Earth History Evolution Art Earth And Space Science History Of Eart

3d Conceptual Design The history of earth concerns the development of planet earth from its formation to the present day. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of earth's past, characterized by constant geological change and biological evolution . The early earth: accretion and differentiation provides a multidisciplinary overview of the state of the art in understanding the formation and primordial evolution of the earth. the fundamental structure of the earth as we know it today was inherited from the initial conditions 4.56 billion years ago as a consequence of planetesimal accretion, large impacts among planetary objects, and.
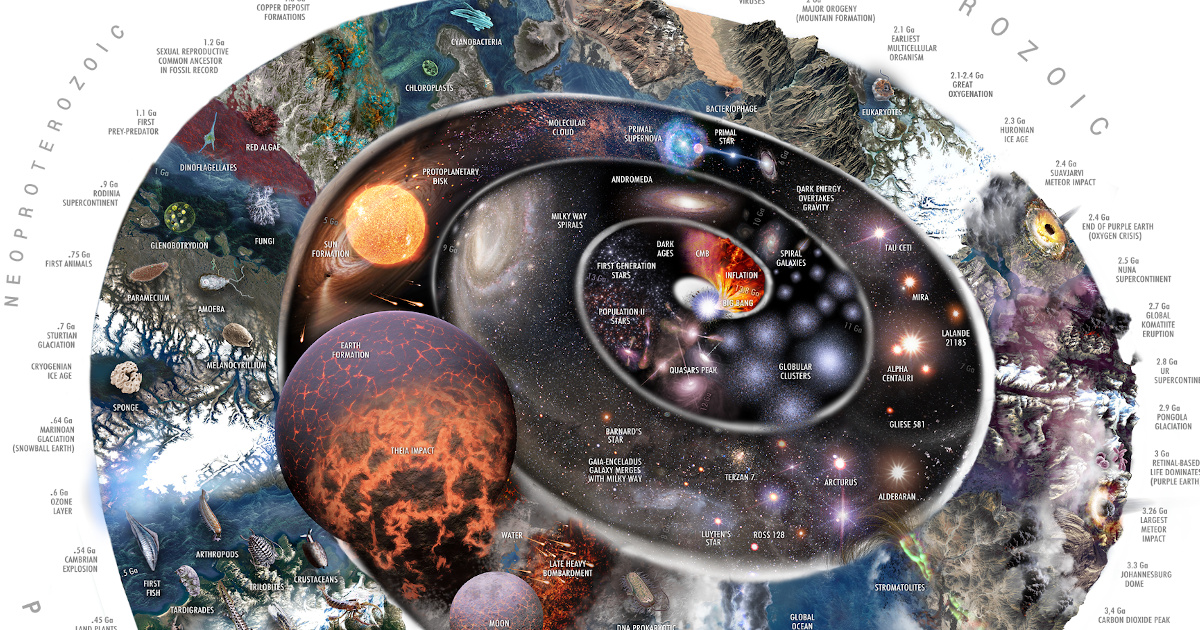
Top 121 Origin Of Life On Earth Animation Merkantilaklubben Org Objects were chaotically flying around at the start of the solar system, building the planets and moons. there is evidence that after the planets formed, about 4.1–3.8 billion years ago, a second large spike of asteroid and comet impacted the earth and moon in an event called late heavy bombardment. Origin and evolution of earth research questions for a changing planet questions about the origins and nature of earth have long preoccupied human thought and the scientific endeavor. deciphering the planet’s history and processes could improve the abil ity to predict catastrophes like earthquakes and volcanoes, to manage earth’s resources, and. At that time 4.44 billion to 4.41 billion years ago earth began to retain its atmosphere and create its core. this possibility had already been suggested by bruce r. doe and robert e. zartman of. The hall features 168 rock specimens, and 11 full scale models of classic outcrops chosen to illustrate an important aspect of earth’s dynamic story. explore geologic time, peer into the planet’s depths, and understand the scientific methods used to study it. the regularly updated earth bulletin highlights important topics in earth science.
Astronomers Expand Cosmic Cheat Sheet In Hu Eurekalert At that time 4.44 billion to 4.41 billion years ago earth began to retain its atmosphere and create its core. this possibility had already been suggested by bruce r. doe and robert e. zartman of. The hall features 168 rock specimens, and 11 full scale models of classic outcrops chosen to illustrate an important aspect of earth’s dynamic story. explore geologic time, peer into the planet’s depths, and understand the scientific methods used to study it. the regularly updated earth bulletin highlights important topics in earth science. Questions about the origin and nature of earth and the life on it have long preoccupied human thought and the scientific endeavor. deciphering the planet's history and processes could improve the ability to predict catastrophes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, to manage earth's resources, and to anticipate changes in climate and geologic processes. Definition. earth formed as a silicate and metal rich body in the context of the other inner solar system “terrestrial” worlds. in its early evolution, it separated into layers (core, mantle, crust) as a consequence of the chemical and mechanical properties of the materials that accreted to the earth. the surface zone stabilized within the.

Dinosaurs Dawn To Extinction At Artscience Museum 365days2play Fun Questions about the origin and nature of earth and the life on it have long preoccupied human thought and the scientific endeavor. deciphering the planet's history and processes could improve the ability to predict catastrophes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, to manage earth's resources, and to anticipate changes in climate and geologic processes. Definition. earth formed as a silicate and metal rich body in the context of the other inner solar system “terrestrial” worlds. in its early evolution, it separated into layers (core, mantle, crust) as a consequence of the chemical and mechanical properties of the materials that accreted to the earth. the surface zone stabilized within the.

Comments are closed.