Estimation Of D Spacing D And Lattice Constant A For Cubic Crystal System Using Xrd Pattern

Estimation Of D Spacing D And Lattice Constant A For Cubic #latticeconstant #d spacing #xrdpattern #originsoftware #nanoencryption #crystalsystem #cubic. Draw the lattice planes (1,1,1) (0,1,2) and (1,0,1) in a cubic lattice. if we use cu αradiation as x ray source, and the first order bragg diffraction peak is found at the semi angle 35 。 ,calculate the d spacing of the crystal. x rays with wavelength 1.54 a are reflected from the (2,1,1) planes of a cubic crystal.

How To Calculate D Spacing And Lattice Constant From Xrd And From X Crystals consist of planes of atoms that are spaced a distance d apart, but can be resolved into many atomic planes, each with a different d spacing. a,b and c (length) and α, β and γ angles between a,b and c are lattice constants or parameters which can be determined by xrd. beryl crystals smallest building block unit cell (cm) lattice (Å. Three common cubic crystal structures (nacl, diamond, and zns) are based on the fcc structure and are generated by repeating a two‐atom basis at each lattice point of the centered cubic bravais lattice. the basis for nacl consists of an atom of type a at (0,0,0) and an atom of type b at (1⁄2, 0, 0). The value of d for each of these planes can be calculated using 7.3.3 7.3.3, where a is the lattice parameter of the crystal. the lattice constant, or lattice parameter, refers to the constant distance between unit cells in a crystal lattice. 1 d2 = h2 k2 l2 a2 (7.3.3) (7.3.3) 1 d 2 = h 2 k 2 l 2 a 2. X ray diffraction from polycrystalline materials. according to euclid: “the angles in the same segment of a circle are equal to one another” and “the angle at the center of a circle is double that of the angle at the circumference on the same base, that is, on the same arc”. for any two points s and d on the circumference of a circle.
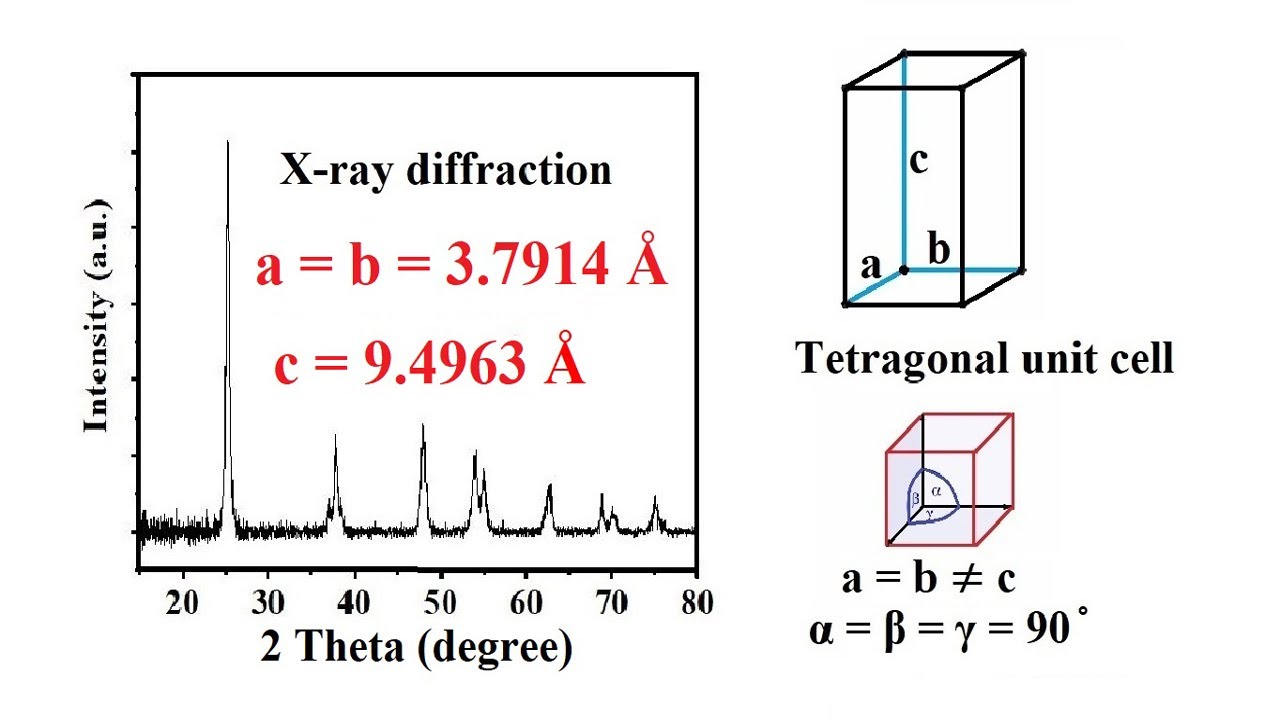
How To Calculate Lattice Constant A B C Values Of A Unit Cell From The value of d for each of these planes can be calculated using 7.3.3 7.3.3, where a is the lattice parameter of the crystal. the lattice constant, or lattice parameter, refers to the constant distance between unit cells in a crystal lattice. 1 d2 = h2 k2 l2 a2 (7.3.3) (7.3.3) 1 d 2 = h 2 k 2 l 2 a 2. X ray diffraction from polycrystalline materials. according to euclid: “the angles in the same segment of a circle are equal to one another” and “the angle at the center of a circle is double that of the angle at the circumference on the same base, that is, on the same arc”. for any two points s and d on the circumference of a circle. When analyzing the x ray diffraction pattern of a cubic crystal, it is crucial to correctly index the observed peaks. indexing is the procedure of determining the orientation and spacing of a crystal lattice based on the observed diffraction peaks. this data can then be used to calculate the parameters of the unit cell and the crystal structure. What you need to do to get the best answer: use the actual l value in your calculations. cu ka1 = 1.540562 Å. obtain as many reflections as possible in the high angle region. can decrease the l of radiation by using mo ka instead of cu ka. when a 1 and a 2 are resolved, use both points in your graph.
Xrd Cubic Simulation Of Unit Cell Dimension H K L Miller When analyzing the x ray diffraction pattern of a cubic crystal, it is crucial to correctly index the observed peaks. indexing is the procedure of determining the orientation and spacing of a crystal lattice based on the observed diffraction peaks. this data can then be used to calculate the parameters of the unit cell and the crystal structure. What you need to do to get the best answer: use the actual l value in your calculations. cu ka1 = 1.540562 Å. obtain as many reflections as possible in the high angle region. can decrease the l of radiation by using mo ka instead of cu ka. when a 1 and a 2 are resolved, use both points in your graph.

Python Code To Simulate Unit Cell Data H K L Miller Indices D

Comments are closed.