Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Arthroplasty
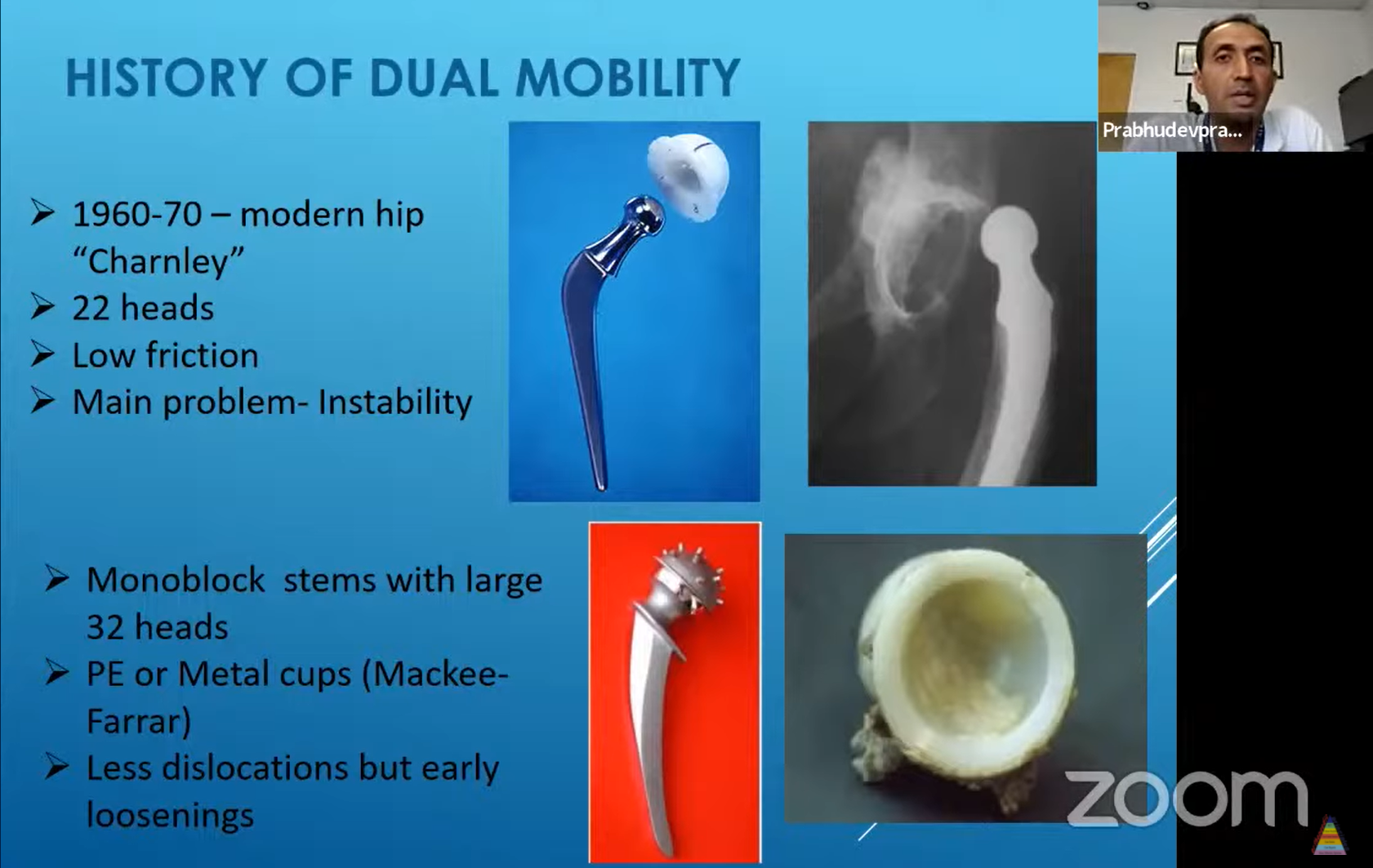
Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Arthroplasty Sanders rj, swierstra ba, goosen jh. the use of a dual mobility concept in total hip arthroplasty patients with spastic disorders: no dislocations in a series of ten cases at midterm follow up. archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery. 2013; 133 (7):1011–1016. doi: 10.1007 s00402 013 1759 9. [google scholar]. Total hip arthroplasty (tha) is one of the most successful surgical procedures – reducing pain and providing functional improvement. however, tha instability is a disabling condition and remains the most common indication for revision tha. to combat the risk of instability, the concept of dual mobility (dm) was developed.

Dual Mobility In Total Hip Arthroplasty Orthopedic Clinics Abstract. : dual mobility (dm) refers to a now widely available option for total hip articulation. dm implants feature a small inner head, a hard bearing, that connects via a taper fit onto the femoral trunnion. this head freely rotates but is encased inside a larger, outer polyethylene head that articulates with a smooth acetabular component. Adam p, philippe r, ehlinger m, roche o, bonnomet f, molé d, fessy mh. dual mobility cups hip arthroplasty as a treatment for displaced fracture of the femoral neck in the elderly. a prospective, systematic, multicenter study with specific focus on postoperative dislocation. orthop traumatol surg res. 2012;98:296–300. Dual mobility (dm) total hip arthroplasty (tha) combines the stabilization advantage provided by large head articulation with the low friction advantage provided by small head articulation. there is momentum for dm to be used in a wider selection of patients, with some advocating for dm to be the routine primary total hip construct. further investigation is needed to determine whether the use. Aims: instability remains a challenging problem in both primary and revision total hip arthroplasty (tha). dual mobility components confer increased stability, but there are concerns about the unique complications associated with these designs, as well as the long term survivorship.

Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Replacement Youtube Dual mobility (dm) total hip arthroplasty (tha) combines the stabilization advantage provided by large head articulation with the low friction advantage provided by small head articulation. there is momentum for dm to be used in a wider selection of patients, with some advocating for dm to be the routine primary total hip construct. further investigation is needed to determine whether the use. Aims: instability remains a challenging problem in both primary and revision total hip arthroplasty (tha). dual mobility components confer increased stability, but there are concerns about the unique complications associated with these designs, as well as the long term survivorship. Instability following total hip arthroplasty (tha) accounts for approximately 22.5% of all revisions in the united states [].several strategies have been implemented to address this substantial problem: optimization of acetabular component position, the use of larger femoral head components, restoring or increasing offset, the use of constrained liners, and the use of dual mobility (dm. Large prosthetic heads, trochanteric advancement, constrained liners, modular components, neri, t. et al. intraprosthetic dislocation of dual mobility total hip arthroplasty: still occurring?.

Pdf Modeling The Functioning Of Dual Mobility Total Hip Arthroplasty Instability following total hip arthroplasty (tha) accounts for approximately 22.5% of all revisions in the united states [].several strategies have been implemented to address this substantial problem: optimization of acetabular component position, the use of larger femoral head components, restoring or increasing offset, the use of constrained liners, and the use of dual mobility (dm. Large prosthetic heads, trochanteric advancement, constrained liners, modular components, neri, t. et al. intraprosthetic dislocation of dual mobility total hip arthroplasty: still occurring?.

Dual Mobility Constructs In Revision Total Hip Arthroplasties The

Comments are closed.