Dna Chemical Structure Details Of Strands Compounds Adenine Thymine

Dna Chemical Structure Details Of Strands Compounds Adenine Thymine Dna structure, showing the nucleotide bases cytosine (c), thymine (t), adenine (a), and guanine (g) linked to a backbone of alternating phosphate (p) and deoxyribose sugar (s) groups. two sugar phosphate chains are paired through hydrogen bonds between a and t and between g and c, thus forming the twin stranded double helix of the dna molecule. Dna structure and function. dna is the information molecule. it stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. these instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. these chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes.
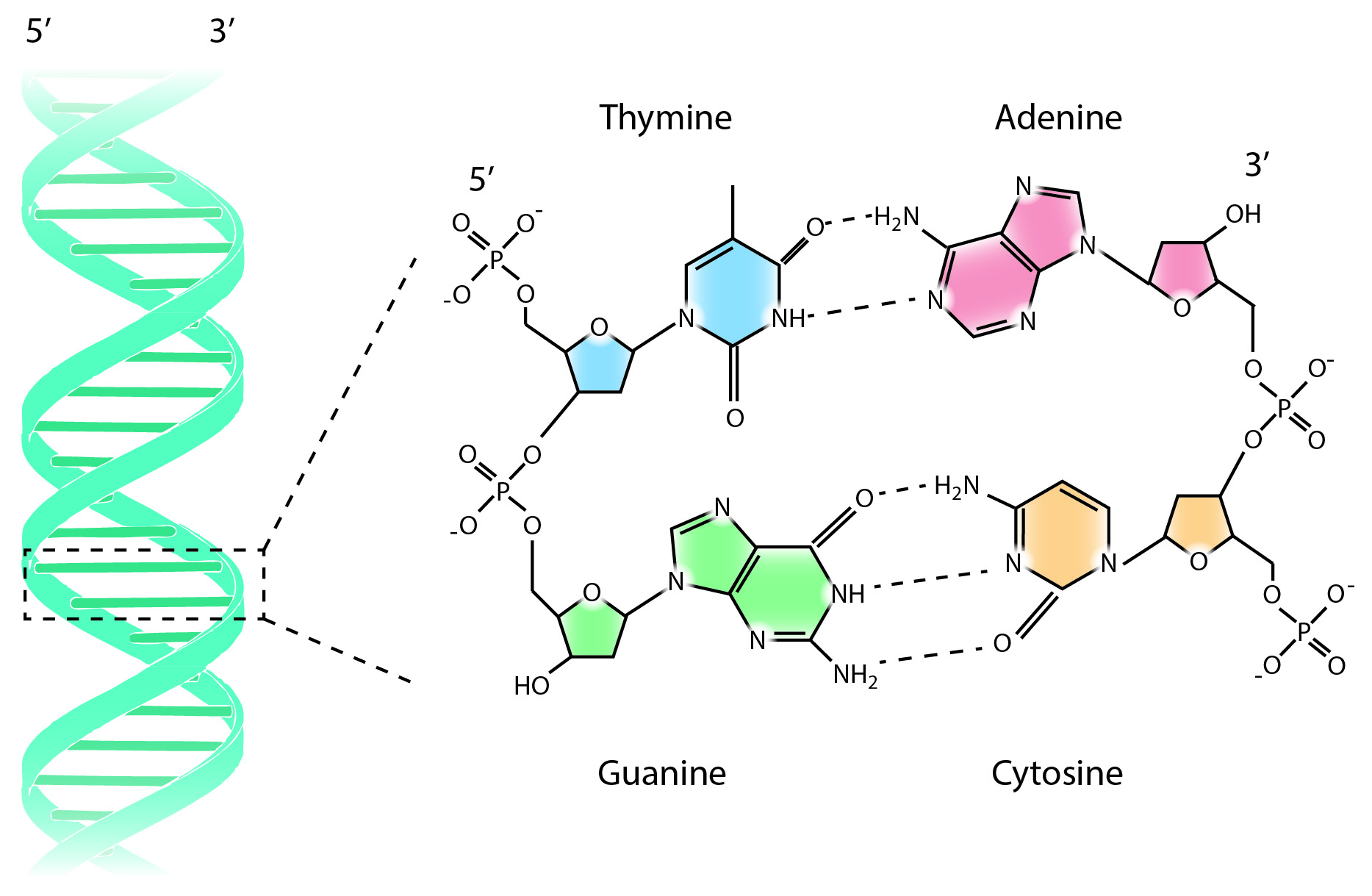
A Analise De Um Segmento De Dna Com 1500 Pares Educa Chemical structure of dna, showing four nucleobase pairs produced by eight nucleotides: adenine (a) is joined to thymine (t), and guanine (g) is joined to cytosine (c). this structure also shows the directionality of each of the two phosphate deoxyribose backbones, or strands. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed. The nitrogenous bases also form hydrogen bonds with one another based on predictable base pairing rules: adenine (a) pairs with thymine (t), and cytosine (c) pairs with guanine (g). depending on students’ background, it may be helpful to pause the animation at various points to discuss different parts of dna’s structure. These strands are made up of nucleotides, which themselves consist of three component parts: a sugar group, a phosphate group, and a base. the sugar and phosphate groups combined form the repeating ‘backbone’ of the dna strands. there are four different bases that can potentially be attached to the sugar group: adenine, thymine, guanine and.

Comments are closed.