Dysphagia Aspiration Syndromes Tube Feeding Decisions
Children Free Full Text Feeding Problems And Long Term Outcomes In Emory medicine grand rounds 10 18 2016speaker: anna von, md (emory division of hospital medicine)topic: “hard to swallow: dysphagia, aspiration syndromes,. A cross national survey of tube feeding decisions in cognitively impaired older persons. journal of the american geriatric society , 48 , 391–397. google scholar.

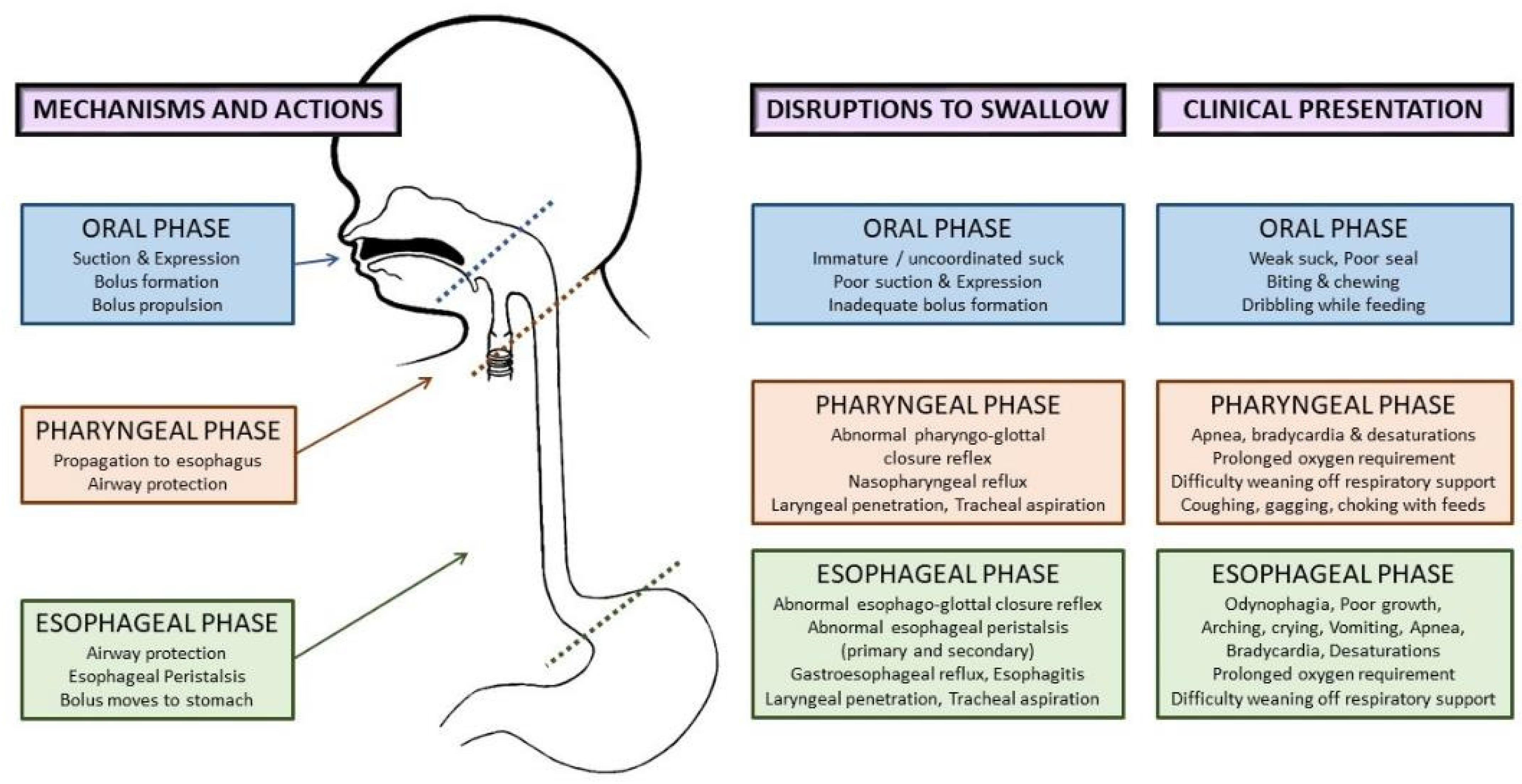
Dysphagia Aspiration Syndromes Tube Feeding Decisions Youtube Clinical decisions must integrate best clinical judgment, patient values and expectations, and best external evidence of a patient's whole health status not just dysphagia. we must carefully consider ethical imperatives governing health care practice, especially when a feeding tube is a possible intervention choice. This role requires familiarity with supplemental and alternative forms of nutrition and hydration (anh). decision making for anh in dysphagia care typically involves interdisciplinary collaboration between members of the medical team, including the patient and their family. the role of the slp is to make diet recommendations based on all. Amount: 2–4 drops (not ml) per 250 ml (1 can) of tube feeding formula. the fd&c blue no. 1 product was considered safe in healthy humans and animal studies. although it was never approved for use as an additive to enteral feeding, it became popular in the hospital setting for coloring enteral formulas (8). Severe dysphagia poses a significant challenge for clinicians regarding feeding tube choices, practices, and timing due to a lack of evidence based guidance. objectives to assess national clinical practices and opinions on gastrostomy use in patients with atypical parkinsonian syndromes (aps) across the uk.
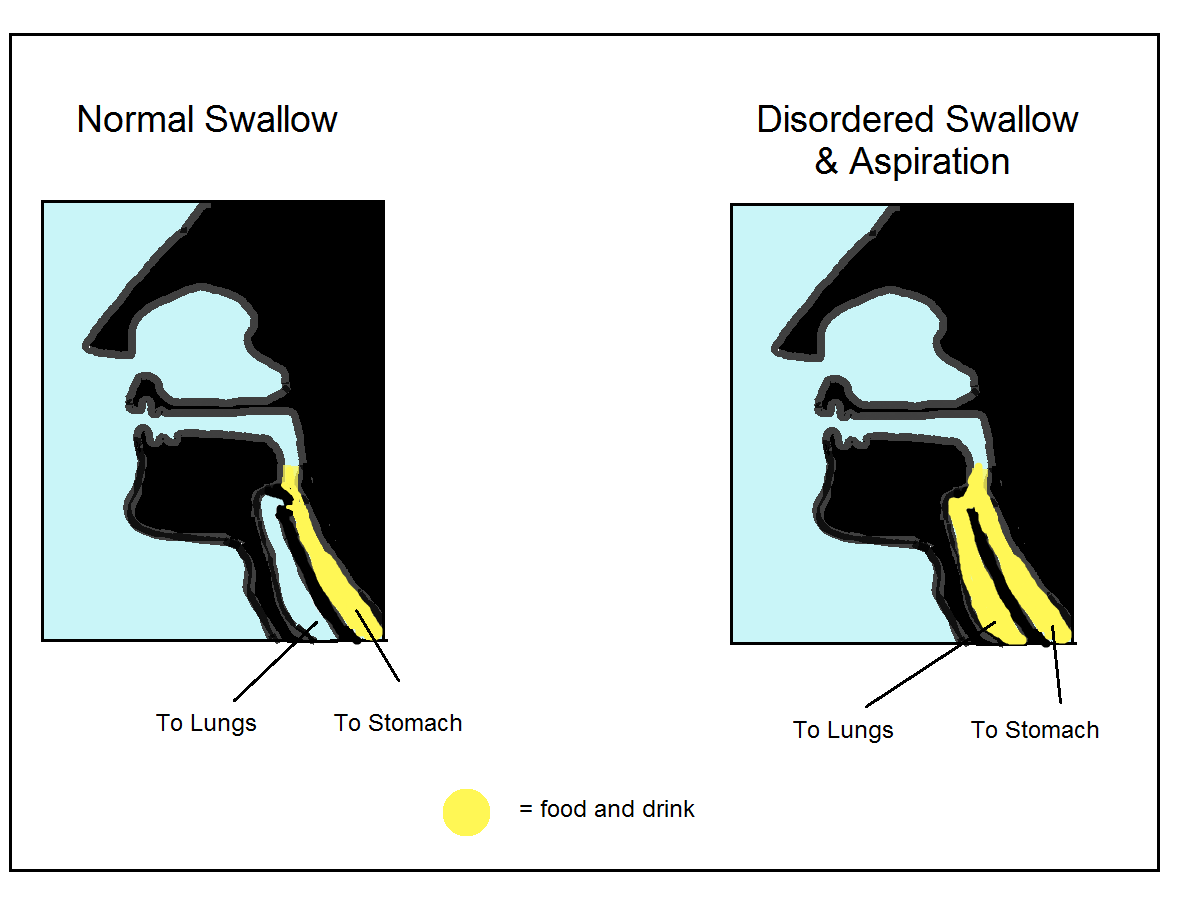
Aspiration Dysphagia Amount: 2–4 drops (not ml) per 250 ml (1 can) of tube feeding formula. the fd&c blue no. 1 product was considered safe in healthy humans and animal studies. although it was never approved for use as an additive to enteral feeding, it became popular in the hospital setting for coloring enteral formulas (8). Severe dysphagia poses a significant challenge for clinicians regarding feeding tube choices, practices, and timing due to a lack of evidence based guidance. objectives to assess national clinical practices and opinions on gastrostomy use in patients with atypical parkinsonian syndromes (aps) across the uk. Finally, tube feeding does not always improve physical function, weight gain, nutritional status, or wound healing. in addition, finucane et al. (1999, 1995) notes that tube feeding has no effect on malnutrition or wasting syndrome in chronically ill patients. they also find that tube feeding does not assist in healing pressure ulcers. 2) nil by mouth with tube feeding. you will stop having any food or drink by mouth. a feeding tube will usually be inserted directly into the stomach or via the nose, through which you will receive all your nutrition and hydration. this aims to minimise aspiration risk but may not eliminate all risk, as you can remain at risk of aspirating on.

Comments are closed.