Difference Between Microtubules And Microfilaments Structure
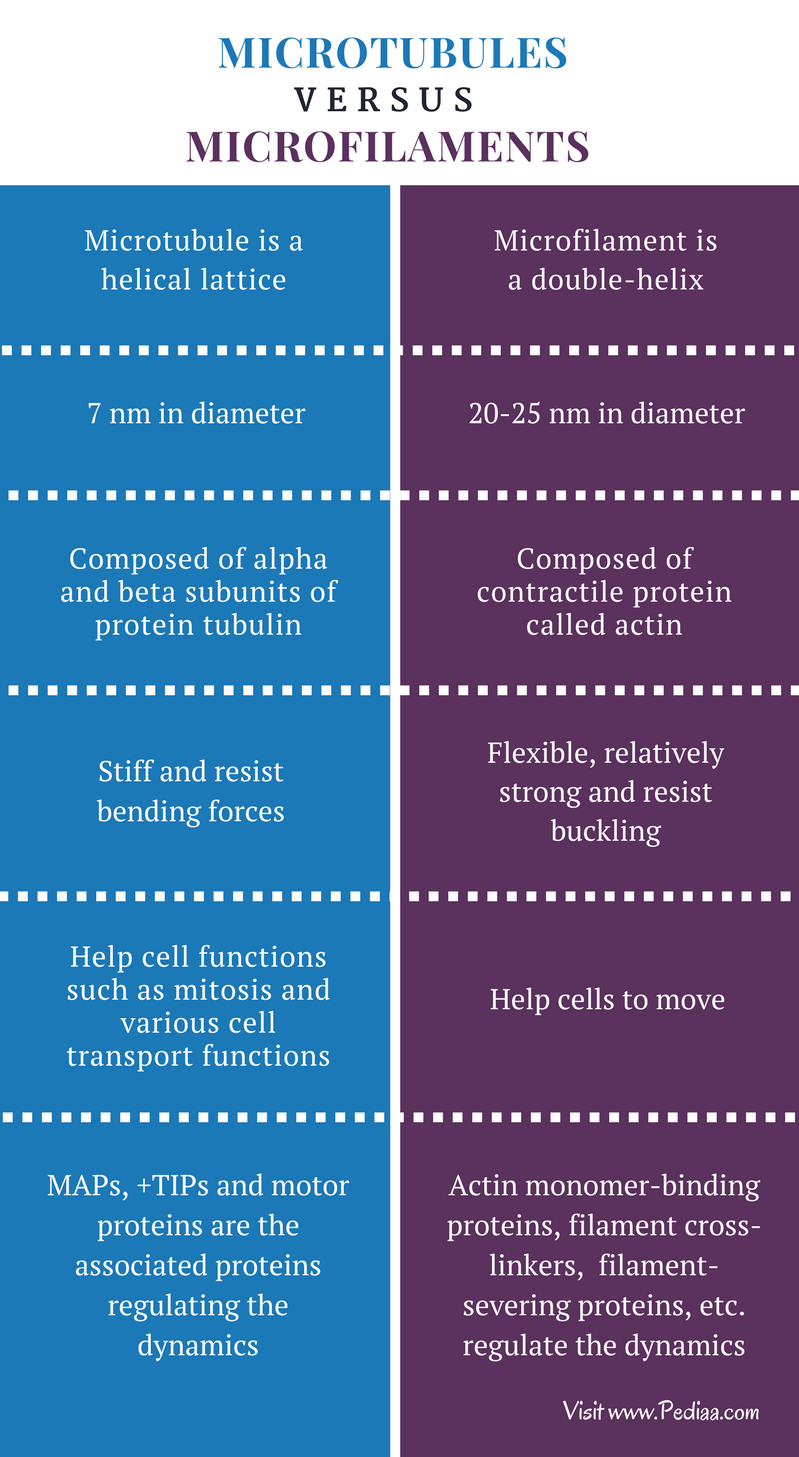
Difference Between Microtubules And Microfilaments Structure Resist buckling due to compressive forces and filament fracture by tensile forces. stiff and resist bending forces. function. micro filaments are smaller and thinner and mostly help cells move. microtubules are shaped similarly but are larger, and help with cell functions such as mitosis and various cell transport functions. The main difference between microtubules and microfilaments is that microtubules are long, hollow cylinders, made up of tubulin protein units whereas microfilaments are double stranded helical polymers, made up of actin proteins . 1. what are microtubules. – structure, function, characteristics.
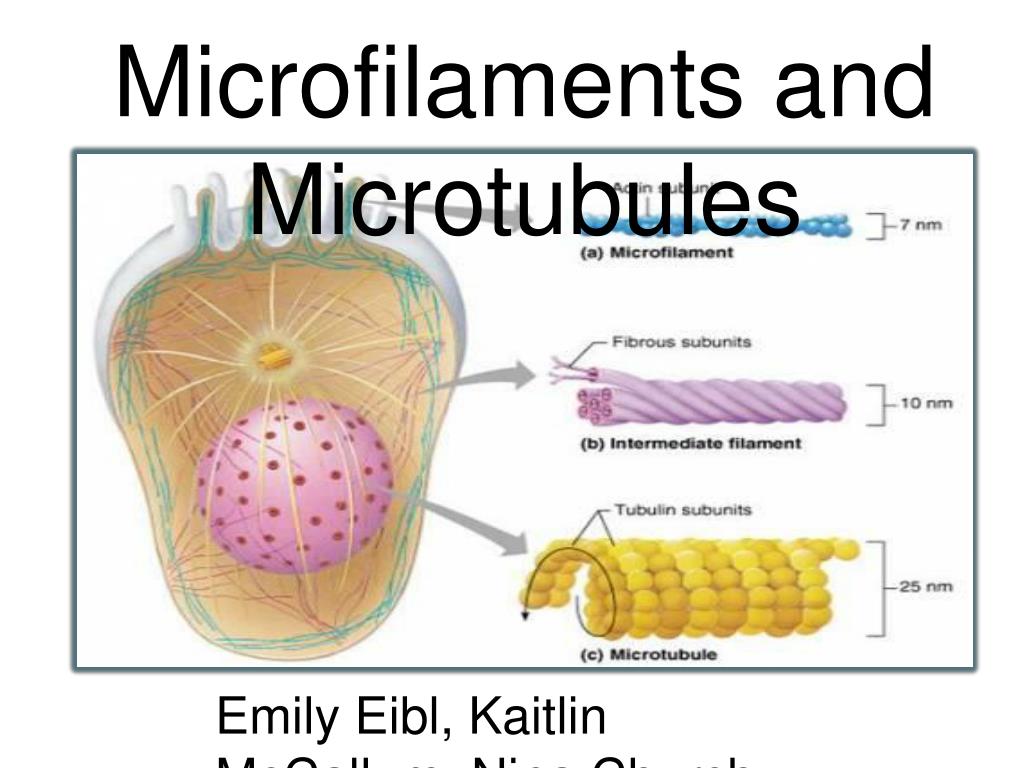
Microfilaments And Microtubules Microtubules are the largest type of filament, with a diameter of about 25 nanometers (nm), and they are composed of a protein called tubulin . actin filaments are the smallest type, with a. Microtubules and microfilaments provide structural support to the cell, contributing to its overall integrity and shape. differences between microtubules and microfilaments 1. structure: microtubules are hollow tubes made of tubulin, while microfilaments are solid fibers composed of actin. Like microfilaments, microtubules can dissolve and reform quickly. figure 4.17.1 4.17. 1: micrtubule structure: microtubules are hollow, with walls consisting of 13 polymerized dimers of α tubulin and β tubulin (right image). the left image shows the molecular structure of the tube. microtubules are also the structural elements of flagella. Key differences. microtubules are hollow, cylindrical structures that are integral components of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells. microfilaments, conversely, are solid, thin structures also part of the cytoskeleton. 8. the primary protein that makes up microtubules is tubulin, forming a tube like structure.

Differences Between Microfilaments Microtubules And Intermediate Like microfilaments, microtubules can dissolve and reform quickly. figure 4.17.1 4.17. 1: micrtubule structure: microtubules are hollow, with walls consisting of 13 polymerized dimers of α tubulin and β tubulin (right image). the left image shows the molecular structure of the tube. microtubules are also the structural elements of flagella. Key differences. microtubules are hollow, cylindrical structures that are integral components of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells. microfilaments, conversely, are solid, thin structures also part of the cytoskeleton. 8. the primary protein that makes up microtubules is tubulin, forming a tube like structure. Despite their differences in length and number, flagella and cilia share a common structural arrangement of microtubules called a “9 2 array.” this is an appropriate name because a single flagellum or cilium is made of a ring of nine microtubule doublets, surrounding a single microtubule doublet in the center ( figure 4.26 ). What is the difference between microtubules and microfilaments? microfilaments extend throughout the cytoplasm and help give shape and structure to the cell. microfilaments are also incredibly.

Difference Between Microtubules And Microfilaments Structure Despite their differences in length and number, flagella and cilia share a common structural arrangement of microtubules called a “9 2 array.” this is an appropriate name because a single flagellum or cilium is made of a ring of nine microtubule doublets, surrounding a single microtubule doublet in the center ( figure 4.26 ). What is the difference between microtubules and microfilaments? microfilaments extend throughout the cytoplasm and help give shape and structure to the cell. microfilaments are also incredibly.

Comments are closed.