Diversity Of Microbe Bacteria Shapes Bacteria Types Microorganisms
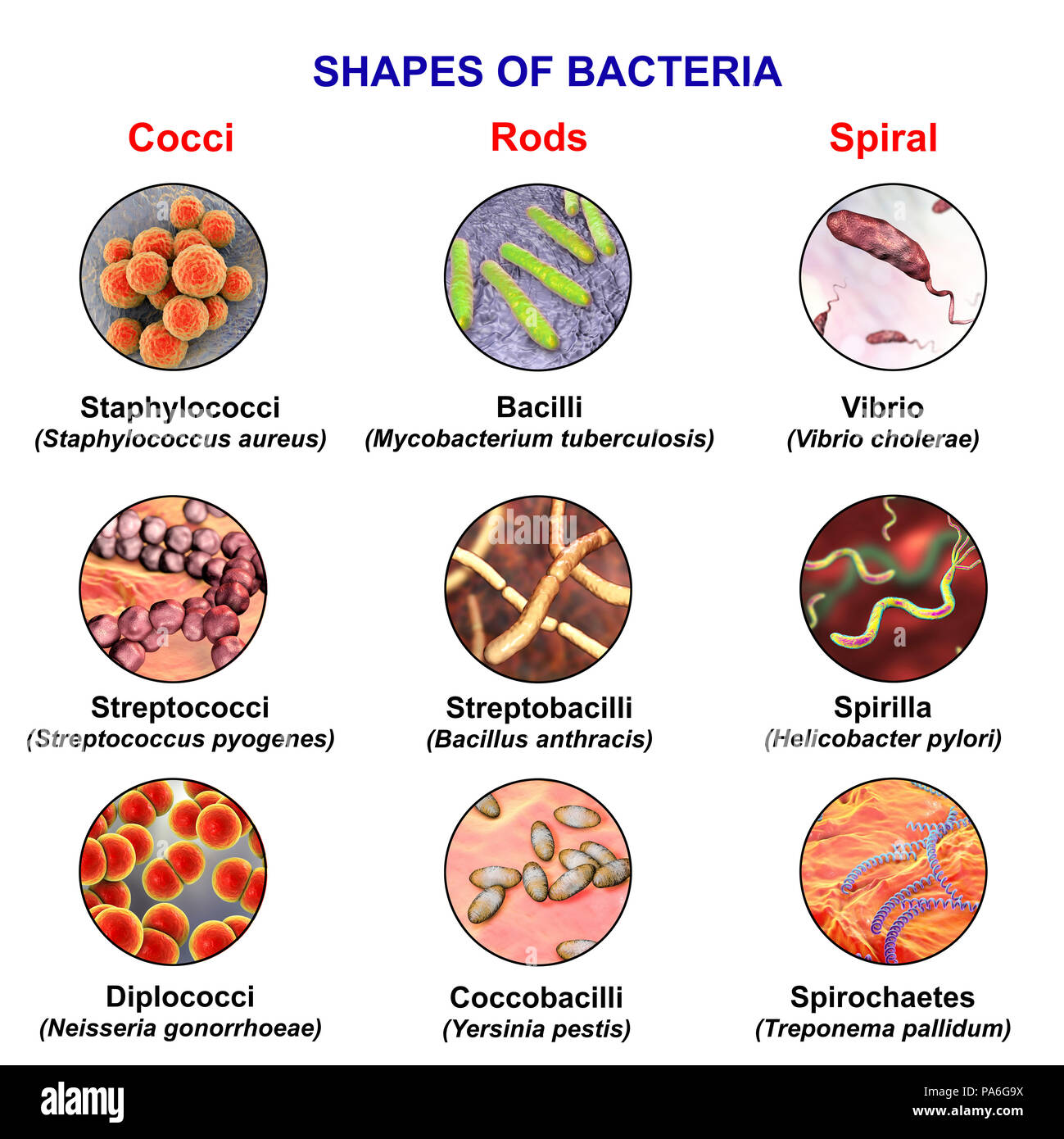
What Is Bacteria Types Structure Shapes Morphology Bacteria prokaryotes, microbes, cells: although bacterial cells are much smaller and simpler in structure than eukaryotic cells, the bacteria are an exceedingly diverse group of organisms that differ in size, shape, habitat, and metabolism. much of the knowledge about bacteria has come from studies of disease causing bacteria, which are more readily isolated in pure culture and more easily. Bacteria are, in general one tenth the size of the eukaryotic cell. on average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 to 5 µm. however, they can be as tiny as 0.3 µm and as large as 0.7mm. the limit of resolution with the unaided eye is about 200 microns, and as many bacteria are smaller than this size, they are not visible with naked eyes.

Bacteria Microbiology Series Techni K Smart Knowledge Review of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells from unit 1. there are three common shapes of bacteria: image 1: these are the different shapes of bacteria and their sizes compared with the width of a human hair. the unit “μm” is a measurement of length, the “micrometer,” or commonly known as the micron. The bacteria, including organisms of the mycoplasma, rickettsia and chlamydia groups, together with the related blue–green algae, comprise the smaller micro organisms, with the form of cellular organization described as prokaryotic. the archaea are a distinct phylogenetic group of prokaryotes that bear only a remote ancestral relationship to. Some microbes, such as viruses, are even acellular (not composed of cells). microorganisms are found in each of the three domains of life: archaea, bacteria, and eukarya. microbes within the domains bacteria and archaea are all prokaryotes (their cells lack a nucleus), whereas microbes in the domain eukarya are eukaryotes (their cells have a. The three main shapes of bacteria are coccus, spiral, and bacillus. cocci are bacteria that are spherical or ovoid in shape. some cocci remain attached after binary fission, even though separate cells have been formed. for example, diplococci are cocci in pairs, streptococci are chains, and staphylococci are clusters of multiple cocci.
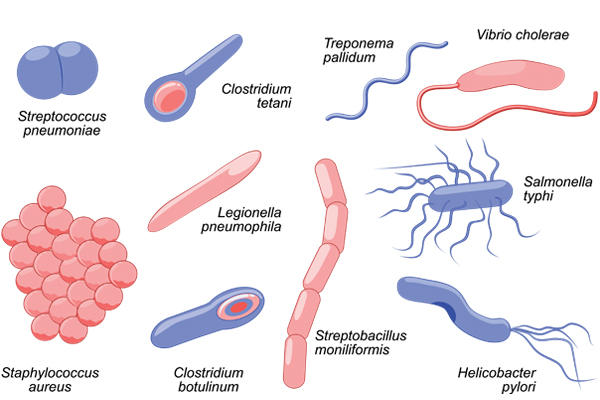
Bacteria What Is Microbiology Microbiology Society Some microbes, such as viruses, are even acellular (not composed of cells). microorganisms are found in each of the three domains of life: archaea, bacteria, and eukarya. microbes within the domains bacteria and archaea are all prokaryotes (their cells lack a nucleus), whereas microbes in the domain eukarya are eukaryotes (their cells have a. The three main shapes of bacteria are coccus, spiral, and bacillus. cocci are bacteria that are spherical or ovoid in shape. some cocci remain attached after binary fission, even though separate cells have been formed. for example, diplococci are cocci in pairs, streptococci are chains, and staphylococci are clusters of multiple cocci. Collectively, this group of microorganisms exhibits tremendous diversity in the chemical changes that it brings to its environments. algae. the cells of eukaryotic microbes are similar to plant and animal cells in that their dna is enclosed within a nuclear membrane, forming the nucleus. eukaryotic microorganisms include algae, protozoa, and fungi. Microorganisms are divided into seven types: bacteria, archaea, protozoa, algae, fungi, viruses, and multicellular animal parasites ( helminths ). each type has a characteristic cellular composition, morphology, mean of locomotion, and reproduction. microorganisms are beneficial in producing oxygen, decomposing organic material, providing.

Comments are closed.