Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Replacement

Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Replacement Youtube A hip replacement implant is a ball in socket mechanism, designed to simulate a human hip joint. typical components include a stem that inserts into the femur (thighbone), a ball that replaces the round head of the thigh bone, and a shell that lines the hip socket. compared to a traditional prosthesis for a hip replacement, a dual mobility. Jobory a, kärrholmovergaard js. reduced revision risk for dual mobility cup in total hip replacement due to hip fracture: a matched pair analysis of 9040 cases from the nordic arthroplasty register association (nara) journal of bone and joint surgery. american volume.
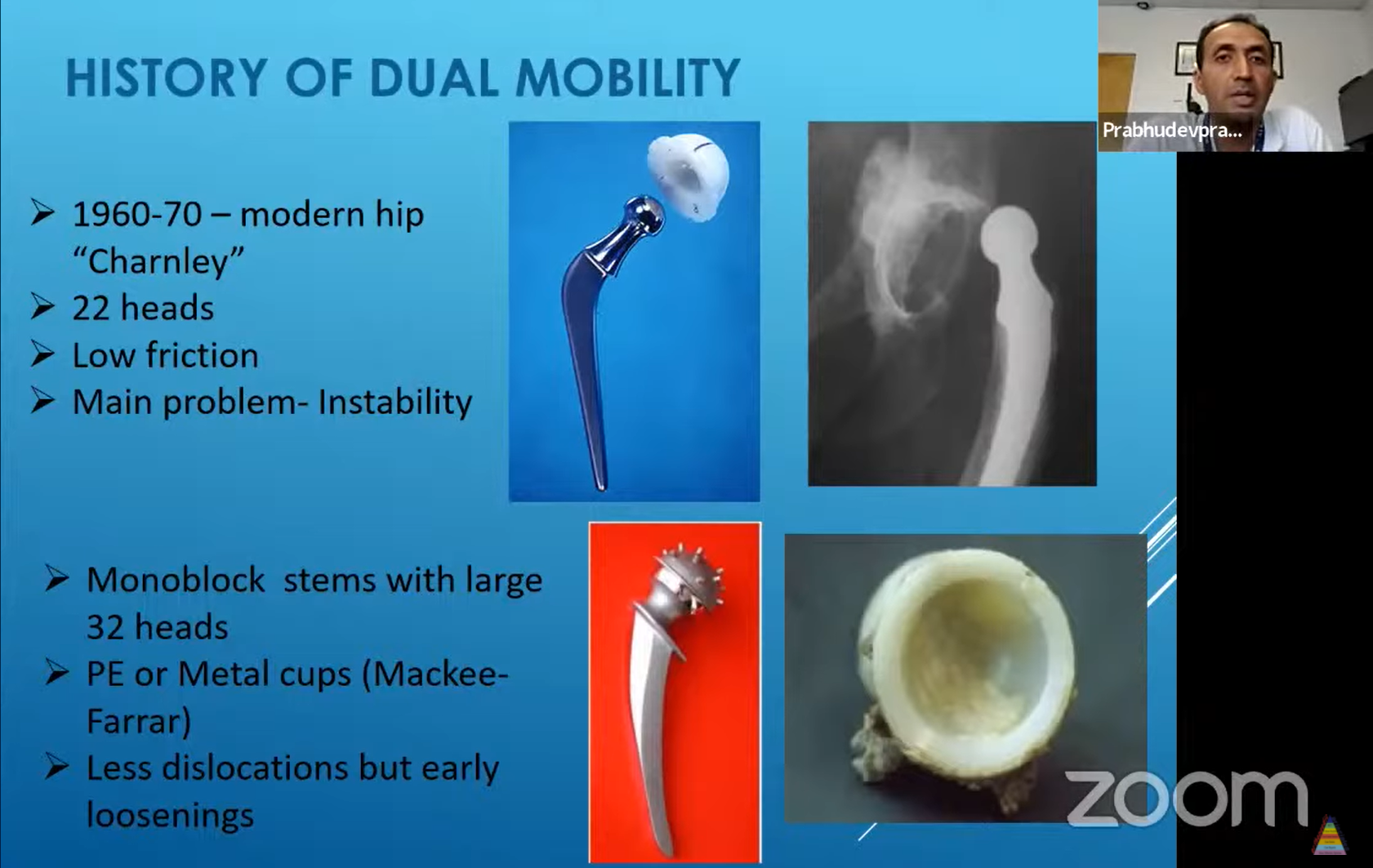
Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Arthroplasty Total hip arthroplasty instability is a disabling condition and remains the most common indication for revision tha in the united states; accounting for 22.5% of revisions. it is particularly prevalent in high risk cohorts (such as those with neuromuscular disease, obesity or cognitive dysfunction) where revision rates have reached up to 14%. Hip instability following total hip arthroplasty (tha) remains a major challenge and is one of the main causes of revision surgery. dual mobility (dm) implants have been introduced to try to overcome this problem. the dm design consists of a small femoral head captive and mobile within a polyethylene liner. Dual mobility (dm) total hip arthroplasty (tha) combines the stabilization advantage provided by large head articulation with the low friction advantage provided by small head articulation. there is momentum for dm to be used in a wider selection of patients, with some advocating for dm to be the routine primary total hip construct. further investigation is needed to determine whether the use. Dual mobility components confer increased stability, but there are concerns about the unique complications associated with these designs, as well as the long term survivorship. materials and methods: we performed a systematic review of all english language articles dealing with dual mobility thas published between 2007 and 2016 in the medline.

Dual Mobility In Total Hip Arthroplasty Orthopedic Clinics Dual mobility (dm) total hip arthroplasty (tha) combines the stabilization advantage provided by large head articulation with the low friction advantage provided by small head articulation. there is momentum for dm to be used in a wider selection of patients, with some advocating for dm to be the routine primary total hip construct. further investigation is needed to determine whether the use. Dual mobility components confer increased stability, but there are concerns about the unique complications associated with these designs, as well as the long term survivorship. materials and methods: we performed a systematic review of all english language articles dealing with dual mobility thas published between 2007 and 2016 in the medline. Dual mobility (dm) has been used in primary total hip arthroplasty recently for their low dislocation rates, low revision rates, and improved patient functional outcomes. we compared 2 dm systems, anatomic dual mobility (adm; stryker, mahwah, nj) and modular dual mobility (mdm; stryker, mahwah, nj), to determine differences in dislocation rates, revision rates, and patient outcome scores. Background there is little consensus on outcomes of dual mobility total hip replacement (dm thr) in younger patients. we performed a systematic review to examine this. methods a systematic review of all observational studies and randomised controlled trials of patients under 70 with primary dm thr in medline, embase, pubmed, cochrane was performed according to prisma guidelines. collected data.

Dual Mobility Total Hip Replacement Dr Avtar Singh Youtube Dual mobility (dm) has been used in primary total hip arthroplasty recently for their low dislocation rates, low revision rates, and improved patient functional outcomes. we compared 2 dm systems, anatomic dual mobility (adm; stryker, mahwah, nj) and modular dual mobility (mdm; stryker, mahwah, nj), to determine differences in dislocation rates, revision rates, and patient outcome scores. Background there is little consensus on outcomes of dual mobility total hip replacement (dm thr) in younger patients. we performed a systematic review to examine this. methods a systematic review of all observational studies and randomised controlled trials of patients under 70 with primary dm thr in medline, embase, pubmed, cochrane was performed according to prisma guidelines. collected data.

Comments are closed.