Expansion Of The Universe Archives Universe Today

Measuring The Expansion Of The Universe Surprising Discrepancies Hint After probing the thermal history of the universe over the last 10 billion years, the team concluded that the mean temperature of cosmic gas has increased more than 10 times and reached about 2.2. The boss results include new and precise measurements of the universe’s expansion rate (called the “hubble constant”) and matter density, which includes dark matter, stars, gas, and dust.

Unknown Physics On The Cosmic Scale 1000 Supernova Explosions Chart We record the weekly space hangout every wednesday at 5:00 pm pacific 8:00 pm eastern. you can watch us live on universe today, or the weekly space hangout page – please subscribe! the. The puzzle, called the "hubble tension," is that the current rate of the expansion of the universe is faster than what astronomers expect it to be, based on the universe's initial conditions and our present understanding of the universe’s evolution. scientists using nasa's hubble space telescope and many other telescopes consistently find a. The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. [ 1] it is an intrinsic expansion, so it does not mean that the universe expands "into" anything or that space exists "outside" it. to any observer in the universe, it appears that all but the nearest galaxies. The universe was born with the big bang as an unimaginably hot, dense point. when the universe was just 10 34 of a second or so old — that is, a hundredth of a billionth of a trillionth of a.
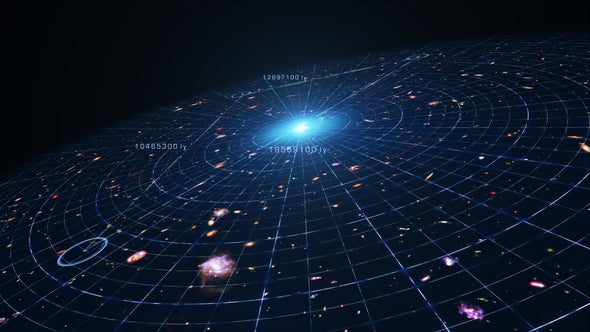
Will The Universe Ever Stop Expanding Scientific American The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. [ 1] it is an intrinsic expansion, so it does not mean that the universe expands "into" anything or that space exists "outside" it. to any observer in the universe, it appears that all but the nearest galaxies. The universe was born with the big bang as an unimaginably hot, dense point. when the universe was just 10 34 of a second or so old — that is, a hundredth of a billionth of a trillionth of a. The answer could reveal whether everything we thought we knew about physics is wrong. let's start by saying the universe is big. when we look in any direction, the furthest visible regions of the. This means that for every megaparsec — 3.3 million light years, or 3 billion trillion kilometers — from earth, the universe is expanding an extra 73.3 ±2.5 kilometers per second. the average from the three other techniques is 73.5 ±1.4 km sec mpc. perplexingly, estimates of the local expansion rate based on measured fluctuations in the.

How Big Is The Universe Space Tonight The answer could reveal whether everything we thought we knew about physics is wrong. let's start by saying the universe is big. when we look in any direction, the furthest visible regions of the. This means that for every megaparsec — 3.3 million light years, or 3 billion trillion kilometers — from earth, the universe is expanding an extra 73.3 ±2.5 kilometers per second. the average from the three other techniques is 73.5 ±1.4 km sec mpc. perplexingly, estimates of the local expansion rate based on measured fluctuations in the.
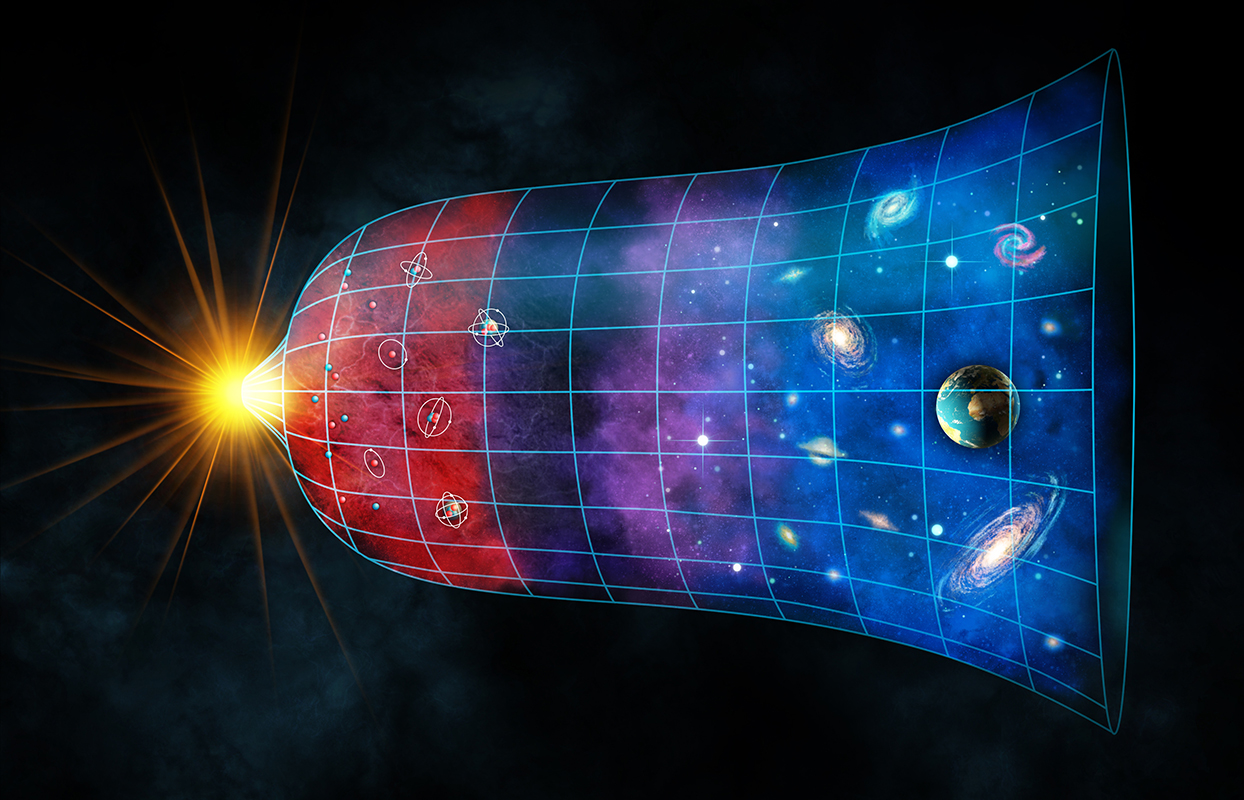
7 Things You Need To Know About The Expansion Of The Universe

Comments are closed.