Ecg Educator Blog Normal Sinus Rhythm
Sinus Rhythm Ecgs Normal heart rate (classically 60 to 100 beats per minute for an adult). regular rhythm, with less than 0.16 second variation in the shortest and longest durations between successive p waves. the sinus node should pace the heart – therefore, p waves must be round, all the same shape, and present before every qrs complex in a ratio of 1:1. Normal heart rates in children. newborn: 110 – 150 bpm. 2 years: 85 – 125 bpm. 4 years: 75 – 115 bpm. 6 years : 60 – 100 bpm. variations on sinus rhythm. sinus tachycardia = sinus rhythm with resting heart rate > 100 bpm in adults, or above the normal range for age in children.

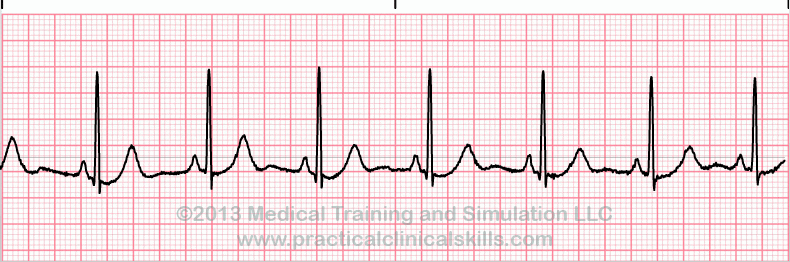
Related Image Sinoatrial Node Ekg Interpretation Nursing Mnemonics The p wave represents atrial depolarisation and is the first positive deflection on the ecg. the normal p wave axis ranges from 0° to 75°. however, the link between p wave abnormalities and cardiovascular death has previously been established. it can be normal, skewed to the left (left axis deviation, or lad), skewed to the right (right axis. Six second ecg rhythm strips. thank you , great clear strips. keep on working, great job! dear mr. winter your blog is great. i have a question i am writing a chapter about arrhythmia for residents. the ecg strips you have are they hand made or real strips?. Sinus rhythm: the normal rhythm of the heart. a rhythm is defined as three consecutive heart beats with identical waveforms on the . the similarity of the waveforms indicates that the origin of the impulse is the same. the sinoatrial (sa) node is the heart’s pacemaker under normal circumstances and the rhythm is referred to as sinus rhythm. Normal sinus rhythm (nsr) is the expected rhythm on an ekg in patients without pathophysiology. it is the normal electrical cycle of the heart which was discovered once a tool capable of detecting it was invented; the electrocardiogram (ekg ecg). normal sinus rhythm ( nsr) and regular sinus rhythm ( rsr) are synonymous.

Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus rhythm: the normal rhythm of the heart. a rhythm is defined as three consecutive heart beats with identical waveforms on the . the similarity of the waveforms indicates that the origin of the impulse is the same. the sinoatrial (sa) node is the heart’s pacemaker under normal circumstances and the rhythm is referred to as sinus rhythm. Normal sinus rhythm (nsr) is the expected rhythm on an ekg in patients without pathophysiology. it is the normal electrical cycle of the heart which was discovered once a tool capable of detecting it was invented; the electrocardiogram (ekg ecg). normal sinus rhythm ( nsr) and regular sinus rhythm ( rsr) are synonymous. Normal sinus rhythm is when the heart's electrical activity is regular and originates in the heart's natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (sa) node. the (sa) node is located in the right atrium and regularly fires electrical impulses. on an ecg, the normal sinus rhythm is characterized by a p wave corresponding to atrial depolarization wave, and. Sinus rhythm is the rhythm category when each of the five steps of rhythm analysis are “normal”. normal sinus rhythm is indicated by a heart rate in the normal range of 60 100 beats per minute with a steady rate, aside from variations due to respiration. p waves should be positive and within a normal amplitude (< 2.5mm at lead ii and iii).

Comments are closed.