Difference Between Mass And Weight Inspirit
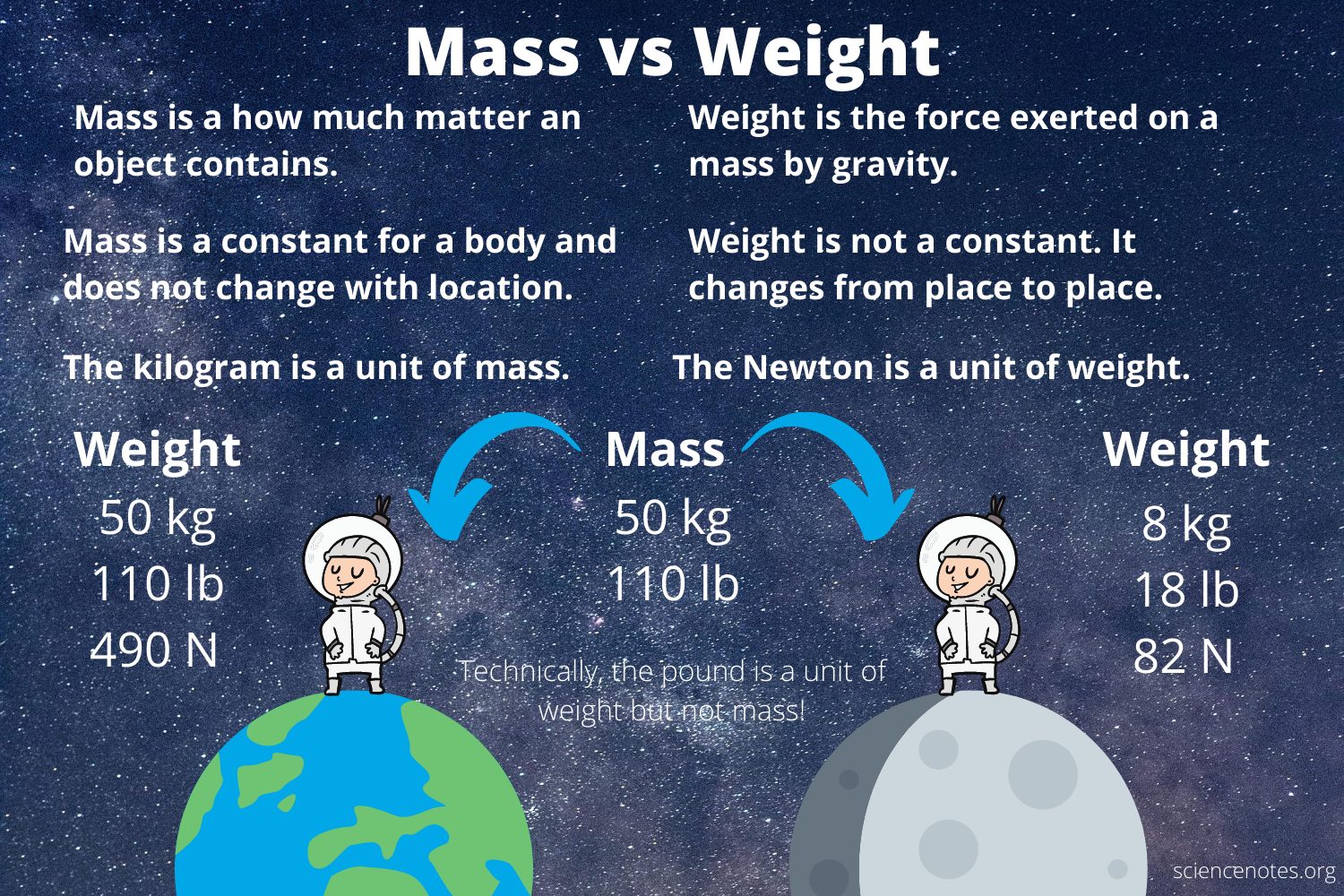
Difference Between Mass And Weight Inspirit Learning Inc We can write the following points when we state the difference between mass and weight: the si unit of mass is kilogram, whereas the si unit of weight is newton. mass of a body remains constant, whereas weight changes with the place. this is how mass and weight are related. mass only has magnitude, and it is a scalar quantity, whereas weight. The difference between mass and weight is the mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the effect of gravity on that mass. in other words, gravity causes a mass to have weight. the relationship between mass and weight is a simple equation: w = m * g. here, w is weight, mass is mass, and g is gravity.

Difference Between Mass And Weight Inspirit Learning Inc Relation between weight and mass newton’s law theory states that a free falling object has an acceleration “g” as the magnitude may be used to deduce the relationship between weight and mass. if a 1 kilogram item descends with an acceleration due to gravity (a) of 9.8 m.s 2, the magnitude of the force can be calculated using f = ma. The difference between mass and weight is that mass is the amount of matter in a material, while weight is a measure of how the force of gravity acts upon that mass. you can think of weight as a function of an object's mass and the force, or acceleration, it experiences due to gravity. mass is the measure of the amount of matter in a body. The weight of an object on the earth is defined as the force acting on the object by the earth’s gravity. weight is measured by a calibrated spring scale. the formula relating mass and weight is w = m g. practice questions. a song about the difference between mass and weight sung by mr. edmunds to the tune of sweet caroline. But your weight differs from place to place because of differences in how hard gravity at each site pulls on you. on earth’s surface, 1 kilogram of mass is equivalent to 2.2 pounds of weight. so your 40 kilogram mass on earth would weigh 40 x 2.2 — or 88 pounds.
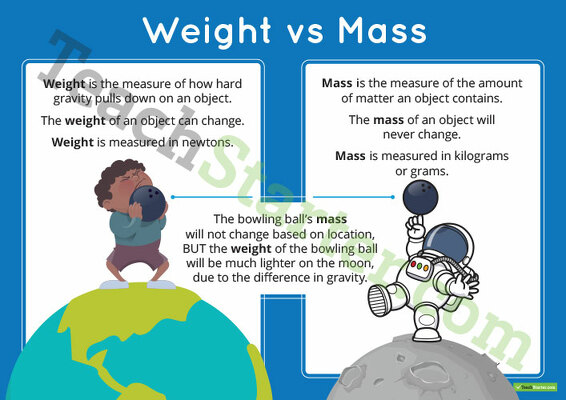
Mass Vs Weight Poster Teach Starter The weight of an object on the earth is defined as the force acting on the object by the earth’s gravity. weight is measured by a calibrated spring scale. the formula relating mass and weight is w = m g. practice questions. a song about the difference between mass and weight sung by mr. edmunds to the tune of sweet caroline. But your weight differs from place to place because of differences in how hard gravity at each site pulls on you. on earth’s surface, 1 kilogram of mass is equivalent to 2.2 pounds of weight. so your 40 kilogram mass on earth would weigh 40 x 2.2 — or 88 pounds. Most humans on the surface of the earth can get away with saying either "weight" or "mass" because they are proportional to each other. if you know the mass of something (m), then the weight (w. Weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity. 4. quantity type. mass is a base quantity. mass only has magnitude and so, it is a scalar quantity. weight is a derived quantity. weight has both magnitude and direction (towards the centre of gravity) and so, it is a vector quantity. 5. unit of measurement.
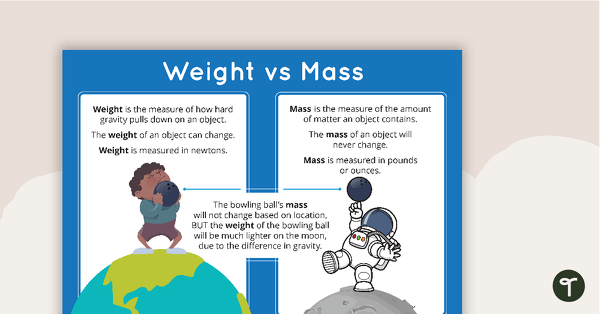
Mass Vs Weight Poster Teach Starter Most humans on the surface of the earth can get away with saying either "weight" or "mass" because they are proportional to each other. if you know the mass of something (m), then the weight (w. Weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity. 4. quantity type. mass is a base quantity. mass only has magnitude and so, it is a scalar quantity. weight is a derived quantity. weight has both magnitude and direction (towards the centre of gravity) and so, it is a vector quantity. 5. unit of measurement.

Comments are closed.