Diverticulitis Radiology Key
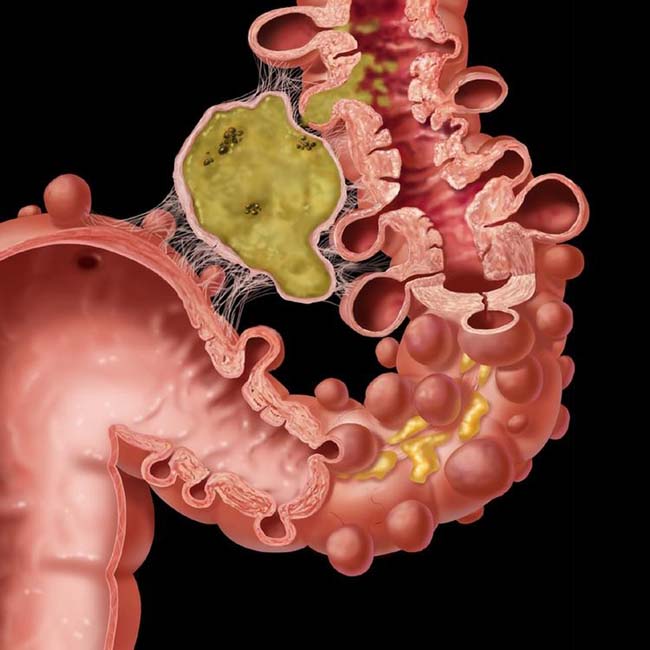
Diverticulitis Radiology Key Diverticulitis is a complication seen in 10 20% of patients with diverticulosis. it occurs when an inspissated piece of fecal material collects within and obstructs the lumen of a diverticulum. the vascular supply to the wall of the diverticulum becomes compromised and renders the diverticular wall susceptible to invasion by colonic bacteria. Diverticula occur mainly where vasa recta vessels pierce muscularis propria, between mesenteric and antimesenteric taeniae. • size. diverticula usually 0.5 1.0 cm. • morphology. • colonic diverticula are pseudodiverticular. saccular outpouchings of mucosa and submucosa, 5 10 mm in diameter.
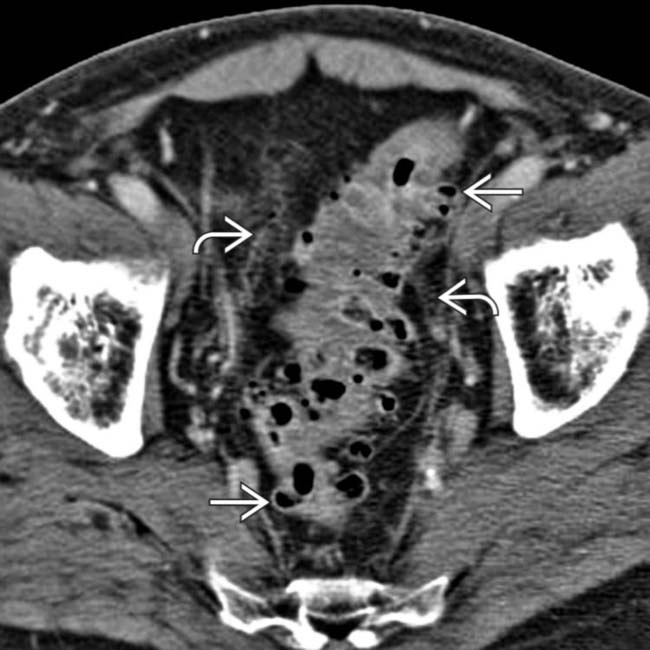
Diverticulitis Radiology Key Acute colonic diverticulitis is a common cause of acute abdominal symptoms, especially in elderly patients. in turn, diverticulitis develops in 10–25 % of the population with diverticulosis (roberts et al. 1995). it is, in virtually all cases, the result of a microperforation of a single diverticulum (fig. 5). fig. 5. Colonic diverticulitis | radiology reference article. A number of key diagnostic features of colonic diverticulitis have been described at sonography , including focal inflammation of a diverticulum, characterized by a thick, hypoechoic wall with variable internal echogenicity depending on the diverticular contents; a thickened area of hyperechoic, inflamed pericolic fat; and scattered diverticula containing air manifest by “dirty shadowing. In this review, we discuss the pathophysiology and key imaging features of acute diverticulitis and its complications. we explore both common and uncommon presentations of the disease involving the colon and small bowel, acute and chronic manifestations of disease, and pitfalls to recognize when imaging alone may be insufficient to distinguish benign from malignant.
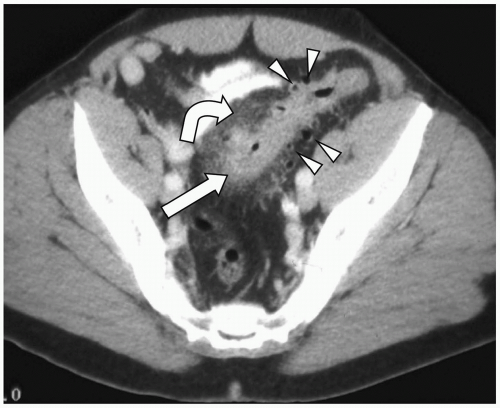
Diverticulitis Radiology Key A number of key diagnostic features of colonic diverticulitis have been described at sonography , including focal inflammation of a diverticulum, characterized by a thick, hypoechoic wall with variable internal echogenicity depending on the diverticular contents; a thickened area of hyperechoic, inflamed pericolic fat; and scattered diverticula containing air manifest by “dirty shadowing. In this review, we discuss the pathophysiology and key imaging features of acute diverticulitis and its complications. we explore both common and uncommon presentations of the disease involving the colon and small bowel, acute and chronic manifestations of disease, and pitfalls to recognize when imaging alone may be insufficient to distinguish benign from malignant. Ce ct allows, in the scenario of suspected diverticulitis, to 1. confirm the diagnosis and identify the inflamed diverticulum; 2. stage the disease, stratifying patients for operative versus nonoperative treatment; 3. identify complications, depicting the extracolonic disease extent; 4. provide a valid tool in preoperative surgical and radiological interventional planning; and 5. suggest. Hinchey classification of acute diverticulitis.
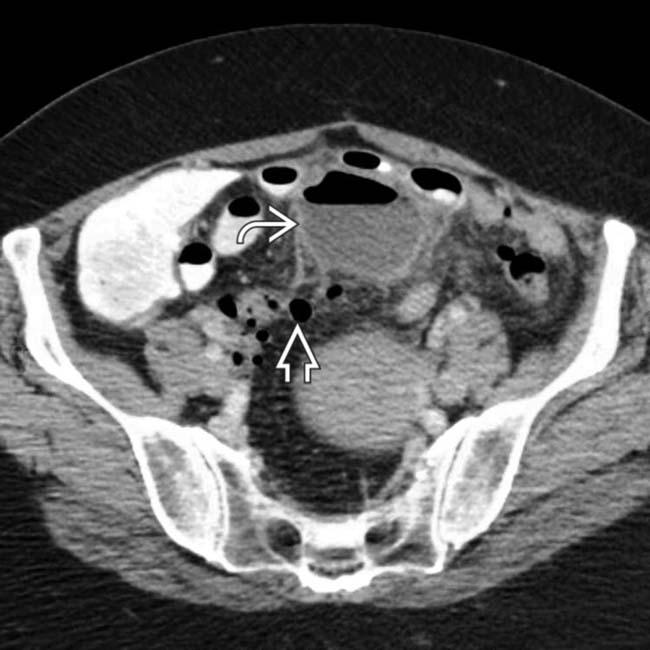
Diverticulitis Radiology Key Ce ct allows, in the scenario of suspected diverticulitis, to 1. confirm the diagnosis and identify the inflamed diverticulum; 2. stage the disease, stratifying patients for operative versus nonoperative treatment; 3. identify complications, depicting the extracolonic disease extent; 4. provide a valid tool in preoperative surgical and radiological interventional planning; and 5. suggest. Hinchey classification of acute diverticulitis.

Comments are closed.