Ecg Blocks Infarctions And Electrolyte Abnormalities

Ecg Blocks Infarctions And Electrolyte Abnormalities Youtube Ecg changes due to electrolyte imbalance (disorder). Significant electrolyte imbalances can precipitate cardiac arrest and are potentially reversible etiologies when promptly and appropriately addressed. both venous and arterial blood gases can be utilized for the analysis of electrolyte levels. electrocardiography (ecg) serves as a valuable tool for detecting and assessing the severity of.

Ekg Change In Electrolyte Imbalance Ecg Changes Associated With Wilkins,2008 geared to lpns lvns this quick reference pocket book provides an easy to understand guide to ecg interpretation and features over 200 clearly explained ecg rhythm strips following a refresher on relevant cardiac anatomy. Ecg frequency changes in potassium disorders. Take home points on ecg interpretation in electrolyte emergencies. hyperkalemia – bradycardia blocks, wide pr qrs and peaked t waves, multiple abnormalities indicate a critically high level: empiric calcium and stat vbg. hypokalemia – diffuse st depression, down up t waves, prominent u waves with a long qu interval (mimicking prolonged qt. The use of diagnostic ecg is a long established and powerful tool for assessing patients with a wide range of presentations. it can reveal myocardial ischemia and infarction, other forms of myocardial injury such as myocarditis or arrhythmias, and electrolyte abnormalities, among other conditions. any of these ecg findings may be present in.
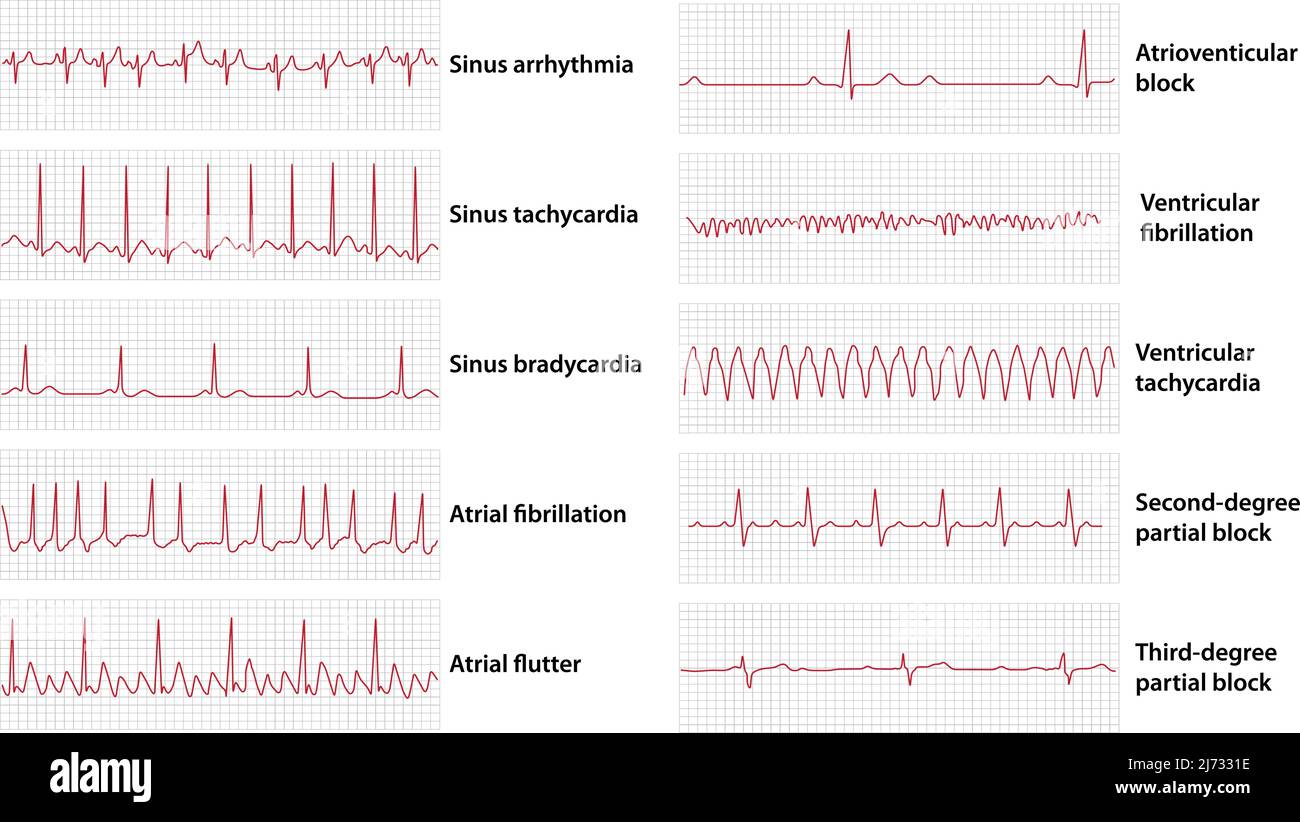
Schemes Set Of Common Electrocardiogram Ecg Abnormalities Including Take home points on ecg interpretation in electrolyte emergencies. hyperkalemia – bradycardia blocks, wide pr qrs and peaked t waves, multiple abnormalities indicate a critically high level: empiric calcium and stat vbg. hypokalemia – diffuse st depression, down up t waves, prominent u waves with a long qu interval (mimicking prolonged qt. The use of diagnostic ecg is a long established and powerful tool for assessing patients with a wide range of presentations. it can reveal myocardial ischemia and infarction, other forms of myocardial injury such as myocarditis or arrhythmias, and electrolyte abnormalities, among other conditions. any of these ecg findings may be present in. Ecg manifestations of multiple electrolyte imbalance. A variety of electrocardiographic (ecg) changes suggest hyperkalemia. early findings include peaked t waves (tenting). as the serum potassium rises further, flattened p waves, prolonged pr interval (first degree heart block), widened qrs complex, deepened s waves, and merging of s and t waves can be seen.
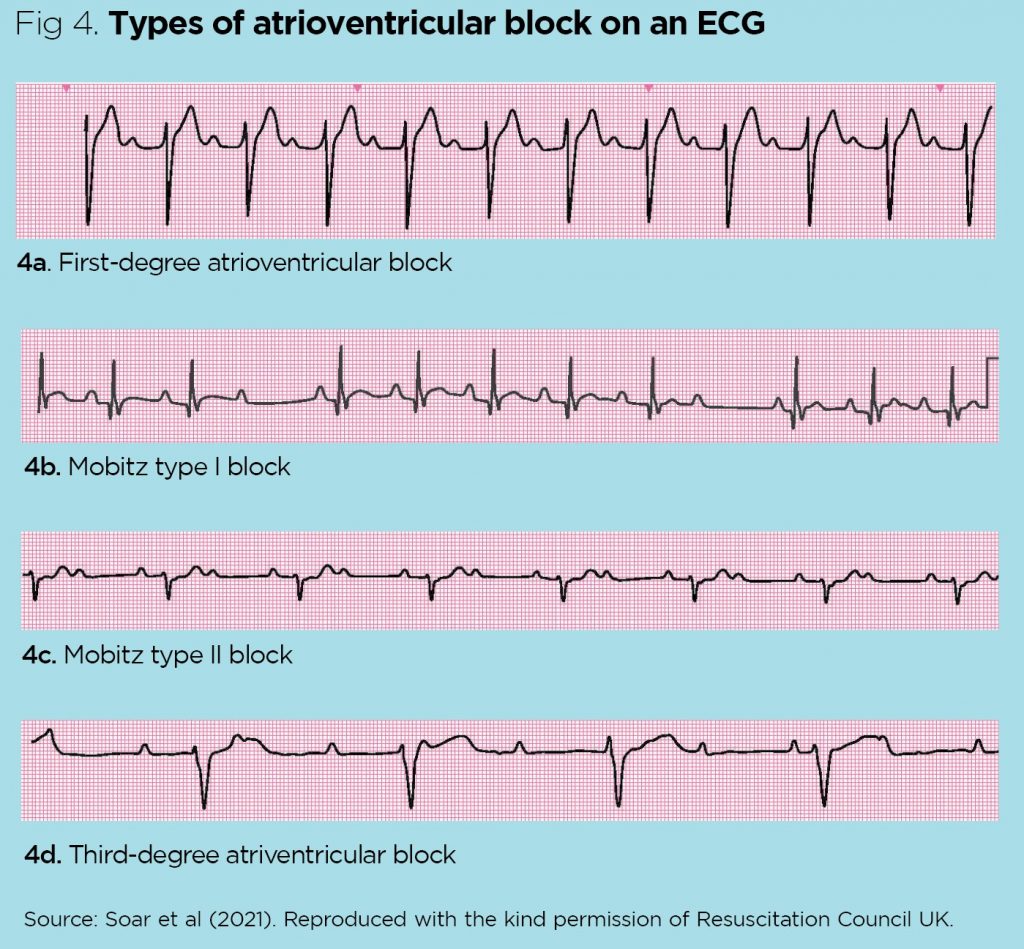
Electrocardiogram 3 Cardiac Rhythm And Conduction Abnormalities Ecg manifestations of multiple electrolyte imbalance. A variety of electrocardiographic (ecg) changes suggest hyperkalemia. early findings include peaked t waves (tenting). as the serum potassium rises further, flattened p waves, prolonged pr interval (first degree heart block), widened qrs complex, deepened s waves, and merging of s and t waves can be seen.

Comments are closed.