Dual Mobility In Total Hip Arthroplasty Orthopedic Clinics

Dual Mobility In Total Hip Arthroplasty Orthopedic Clinics Dual mobility articulations have shown promising results. postoperative instability remains the most common reason for revision of a total hip arthroplasty (tha). dual mobility cups have been shown to decrease the rate of dislocation in primary tha and have been used to treat and prevent instability in revision tha. greater range of motion and a greater head to neck ratio and a greater jump. Postoperative instability remains the most common reason for revision of a total hip arthroplasty (tha). dual mobility cups have been shown to decrease the rate of dislocation in primary tha and have been used to treat and prevent instability in revision tha. greater range of motion and a greater head to neck ratio and a greater jump distance.
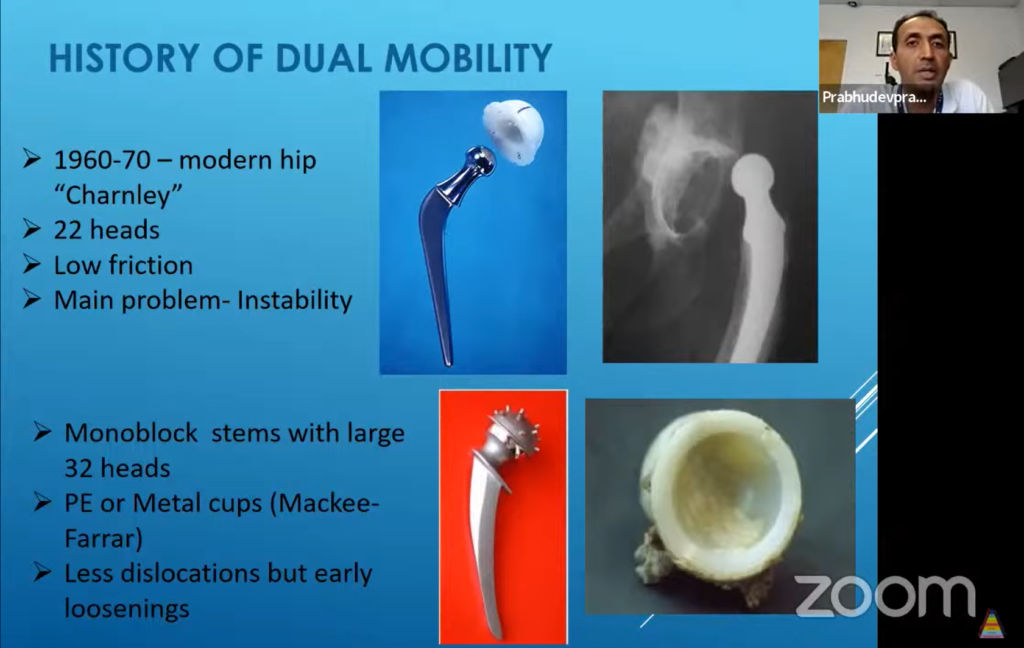
Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Arthroplasty The dual mobility socket was originally designed to be used in patients undergoing primary tha who were considered to be at high risk for disloca tion. current literature suggests those patients. fig. 3. (a) restoration anatomic dual mobility (adm) x3 dual mobility hip system by stryker orthopaedics. (b) modular dual mobility (mdm) x3 dual. Dual mobility (dm) has been used in primary total hip arthroplasty recently for their low dislocation rates, low revision rates, and improved patient functional outcomes. we compared 2 dm systems, anatomic dual mobility (adm; stryker, mahwah, nj) and modular dual mobility (mdm; stryker, mahwah, nj), to determine differences in dislocation rates, revision rates, and patient outcome scores. Hip instability following total hip arthroplasty (tha) remains a major challenge and is one of the main causes of revision surgery. dual mobility (dm) implants have been introduced to try to overcome this problem. the dm design consists of a small femoral head captive and mobile within a polyethylene liner. Department of orthopedic surgery, mayo clinic, rochester, mn article info article history: received 14 august 2018 received in revised form 5 november 2018 accepted 10 november 2018 available online 17 november 2018 keywords: dual mobility primary revision total hip arthroplasty systematic review abstract.

Dual Mobility Constructs In Revision Total Hip Arthroplasties The Hip instability following total hip arthroplasty (tha) remains a major challenge and is one of the main causes of revision surgery. dual mobility (dm) implants have been introduced to try to overcome this problem. the dm design consists of a small femoral head captive and mobile within a polyethylene liner. Department of orthopedic surgery, mayo clinic, rochester, mn article info article history: received 14 august 2018 received in revised form 5 november 2018 accepted 10 november 2018 available online 17 november 2018 keywords: dual mobility primary revision total hip arthroplasty systematic review abstract. Utilization of dual mobility constructs in total hip arthroplasties (tha) has increased in the recent years. benefits and risks of these implants in terms of reducing dislocations, long term survivorship, and associated complications are uncertain when compared to non dual mobility articulations. Abstract. : dual mobility (dm) refers to a now widely available option for total hip articulation. dm implants feature a small inner head, a hard bearing, that connects via a taper fit onto the femoral trunnion. this head freely rotates but is encased inside a larger, outer polyethylene head that articulates with a smooth acetabular component.

Component Selection In Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Orthopedic Clinics Utilization of dual mobility constructs in total hip arthroplasties (tha) has increased in the recent years. benefits and risks of these implants in terms of reducing dislocations, long term survivorship, and associated complications are uncertain when compared to non dual mobility articulations. Abstract. : dual mobility (dm) refers to a now widely available option for total hip articulation. dm implants feature a small inner head, a hard bearing, that connects via a taper fit onto the femoral trunnion. this head freely rotates but is encased inside a larger, outer polyethylene head that articulates with a smooth acetabular component.

Dual Mobility Components In Total Hip Replacement Youtube

Comments are closed.