Dna Structure Base Pairing And Nucleotide Cytosine Thymine Guanine
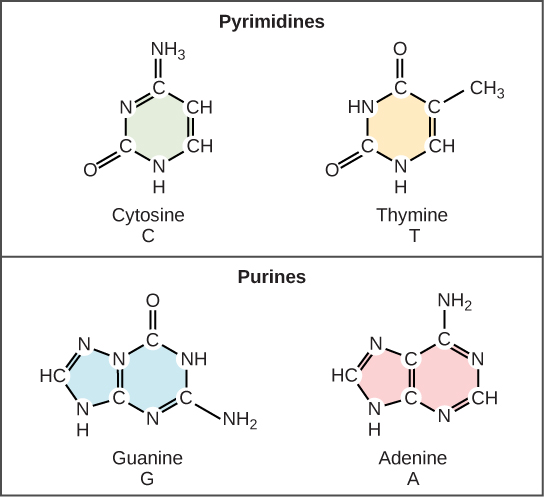
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Biology Libretexts The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed. Five nucleobases— adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g), thymine (t), and uracil (u)—are called primary or canonical. they function as the fundamental units of the genetic code, with the bases a, g, c, and t being found in dna while a, g, c, and u are found in rna. thymine and uracil are distinguished by merely the presence or absence of a.
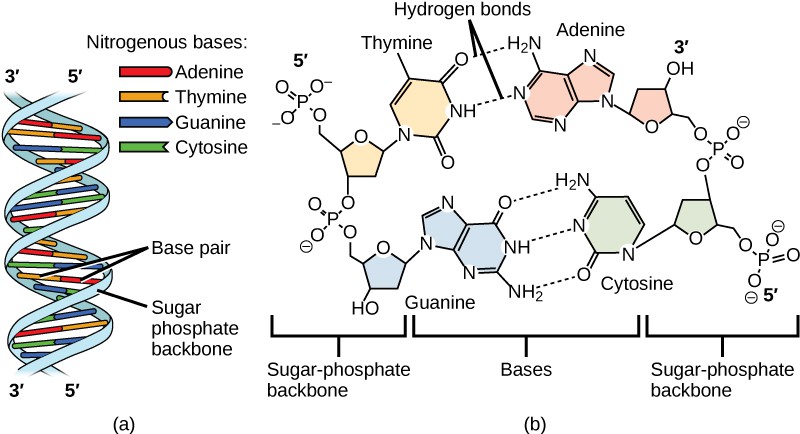
The Structure Of Dna Openstax Concepts Of Biology Molecular structure of dna. dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. the bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) or cytosine (c). c and t bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines , while a and g bases, which have two rings, are called purines . Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine. in dna, adenine (a) and thymine (t) are complementary base pairs, and cytosine (c) and guanine (g) are also complementary base pairs, explaining chargaff’s rules (figure 10.17). the base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds between them. Adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. the nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. figure 9.3 (a) each dna nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base.
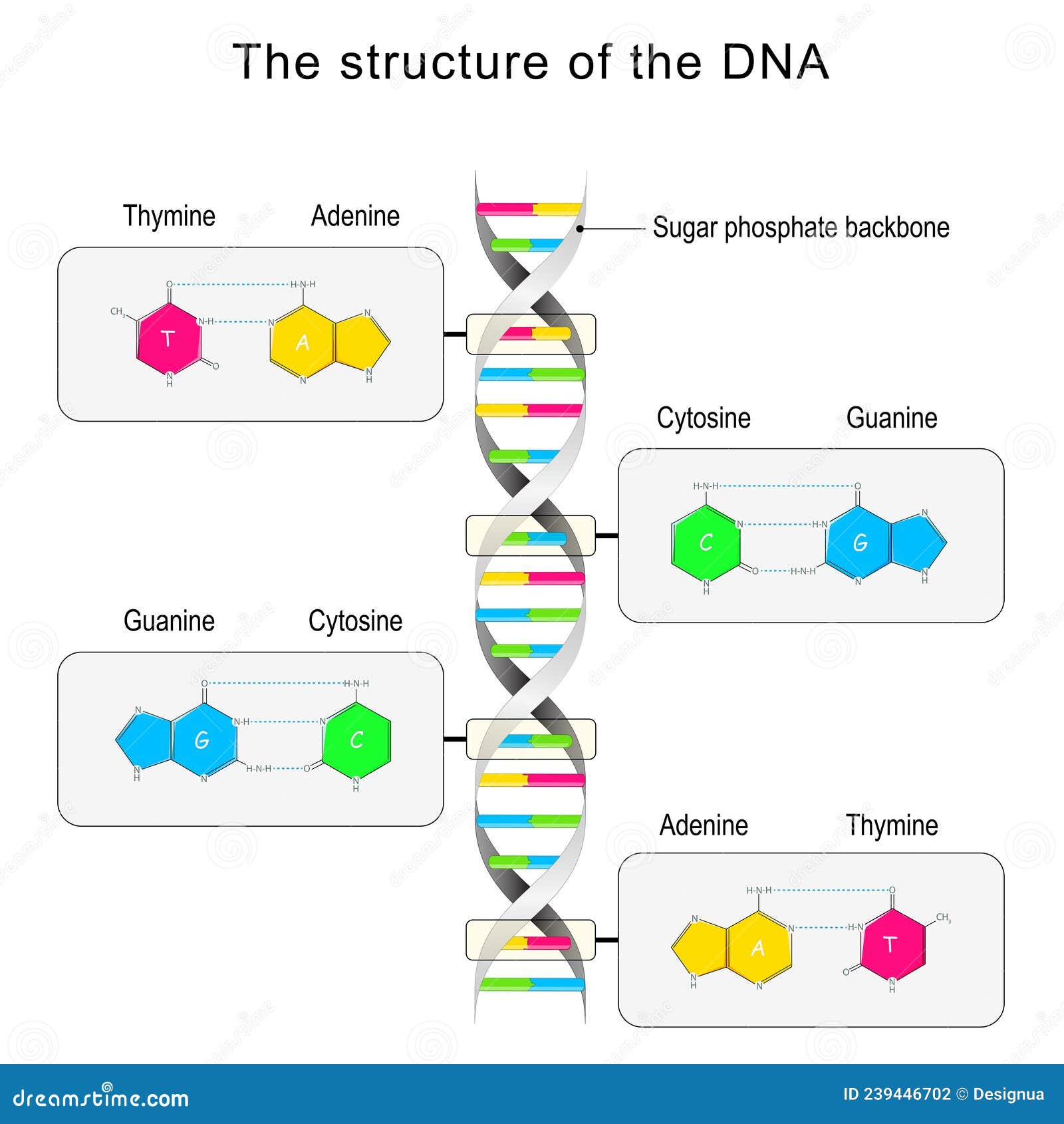
Dna Structure Base Pairing And Nucleotide Stock Vector Illustration Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine. in dna, adenine (a) and thymine (t) are complementary base pairs, and cytosine (c) and guanine (g) are also complementary base pairs, explaining chargaff’s rules (figure 10.17). the base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds between them. Adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. the nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. figure 9.3 (a) each dna nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base. Figure 7.1.1 7.1. 1. dna. deoxyribonucleic acid is a polymer chain of nucleotides connected by 5’ to 3’ phosphodiester bonds. dna normally exists as a two antiparallel complementary strands held together by hydrogen bonds between adenines (a) and thymines (t), and between guanines (g) and cytosines (c). Figure 5.4.1: base pairing. the rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: a with t: the purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g: the pyrimidine cytosine (c) always pairs with the purine guanine (g) this is consistent with there not being enough space (20 Å) for two purines to fit within the helix and.
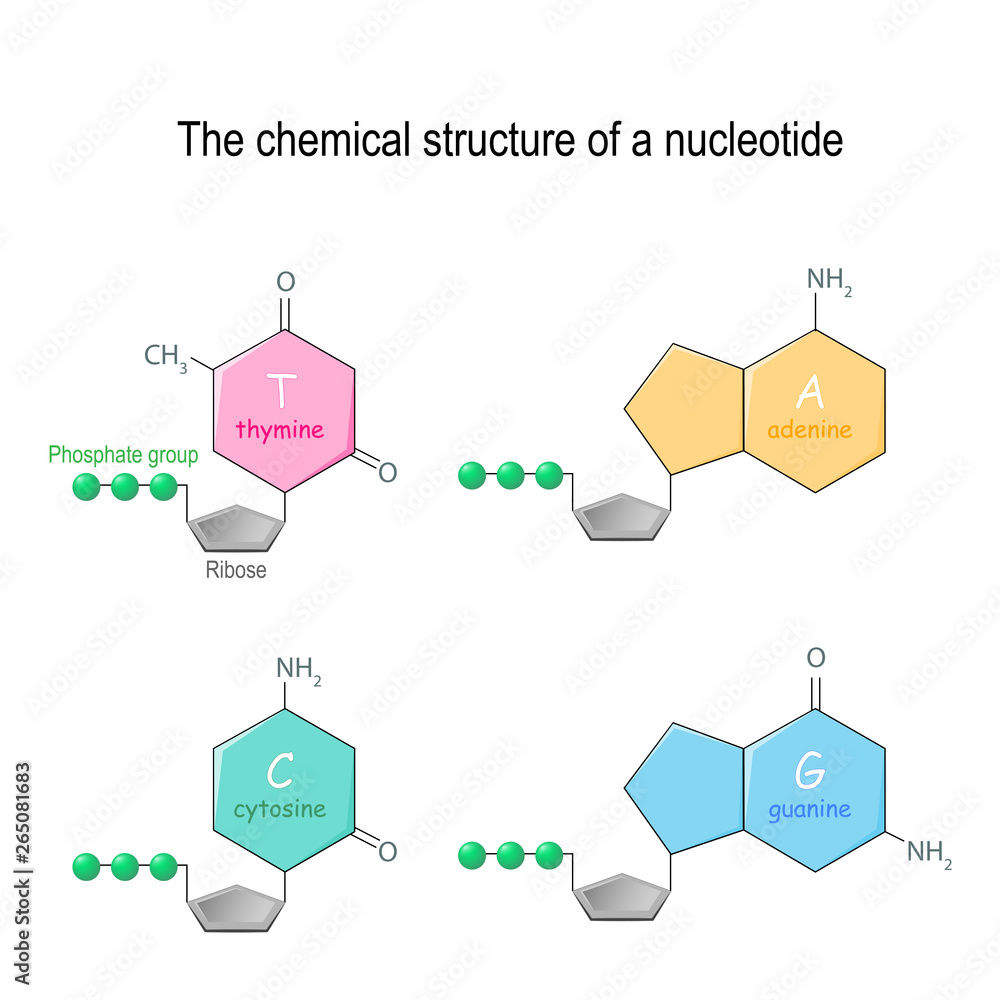
The Chemical Structure Of A Nucleotide Four Main Bases Found In Dna Figure 7.1.1 7.1. 1. dna. deoxyribonucleic acid is a polymer chain of nucleotides connected by 5’ to 3’ phosphodiester bonds. dna normally exists as a two antiparallel complementary strands held together by hydrogen bonds between adenines (a) and thymines (t), and between guanines (g) and cytosines (c). Figure 5.4.1: base pairing. the rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: a with t: the purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g: the pyrimidine cytosine (c) always pairs with the purine guanine (g) this is consistent with there not being enough space (20 Å) for two purines to fit within the helix and.

Nitrogenous Bases In Dna

Comments are closed.