Dna Structure Adenine Cytosine Thymine Guanine Sugar
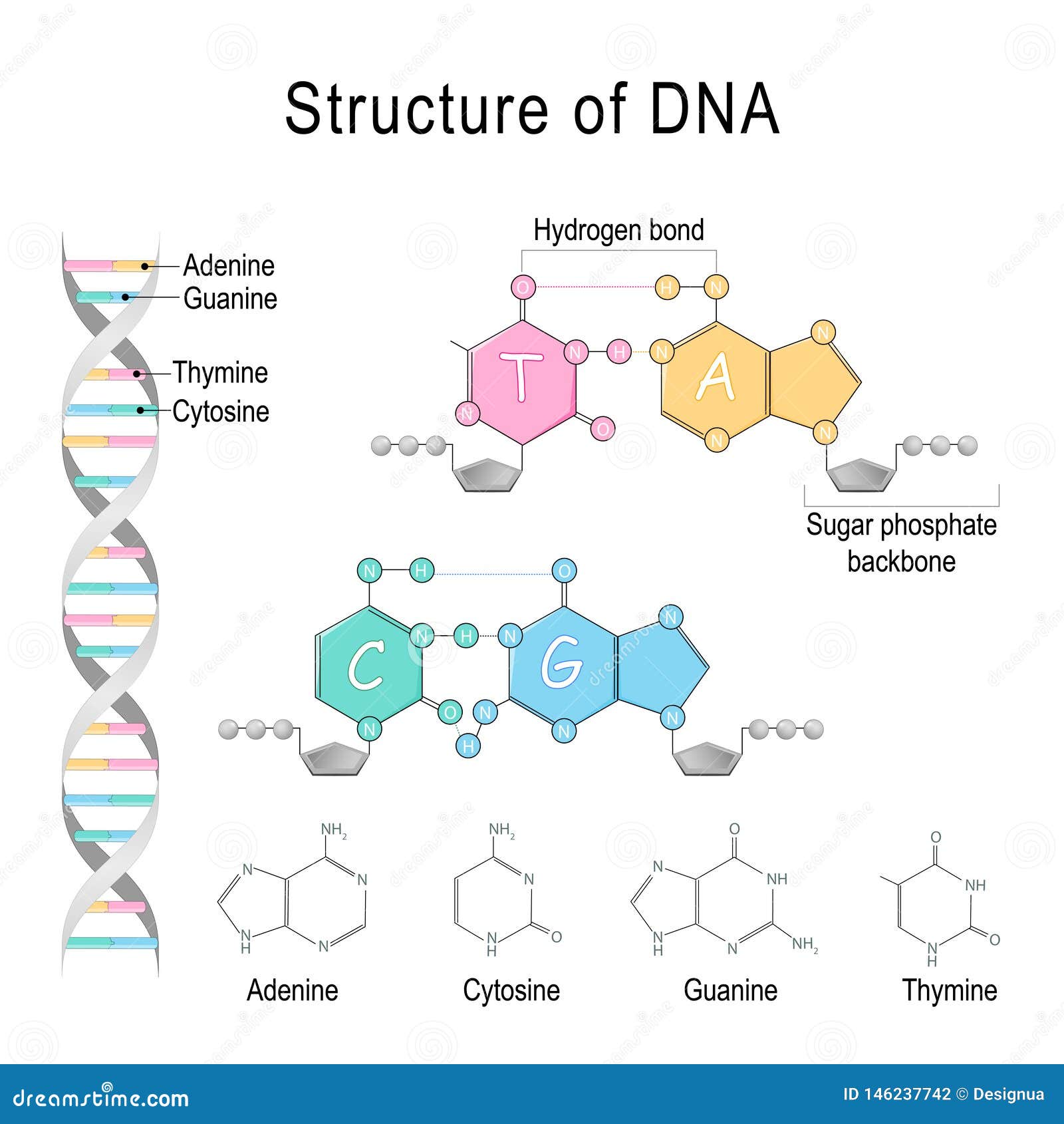
Dna Structure Adenine Cytosine Thymine Guanine Sugar My Xxx Hot Girl Dna structure and function. dna is the information molecule. it stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. these instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. these chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes. A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) or cytosine (c). c and t bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines , while a and g bases, which have two rings, are called purines .
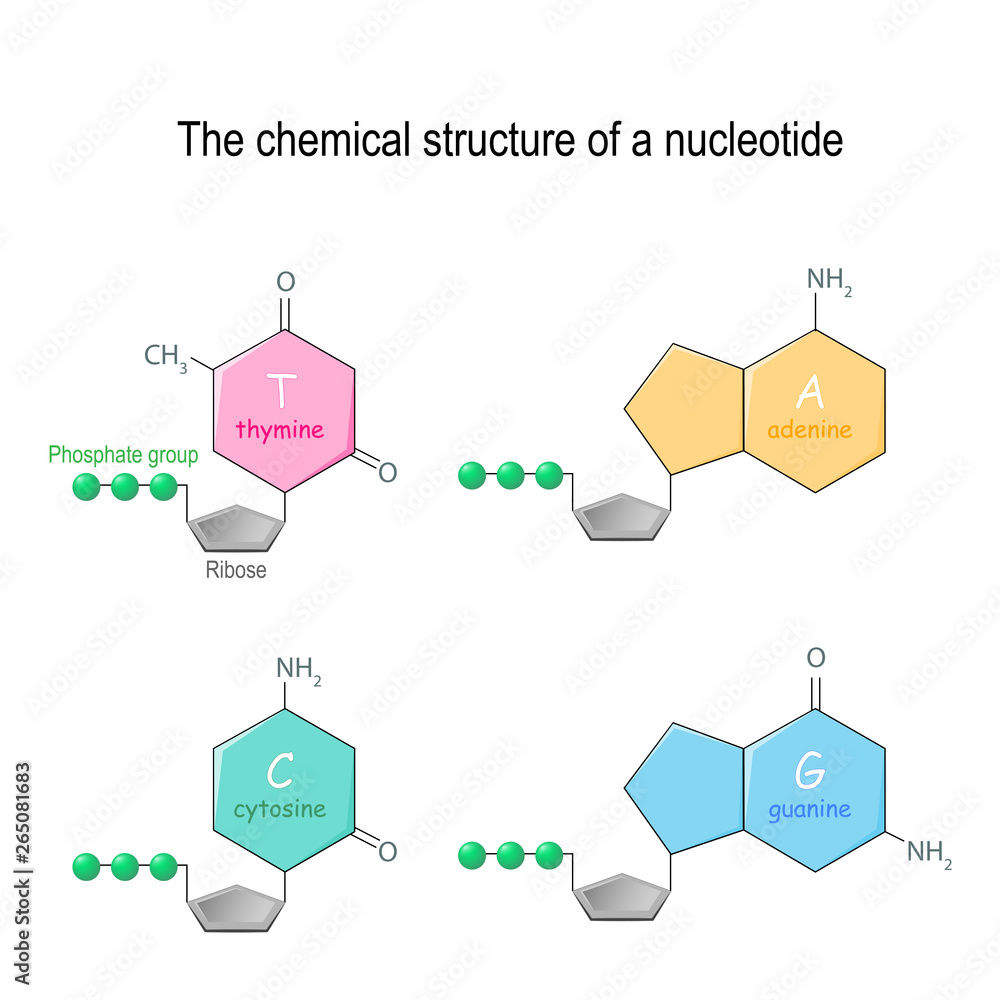
The Chemical Structure Of A Nucleotide Four Main Bases Found In Dna While dna is double stranded and has the nitrogenous bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, rna is usually single stranded and contains uracil instead of thymine. as for the similarities between dna and rna, they are both important biological polymers and contain four bases and a phosphate sugar backbone. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed. In dna, these bases are cytosine (c), thymine (t), adenine (a) and guanine (g).these bases attach in place of the oh group on the 1' carbon atom in the sugar ring. joining the nucleotides into a dna strand; building a dna chain concentrating on the essentials ; joining the two dna chains together; a final structure for dna showing the. This unit joins to a third nucleotide, and the process is repeated to produce a long nucleic acid chain (figure 14.5.3.1 14.5.3. 1 ). the backbone of the chain consists of alternating phosphate and sugar units (2 deoxyribose in dna and ribose in rna). the purine and pyrimidine bases branch off this backbone.
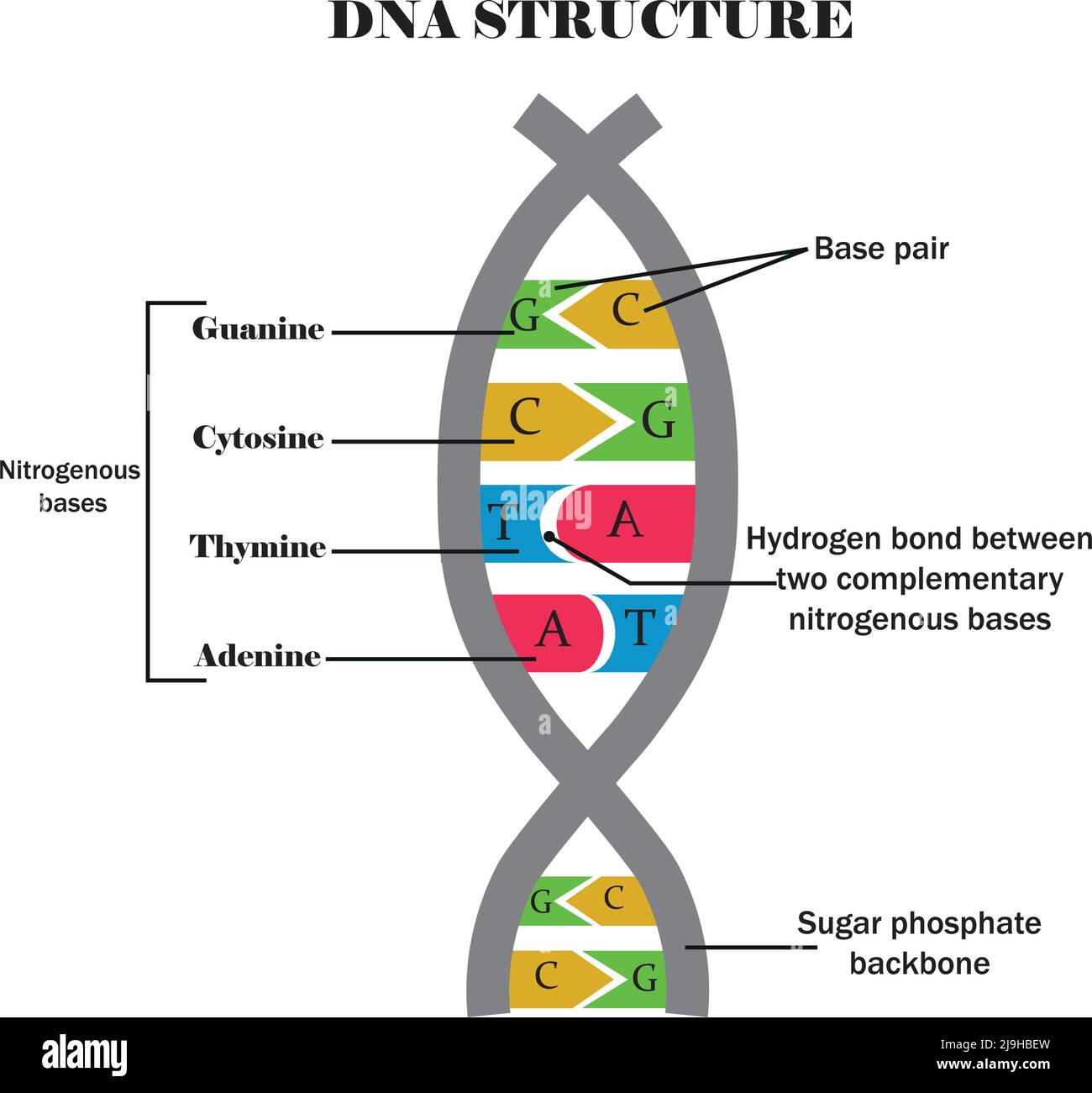
Estructura Del Adn Dibujo Porn Sex Picture In dna, these bases are cytosine (c), thymine (t), adenine (a) and guanine (g).these bases attach in place of the oh group on the 1' carbon atom in the sugar ring. joining the nucleotides into a dna strand; building a dna chain concentrating on the essentials ; joining the two dna chains together; a final structure for dna showing the. This unit joins to a third nucleotide, and the process is repeated to produce a long nucleic acid chain (figure 14.5.3.1 14.5.3. 1 ). the backbone of the chain consists of alternating phosphate and sugar units (2 deoxyribose in dna and ribose in rna). the purine and pyrimidine bases branch off this backbone. Figure 2: the four nitrogenous bases that compose dna nucleotides are shown in bright colors: adenine (a, green), thymine (t, red), cytosine (c, orange), and guanine (g, blue). Each nucleotide in dna contains one of four possible nitrogenous bases: adenine (a), guanine (g) cytosine (c), and thymine (t). adenine and guanine are classified as purines. the primary structure of a purine is two carbon nitrogen rings. cytosine, thymine, and uracil are classified as pyrimidines which have a single carbon nitrogen ring as.

9 1 The Structure Of Dna вђ Concepts Of Biology вђ 1st Canadian Edition Figure 2: the four nitrogenous bases that compose dna nucleotides are shown in bright colors: adenine (a, green), thymine (t, red), cytosine (c, orange), and guanine (g, blue). Each nucleotide in dna contains one of four possible nitrogenous bases: adenine (a), guanine (g) cytosine (c), and thymine (t). adenine and guanine are classified as purines. the primary structure of a purine is two carbon nitrogen rings. cytosine, thymine, and uracil are classified as pyrimidines which have a single carbon nitrogen ring as.

Comments are closed.