Experimental Probability For Kids

Theoretical And Experimental Probability Worksheet Answers The experimental probability of an event is based on the number of times the event has occurred during the experiment and the total number of times the experiment was conducted. each possible outcome is uncertain and the set of all the possible outcomes is called the sample space. the formula to calculate the experimental probability is: p (e. Dedicated to elsian students ️5th primary | 1st term | math | unit 4 | lesson 1 | experimental probability lesson.
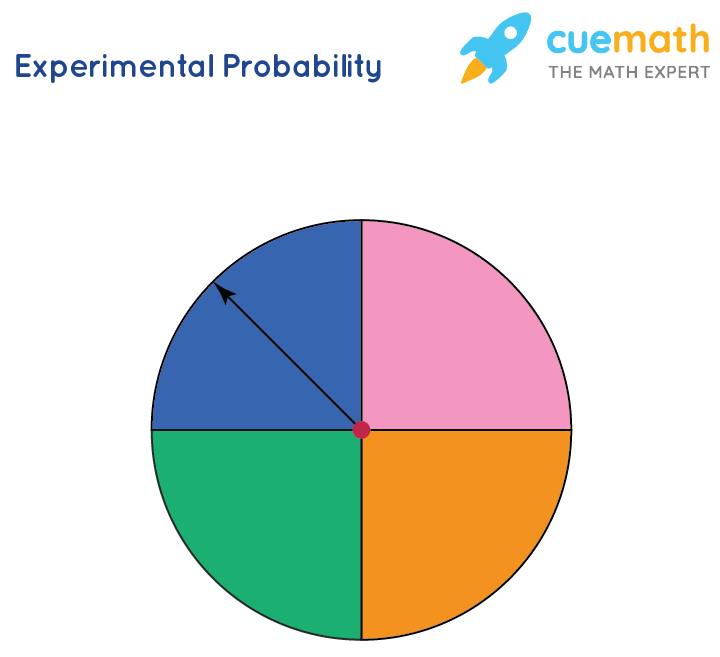
Experimental Probability For Kids The relative frequency of flipping a head is calculated by dividing the number of heads by the number of trials. the relative frequency varies. one trial gives a probability of 0, p (head) = 0. The formula for calculating experimental probability is: p (e) = number of times event e occurs total number of trials. for example, if you roll a dice 60 times, and the number 4 comes up 15 times, the experimental probability of rolling a 4 is calculated as 15 (the number of times 4 occurs) divided by 60 (the total number of trials), which. Random experiments are repeated multiple times to determine their likelihood. an experiment is repeated a fixed number of times and each repetition is known as a trial. mathematically, the formula for the experimental probability is defined by; probability of an event p (e) = number of times an event occurs total number of trials. Experimental probability: examples. let’s take a look at some of the examples of experimental probability. example 1: ben tried to toss a ping pong ball in a cup using 10 trials, out of which he succeeded 4 times. p (win) = n u m b e r o f s u c c e s s n u m b e r o f t r i a l s. = 4 10. = 2 5.
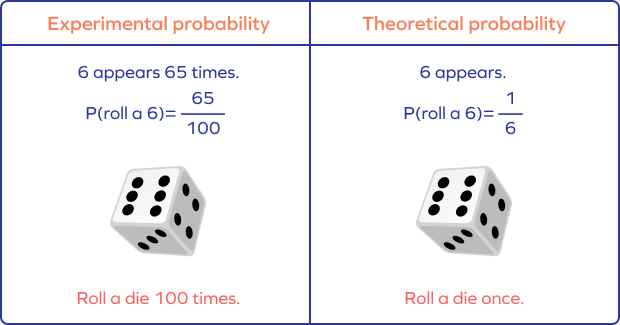
Experimental Probability Definition Formula Examples Random experiments are repeated multiple times to determine their likelihood. an experiment is repeated a fixed number of times and each repetition is known as a trial. mathematically, the formula for the experimental probability is defined by; probability of an event p (e) = number of times an event occurs total number of trials. Experimental probability: examples. let’s take a look at some of the examples of experimental probability. example 1: ben tried to toss a ping pong ball in a cup using 10 trials, out of which he succeeded 4 times. p (win) = n u m b e r o f s u c c e s s n u m b e r o f t r i a l s. = 4 10. = 2 5. Number of tosses = 30. p (3) = 7 30. b. frequency of primes = 6 7 2 = 15. number of trials = 30. p (prime) = 15 30 = 1 2. experimental probability can be used to predict the outcomes of experiments. this is shown in the following examples. example 3: the table shows the attendance schedule of an employee for the month of may. Watch a video that explains how to find the experimental probability of an event based on repeated trials and compare it with the theoretical probability.

Comments are closed.