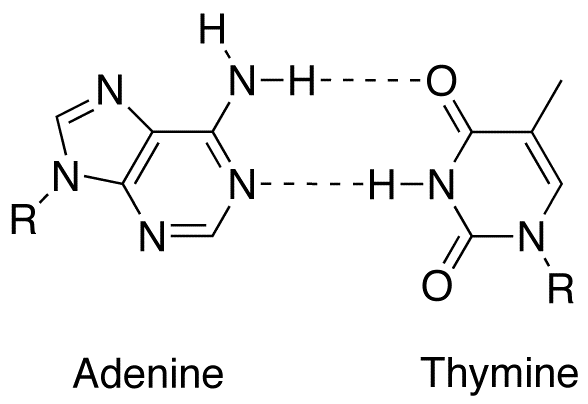
Dna Structure Including Dinucleotide Base Pairs Of Adenine To Thymine

Dna Structure Including Dinucleotide Base Pairs Of Adenine To Thymine Dna structure and function. dna is the information molecule. it stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. these instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. these chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed.
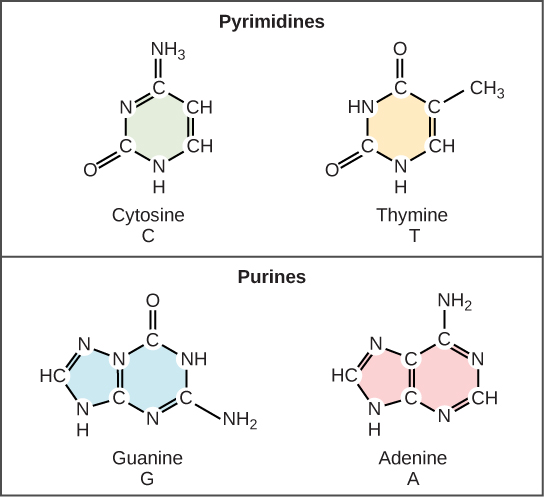
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Biology Libretexts The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base . there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. the nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. figure 9.3 (a) each dna nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base. Molecular structure of dna. dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. the bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. Dna (deoxyribose nucleic acid), discovered in 1869 by friedrich miescher, is composed of four bases (guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine). the bases are connected to a sugar (deoxyribose), and sugars are interconnected through phosphate linkages to form a long, unbranched chain. for much of the first half of the 20th century, the chemical agent.
Dna Structure And Replication Writework Molecular structure of dna. dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. the bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. Dna (deoxyribose nucleic acid), discovered in 1869 by friedrich miescher, is composed of four bases (guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine). the bases are connected to a sugar (deoxyribose), and sugars are interconnected through phosphate linkages to form a long, unbranched chain. for much of the first half of the 20th century, the chemical agent. Dna nucleotides. the building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. nucleotides that compose dna are called deoxyribonucleotides. the three components of a deoxyribonucleotide are a five carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, a nitrogen containing ring structure that is responsible for complementary base pairing between nucleic acid strands (figure. Rna nucleotides may also contain adenine, guanine and cytosine bases, but instead of thymine they have another base called uracil (u). chargaff's rules in the 1950s, a biochemist named erwin chargaff discovered that the amounts of the nitrogenous bases (a, t, c, and g) were not found in equal quantities.

Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Hot Sex Picture Dna nucleotides. the building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. nucleotides that compose dna are called deoxyribonucleotides. the three components of a deoxyribonucleotide are a five carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, a nitrogen containing ring structure that is responsible for complementary base pairing between nucleic acid strands (figure. Rna nucleotides may also contain adenine, guanine and cytosine bases, but instead of thymine they have another base called uracil (u). chargaff's rules in the 1950s, a biochemist named erwin chargaff discovered that the amounts of the nitrogenous bases (a, t, c, and g) were not found in equal quantities.

Comments are closed.