backwash meets the incoming surge and is an area of turbulence.

Comments are closed.