Double Acting Reciprocating Pump

Double Acting Reciprocating Pump Download Scientific Diagram A reciprocating pump is also known as a positive displacement pump. it is a device that converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy by sucking the liquid into a cylinder, it discharges a definite quantity of liquid. it is often used where a small quantity of liquid is to be handled and where delivery pressure is quite significant. Learn the working principle, discharge, work done and power required for a double acting reciprocating pump. a double acting pump has two suction and two delivery strokes for one revolution of the crank and delivers twice as much water as a single acting pump.
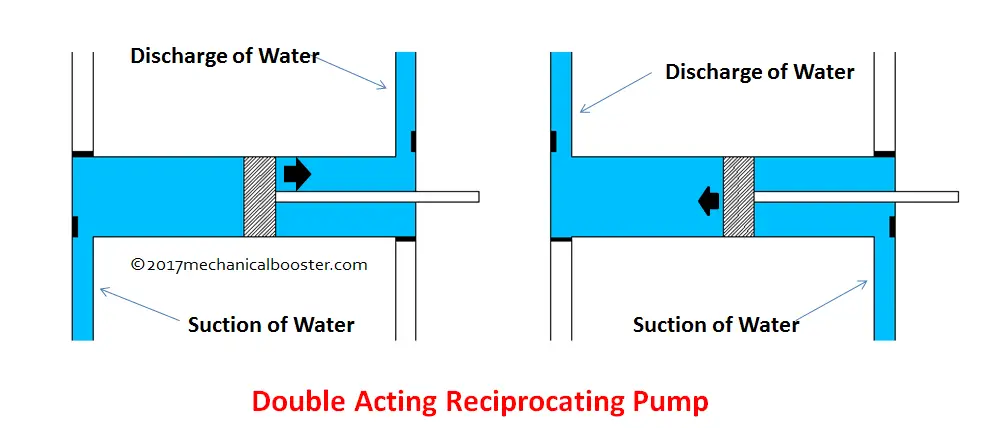
Reciprocating Pump Main Parts Types Working Advantages Learn about the principle, components and working of double acting reciprocating pump, a positive displacement pump that has suction and delivery strokes in each cycle. compare it with single acting pump and centrifugal pump. This video explains the working principle of single acting and double acting reciprocating pumps. it shows the construction and working animation of positive. Learn about the working principle, types, components, and applications of reciprocating pumps. a double acting reciprocating pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses a piston or plunger to pump fluid in both directions. Single acting reciprocating pump consists of a piston of which only one side engages the fluid being displaced. [2] the simplest example would be a syringe . double acting reciprocating pump engage with both sides of the piston, each stroke of the piston carries out both suction and expulsion at the same time.

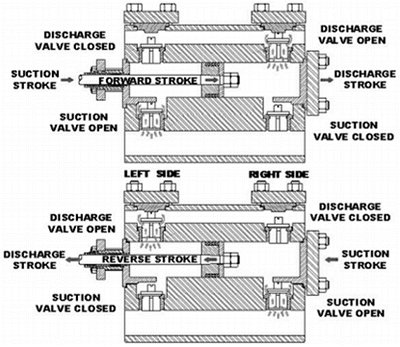
Double Acting Reciprocating Pump Working Principle Discharge Work Learn about the working principle, types, components, and applications of reciprocating pumps. a double acting reciprocating pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses a piston or plunger to pump fluid in both directions. Single acting reciprocating pump consists of a piston of which only one side engages the fluid being displaced. [2] the simplest example would be a syringe . double acting reciprocating pump engage with both sides of the piston, each stroke of the piston carries out both suction and expulsion at the same time. Double acting reciprocating pump: as the name suggests, a double acting reciprocating pump means, both sides of the piston are acting to produce work. in each double acting reciprocating pump, there will be two suctions pipes, two suction valves, two delivery pipes and two delivers valves. In the case of double acting pumps the cross sectional area of the piston is doubled and the cross sectional area of the piston rod (a) is subtracted. in gallons per minute, displacement is: d = ( (2a a) x s x n x rpm) 231. in reality, several factors temper the theoretical capacity of a piston or plunger pump. one is known as slip (s).

Reciprocating Pump Diagram Parts Working Types Pdf Double acting reciprocating pump: as the name suggests, a double acting reciprocating pump means, both sides of the piston are acting to produce work. in each double acting reciprocating pump, there will be two suctions pipes, two suction valves, two delivery pipes and two delivers valves. In the case of double acting pumps the cross sectional area of the piston is doubled and the cross sectional area of the piston rod (a) is subtracted. in gallons per minute, displacement is: d = ( (2a a) x s x n x rpm) 231. in reality, several factors temper the theoretical capacity of a piston or plunger pump. one is known as slip (s).
Virtual Labs

Comments are closed.