Effects Of Social Media On College Students And Their Studies 04
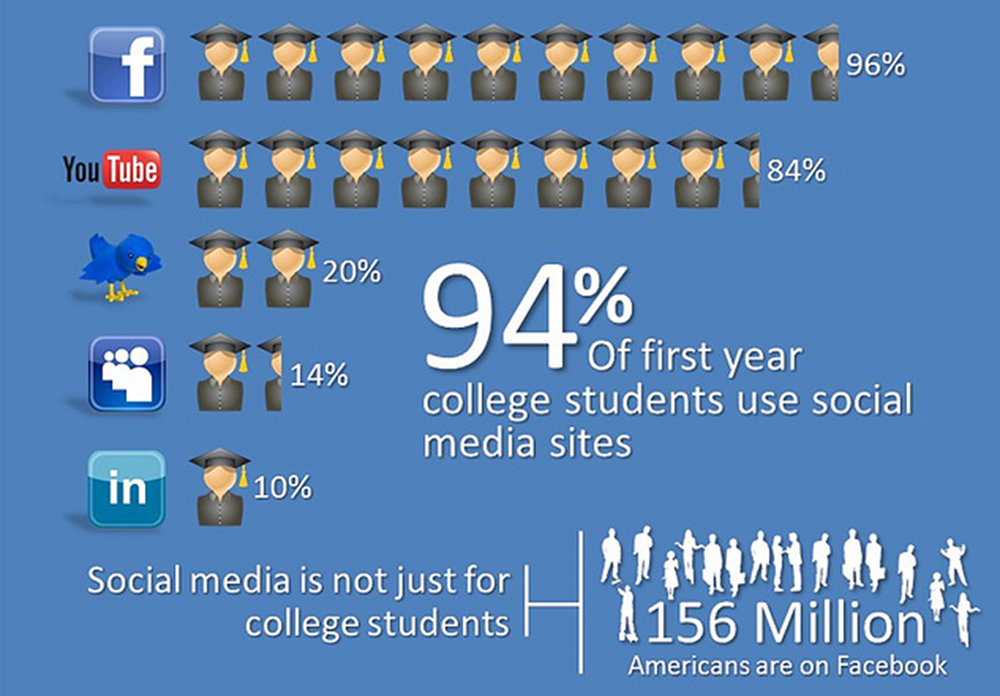
Effects Of Social Media On College Students And Their Studies Baldwin white and gower (2023) found that about 70% of college students use social media every day and more than 75% more than 1 h daily. having such a situation, it is not astonishing that social media users have difficulties in accurately estimating their social media time and use (e.g. verbeij et al., 2021). obviously, social media use has. College students are a major user group of social media, and the focus of relevant studies is placed on how this group actively engages in social media but seldom on how they wrongly use social media (priporas et al., 2017; throuvala et al., 2019).

Effects Of Social Media On College Students And Their Studies The effect of social media on the development of students'. 4.8 hours. average number of hours a day that u.s. teens spend using seven popular social media apps, with , tiktok, and instagram accounting for 87% of their social media time. specifically, 37% of teens say they spend 5 or more hours a day, 14% spend 4 to less than 5 hours a day, 26% spend 2 to less than 4 hours a day, and 23% spend. Social media has become an integral part of our daily routine, especially for college students who use them for studying, communication, and entertainment. Teens and social media: key findings from pew research.

Effects Of Social Media On College Students And Their Studies Social media has become an integral part of our daily routine, especially for college students who use them for studying, communication, and entertainment. Teens and social media: key findings from pew research. Conclusions. a majority of the participants reported prolonged use of social networking sites for nonacademic purposes. these habitual behaviors can distract students from their academic work, adversely affect their academic performance, social interactions, and sleep duration, and lead to a sedentary lifestyle and physical inactivity, which in turn can render them vulnerable to non. Enhance the use of social media which will prove to be helpful to instructors. “the power of television and video for learning lies in the use of. multimedia to engage students visually, cognitively, emotionally, socially, and civically in facets of the academic content. visual learning can result in increased.

Comments are closed.