Earth S Interior Layers Of The Earth Geography4u Read Geography
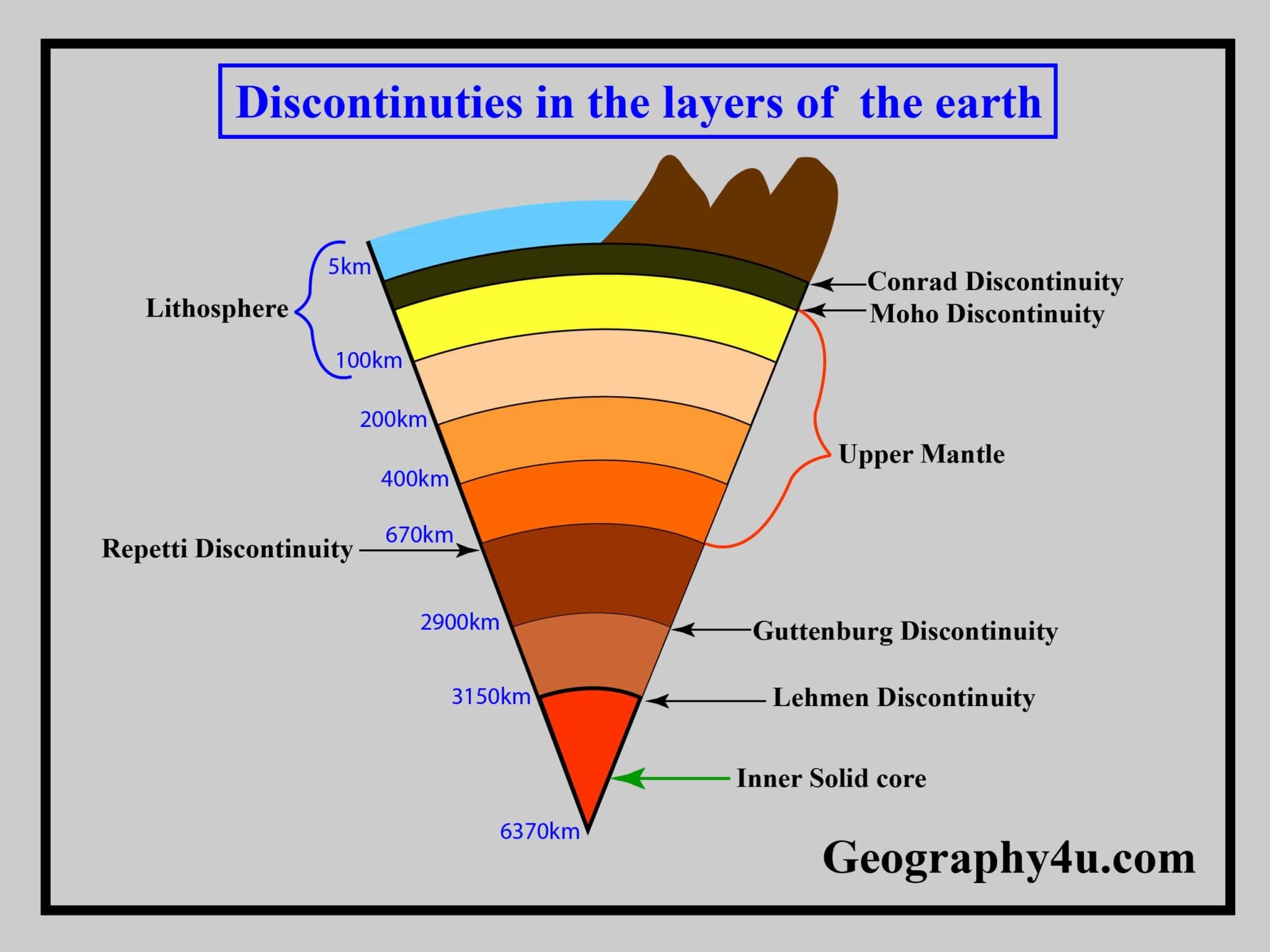
Earth S Interior Layers Of The Earth Geography4u Read Geography The asthenosphere is that part of the layer of earth which is below the lithosphere. it extends at a depth of 100 km to 400 km from the lithosphere. due to the high temperature, this region is partially molten. here the velocity of seismic wave slowdowns abruptly. this region is called low velocity region. There are variations in its social and cultural features too. there are villages, cities, roads, railways, ports, markets and many other elements. geography4u: learn freely about all the branches of geography and related concepts with detailed notes, diagrams and maps. best for bpsc, upsc.

Layers Of The Earth Insights Ias Simplifying Upsc Ias Exam Preparation Earth’s interior structure seismic studies of the earth’s interior have revealed distinct layers, includingthe solid lithosphere and the semi fluid asthenosphere. the lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates, and the semi fluid asthenosphere allows for the movement of these plates. The earth's interior is composed of four layers, three solid and one liquid—not magma but molten metal, nearly as hot as the surface of the sun. the deepest layer is a solid iron ball, about. 9.1: the earth's interior. the deep interior of the earth remains somewhat of a mystery as we have only penetrated the very outermost portion with our deep drilling exploration. what knowledge we do have comes from seismic wave data or lava that has extruded onto the surface. what we do know is that the earth's interior is somewhat like a. All the earth’s layers, their structure and composition. 1. crust. temperature: 475 k (∼200°c) at the surface to 1300 k (∼1000°c) thickness: 25 miles (32 km) for continental crust and 3 5 miles (8 km) for oceanic crust. density: ∼ 2830 kg m 3 at the continental crust and ∼ 3000 kg m 3 at the oceanic crust. it is the outermost and.
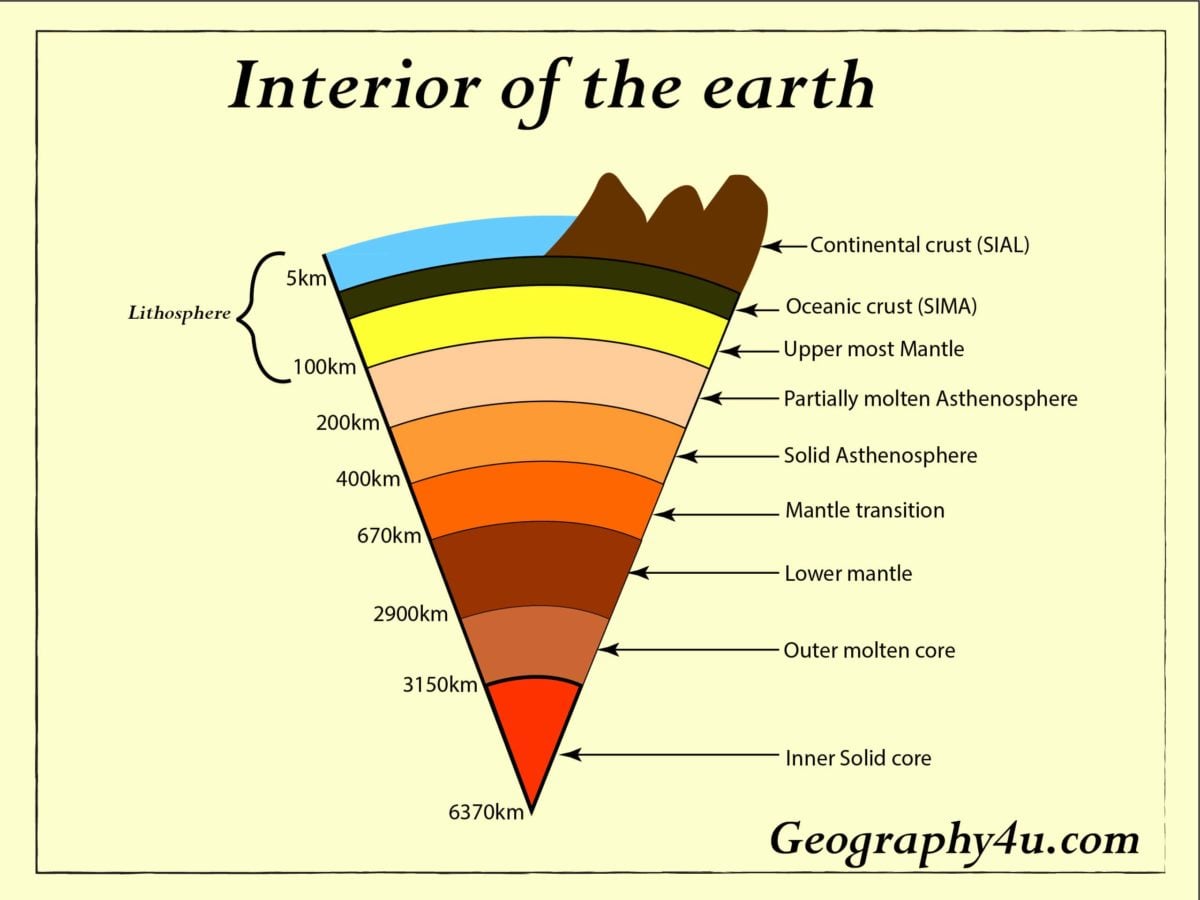
Earth S Interior Layers Of The Earth Geography4u Read Geography 9.1: the earth's interior. the deep interior of the earth remains somewhat of a mystery as we have only penetrated the very outermost portion with our deep drilling exploration. what knowledge we do have comes from seismic wave data or lava that has extruded onto the surface. what we do know is that the earth's interior is somewhat like a. All the earth’s layers, their structure and composition. 1. crust. temperature: 475 k (∼200°c) at the surface to 1300 k (∼1000°c) thickness: 25 miles (32 km) for continental crust and 3 5 miles (8 km) for oceanic crust. density: ∼ 2830 kg m 3 at the continental crust and ∼ 3000 kg m 3 at the oceanic crust. it is the outermost and. Earth’s thickest layer (about 2900 km thick) makes up most of the earth’s interior. unlike the brittle crust, the mantle is mostly solid rock, but with a twist – on geologic timescales, it behaves like a slow flowing, viscous fluid. the mantle primarily comprises silicate rock, a mix of silicon, oxygen, and other elements. Interior of the earth. the crust, the mantle, and the core are the three layers that make up the earth. the core only forms 15 per cent of the earth’s volume, whereas the mantle occupies 84 per cent. the remaining 1 per cent is made up of the crust. from the picture, we see that at the centre of the earth lies the core, then there is the.

Comments are closed.