Explaining The Electrolysis Of Dilute Sulfuric Acid H2so4 Aq Gcse

Explaining The Electrolysis Of Dilute Sulfuric Acid H2so4 Aq Gcse Please also follow me for more content, quizzes and notes on @chem.jungle on instagram!. Dilute sulfuric acid contains water. the ions present in this mixture are h and oh (from the water) and h and so 4 2 from the sulfuric acid. the h ions are attracted to the cathode and the.
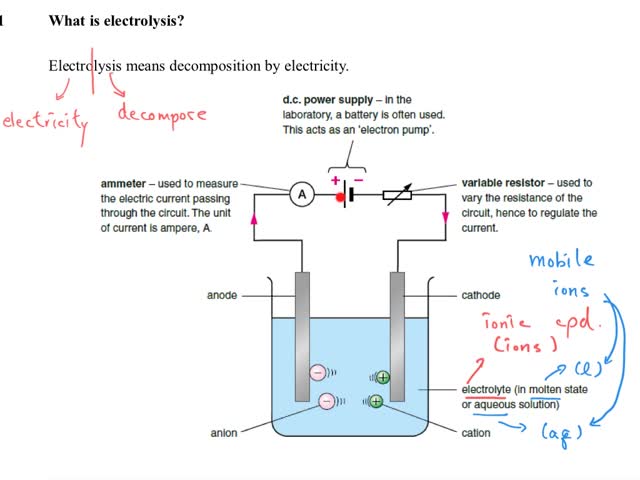
Chemistry Tutorial Ch32 5 Electrolysis Of Dilute H2so4 Aq The ions in dilute sulfuric acid are: h and so 4 2– ions from the sufuric acid h and oh – ions from the water; when electrolysed, it produces bubbles of gas at both electrodes the gases oxygen and hydrogen are produced; electrolysing dilute sulfuric acid in a hoffman voltameter shows that twice as much hydrogen is produced, compared to. The half equations for the electrolysis of water (electrolyte of acidified with dilute sulphuric acid). (a) the negative cathode electrode reaction for the electrolysis of water. the negative cathode electrode reaction is a reduction (electron gain). the hydrogen ions (h ) are attracted to the negative cathode and are discharged as hydrogen gas. Gcse: a video describing how the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid occurs#ccea #aqa #easychemistry #aqa #revision #chemistryrevision #electrolysis #elect. However, do take note that they are in fact heavily solvated in aqueous solution. in some textbooks, it may be said that for the electrolysis of dilute h2so4 h 2 s o 4, the oxidation half equation is written as 2hx 2ex− hx2 2 h x 2 e x − h x 2 and the reduction half equation is written as 4ohx− 2hx2o ox2 4ex− 4 o h x − 2 h x 2.

Comments are closed.