Example Of A Defective Matrix

System Of Differential Equations Defective Matrix Example Part 4 Defective matrix. in linear algebra, a defective matrix is a square matrix that does not have a complete basis of eigenvectors, and is therefore not diagonalizable. in particular, an matrix is defective if and only if it does not have linearly independent eigenvectors. [ 1] a complete basis is formed by augmenting the eigenvectors with. Defective. for example, consider the matrix a= 1 1 0 1 : this matrix has a characteristic polynomial l2 2l 1, with a repeated root (a single eigenvalue) l 1 =1. (equiv alently, since a is upper triangular, we can read the de terminant of a li, and hence the eigenvalues, off the diagonal.) however, it only has a singleindepenent eigen vector.

System Of Differential Equations Defective Matrix Example Part 2 Defective. for example, consider the matrix a= 1 1 0 1 : this matrix has a characteristic polynomial l2 2l 1, with a repeated root (a single eigenvalue) l 1 =1. (equiv alently, since a is upper triangular, we can read the de terminant of a li, and hence the eigenvalues, off the diagonal.) however, it only has a singleindepenent eigen vector. Defective eigenvalues. if an \(n \times n\) matrix has less than n linearly independent eigenvectors, it is said to be deficient. then there is at least one eigenvalue with an algebraic multiplicity that is higher than its geometric multiplicity. we call this eigenvalue defective and the difference between the two multiplicities we call the defect. Bit.ly pavelpatreon lem.ma la linear algebra on lemma bit.ly itcytnew dr. grinfeld's tensor calculus textbook lem.ma prep c. A matrix a a is called defective if a a has an eigenvalue λ λ of multiplicity m > 1 m > 1 for which the associated eigenspace has a basis of fewer than m m vectors; that is, the dimension of the eigenspace associated with λ λ is less than m m. use the eigenvalues of the following matrices to determine which matrices are defective.

Example Of A Defective Matrix Youtube Bit.ly pavelpatreon lem.ma la linear algebra on lemma bit.ly itcytnew dr. grinfeld's tensor calculus textbook lem.ma prep c. A matrix a a is called defective if a a has an eigenvalue λ λ of multiplicity m > 1 m > 1 for which the associated eigenspace has a basis of fewer than m m vectors; that is, the dimension of the eigenspace associated with λ λ is less than m m. use the eigenvalues of the following matrices to determine which matrices are defective. Geometric multiplicity is called a defective eigenvalue. a matrix that has at least one defective eigenvalue is a defective matrix i.e., it does not possess a full set of m linearly independent eigenvectors. every diagonal matrix is non defective, with algebraic multiplicity of every eigenvalue λ equal to its geometric multiplicity (equal to. Defective matrices cannot be diagonalized because they do not possess enough eigenvectors to make a basis. how can we correct this defect? example the matrix a= 1 1 0 1 is defective. 1.only eigenvalue is = 1. 2. a i= 0 1 0 0 3.single eigenvector v = (1;0). 4.we could use u = (0;1) to complete a basis. 5.notice that (a i)u = v and (a i)2u = 0.
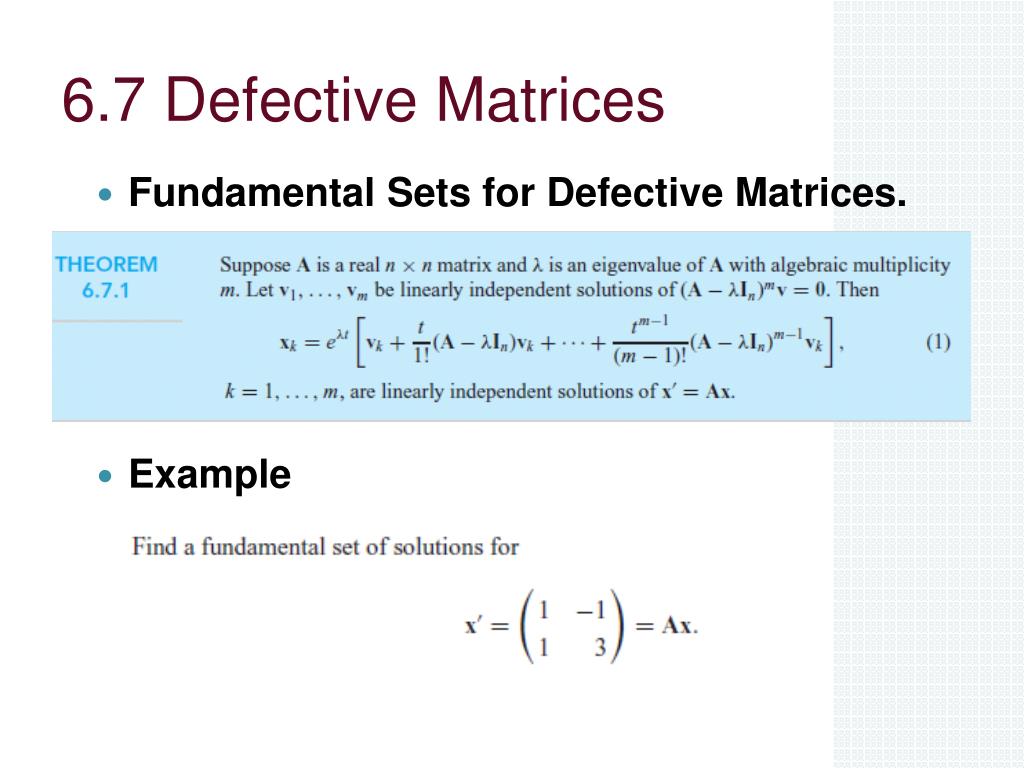
Ppt 6 5 Fundamental Matrices And The Exponential Of A Matrix Geometric multiplicity is called a defective eigenvalue. a matrix that has at least one defective eigenvalue is a defective matrix i.e., it does not possess a full set of m linearly independent eigenvectors. every diagonal matrix is non defective, with algebraic multiplicity of every eigenvalue λ equal to its geometric multiplicity (equal to. Defective matrices cannot be diagonalized because they do not possess enough eigenvectors to make a basis. how can we correct this defect? example the matrix a= 1 1 0 1 is defective. 1.only eigenvalue is = 1. 2. a i= 0 1 0 0 3.single eigenvector v = (1;0). 4.we could use u = (0;1) to complete a basis. 5.notice that (a i)u = v and (a i)2u = 0.

System Of Differential Equations Defective Matrix Example Part 3

Comments are closed.